Results analysis
Analysis of selenoproteins
15kDa selenoprotein (Sel15)
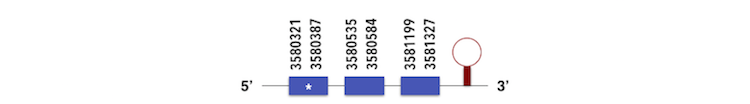
The 15kDa selenoprotein can be predicted using the contig KQ557225.1. The gene is located between 3580321 and 3581327 position in the forward chain and it contains 146 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image. The sequence with one Sec residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element.
 Fish Selenoprotein 15 (SELENOE)
Fish Selenoprotein 15 (SELENOE)
The 15kDa selenoprotein can be predicted using the contig KQ557225.1. The gene is located between 3580321 and 3581327 position in the forward chain and it contains 146 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image. The sequence with one Sec residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element.
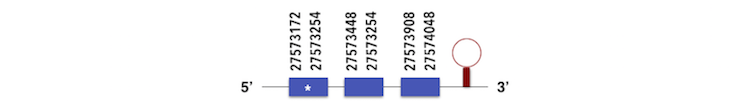
The sequence contained one Sec residue so it was analyzed by Seblastian. It predicted a SECIs element with graded as A in the position 27574080 - 27574163 as shown in the image. The selenoprotein predicted had 4 exons instead of 3, being in the position 27572746 - 27572853. This could mean that the positions taken to analyse the query were not enough long to predict the entire protein.
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
This is a family containing 8 subfamilies but only six of them could be found in the genome that it is being analysed.
GPx1a can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557213.1. The gene is located between positions 15207078 and 15207827 in the forward chain and it contains 190 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 2 exons.
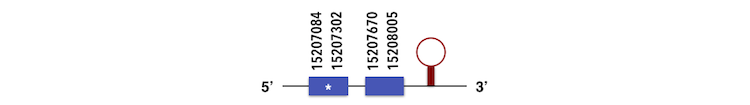
A Sec residue could be found in Zebrafish proteasome and while executing Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could also be found. This SECIs is between 15208203 and 15266476 positions, in the forward chain. Finally, a selenoprotein could be predicted.
GPx2 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557211. The gene is located between positions 9654675 and 9655407 in the reverse chain and it contains 189 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 2 exons.
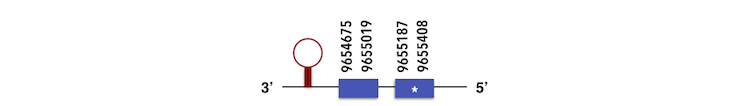
A Sec residue could be found in Zebrafish proteasome and while executing Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could be found. This SECIs is between 9654521 and 9654599 positions, in the reverse chain. Then, a selenoprotein could be predicted.
GPx3a can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557216. The gene is located between positions 21048697 and 21050645 in the reverse chain and it contains 222 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons.
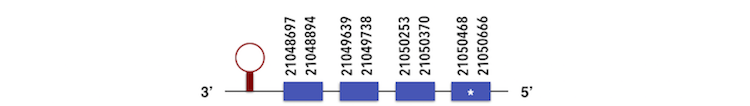
A Sec residue could be found in Zebrafish proteasome and while executing Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could be found. This SECIs is between 21048490 and 21048562 positions, in the reverse chain. Then, a selenoprotein could be predicted.
GPx3b can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557202.1. The gene is located between positions 17124710 and 17126311 in the reverse chain and it contains 178 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons.
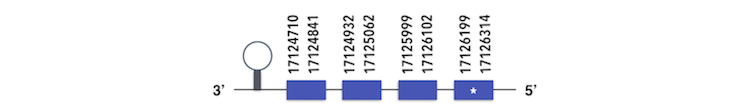
A Sec residue could be found in Zebrafish proteasome and while executing Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could not be found. Then, a selenoprotein could not be predicted by this program. Nevertheless, all the data that has been obtained is consistent enough to consider it as a selenoprotein.
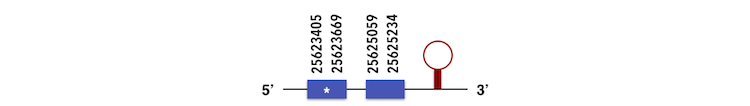
GPx7 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557224. The gene is located between positions 25623405 and 25625233 in the forward chain and it contains 147 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 2 exons.
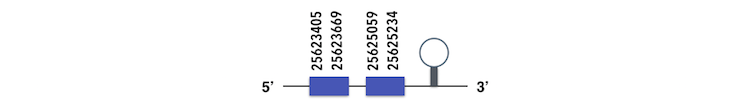
A Sec residue could not be found in Zebrafish proteasome, probably due to its loss for a cysteine residue. While executing the Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could be found, which is far from the forward chain and there is not a Sec residue in the protein predicted in Xiphophorus. So, this element can be considered as a false positive.
GPx8 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557204. The gene is located between positions 24957700 and 24959533 in the forward chain and it contains 153 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 3 exons.
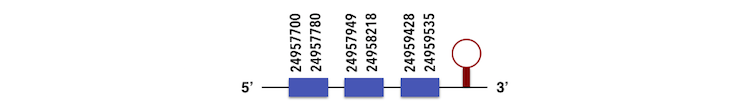
A Sec residue could not be found in Zebrafish proteasome possibly due to its loss for a cysteine residue and while executing Seblastian analysis, a SECIs element could not be found. This is what it was expected so no selenoprotein could be predicted.
Iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO)
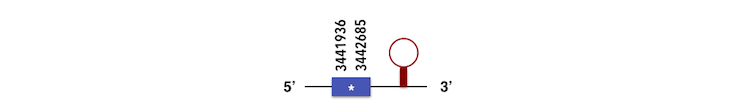
These proteins are members of the same family. However, these proteins haven’t evolved too much so an only scaffold was found, KQ557211. As it was not possible to analyse all proteins with the same scaffold it was necessary to determine the correct protein to be analised depending on similarity to Zebrafish query. The one selected was DIO3a, with a score of 287 and length of 265 nucleotides.
It was found a forward and a reverse chain for the same scaffold. Considering the score the positive chain was analysed. Its gene has a length of 265 nucleotides and is located between 3441891 and 3442685 position. Finally, exonerate and Seblastian predicted the following exons:
 Selenoprotein H (SELENOH)
Selenoprotein H (SELENOH)
Selenoprotein H can be predicted in the contig KQ557216. The gene is located between positions 15575111 and 15575687 in the forward chain and it contains 127 nucleotides.
The exonerate predicted structure is composed by 2 exons as described below.
The sequence with one Sec residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element with an A grade in the position 51003 - 51080. Then, a selenoprotein was found, even though 3 exons were predicted instead of 2.
Selenoprotein I (SELENOI)
Selenoprotein I can be predicted in the contig KQ557207. The gene is located between 17440106 and 17431606 position in the reverse chain and it contains 397 nucleotides.
The exonerate predicted structure is composed by 10 exons as described below.
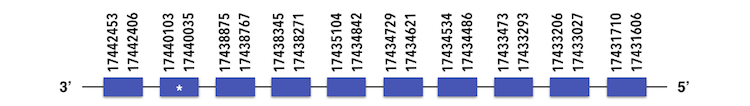
A Sec residue can be found in Zebrafish proteasome, and while executing Seblastian analysis, no SECIs elements or selenoproteins could be predicted.
Selenoprotein J (SELENOJ)
Selenoprotein J can be predicted in the contig KQ557214. The gene is located between 5881510 and 5886363 position in the forward chain and it contains 342 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 8 exons as described below.

Exonerate predicted an extra exon, located between 5886437 - 5886501, which can be omitted as it seems to be part of another gene. While executing Seblastian output, a SECIs element could be predicted in the 5886437-5886501 position. Even three Sec residues were predicted (a sequence with three stop codons), just one of them is valid and a selenoprotein was predicted.
Selenoprotein K (SELENOK)
Selenoprotein K can be predicted in the contig KQ557201. The gene is located between 8675462 and 8676313 position in the forward chain and it contains 94 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described below.
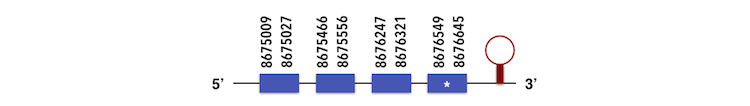
The sequence with one Sec residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element with a B grade in the position 8676980-8677060 as shown in the image. However, no selenoprotein could be predicted.
Selenoprotein L (SELENOL)
In this case, due to the impossibility to align Selenoprotein L sequence with the one from Zebrafish, Selenoprotein L from Gasterosteus aculeatus was used. The gene sequence can be predicted in the contig KQ557207. It is located between 1676543 and 1682052 position in the forward chain and it contains 210 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 7 exons as described below.
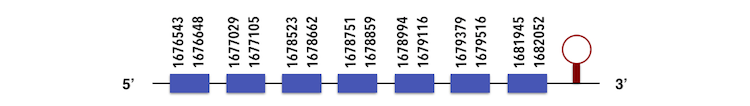
The sequence predicted, which has one selenocysteine residue, was analyzed by Seblastian. There, a SECIs element (grade A) was predicted in the position 1682135-1682207 as shown in the image. For this reason, a selenoprotein could be predicted, but it contained 9 exons rather than 7.
Selenoprotein M (SELENOM)
Selenoprotein M was also obtained from another specie, Gadus morthua. The gene sequence, which can be predicted in the contig KQ557204, is located between 17382909 and 17387799 position in the forward chain and it contains 92 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described below.
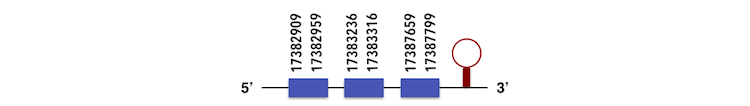
The sequence with one selenocysteine residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element with an A grade in the position 17388167-17388239 as shown in the image. The selenoprotein predicted has 5 exons instead of 3, which started at 17382075 and end at 17387886.
Selenoprotein N (SELENON)
Selenoprotein N can be predicted in the contig K7Q557211. The gene is located between 3126858 and 3134764 position in the reverse chain and it contains 557 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 11 exons as described below.

The sequence with one Sec residue was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element with an A grade in the position 3125578-3125653 as shown in the image. Then, a selenoprotein was predicted. Moreover, there was an extra exon located between 3169073 and 3169159, that could be omitted as it was considered as an exon from another protein.
Selenoprotein O (SELENOO)
This family has two subfamilies. Selenoprotein O1 (SELENOO) can be predicted in the contig KQ557202. The gene is located between 23040774 and 23046422 positions in the forward chain and it contains 692 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 9 exons as described below.
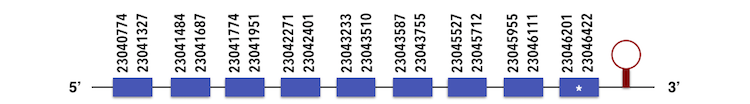
A selenocysteine is present in Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element could be found in the position 23046819.23046892. Moreover, a selenoprotein was predicted with the same 9 exons.
Selenoprotein O2 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557209. Even SelO2 from Zebrafish was aligned with a sequence in Xiphophorus’ genome, this protein is obtained from a duplication of SelO1, meaning that it is just present in Zebrafish. This is the reason why translate could not predicted anything.
Selenoprotein P (SELENOP)
This family also has two subfamilies. SELENOP1 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ577204. The gene is located between 22257363 and 22255308 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 367 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons as described below.
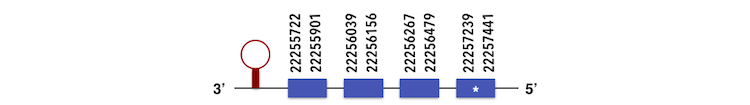
Seventeen selenocysteine are present in this Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIS element could be found between 22254885-22309845, as expected.
The other member of this family, SELENOP2 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ577221.The gene is located between 6339361 and 6337964 position in the reverse chain and it contains 327 nucleotides.The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 3 exons as described below.
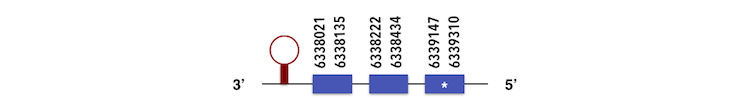
One selenocysteine is present in this Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIS element could be found between 6336630 and 6336705. Then, selenoprotein was predicted as expected.
Selenoprotein R (MSRB)
Methionine-R-sufoxide reductase 1a (MSRB1a) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557208. The gene is located between position 11533214 and 11536264 in the forward chain and it contains 110 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 3 exons.
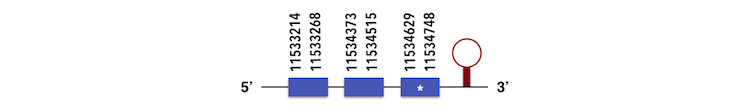
A selenocystein was present in Zebrafish gene and while executing the Seblastian output, a SECIs element could be found located between positions 11534954 and 11535036. Then, selenoprotein was predicted.
Methionine-R-sufoxide reductase 1b (MSRB1b) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557202. The gene is located between position 25288724 and 25287642 in the reverse chain and it contains 104 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 3 exons.
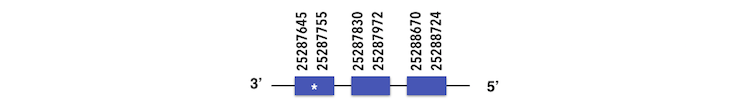
A selenocysteine was present in this Zebrafish gene and while executing Seblastian, no SECIs element or selenoprotein could be found. However, a Sec residue was obtained in the predicted sequence in Xiphophorus and it was aligned with a stop codon in the T-Coffee analysis. Taking into account these results a selenoprotein could be expected.
Methionine-R-sufoxide reductase 2 (MSRB2) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557214. The gene is located between position 8753419 and 8752087 in the reverse chain and it contains 180 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons.
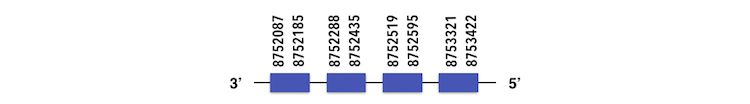
No selenocysteine could be found in Zebrafish genome but a SECIs element could be predicted with a B grade. However, it was located between positions 8784291 and 8784368, in the 5’ side. Considering all results, a false positive could be expected.
Methionine-R-sufoxide reductase 3 (MSRB3) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557209. The gene is located between position 17226624 and 17232738 in the forward chain and it contains 186 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 5 exons.
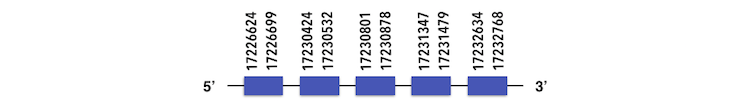
No selenocysteins could be found in Zebrafish genome but a SECIs element could be found between positions 17233057 and 17233137, in the 5’ side. Considering these results and that the SECIs elements was predicted with a B grade, it could be a false positive.
Selenoprotein S (SELENOS)
The Selenoprotein S can be predicted in the contig KQ557219. The gene sequence is located between 1371038 and 1372751 positions in the forward chain and it contains 190 nucleotides.
The exonerate predicted structure is composed by 6 exons as described below.
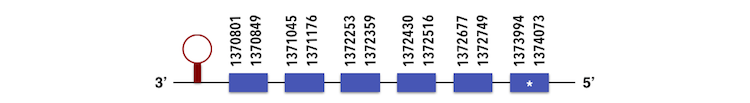
Selenoprotein S has a total number of 1 selenocysteine residue. By using Seblastian, three SECIs elements were predicted, but only one of them was chosen considering the grade and the position in the sequence.
Selenoprotein T (SELENOT)
It is a family containing 3 subgroups. SELENOT1 can be predicted in the contig KQ557221. The gene sequence is located between 14282231 and 14278827 position in the reverse chain and it contains 178 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons.
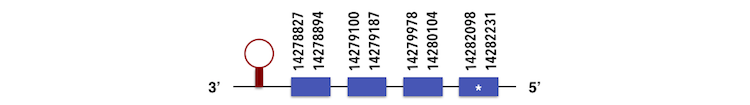
A selenocysteine is present in this Zebrafish gene as well as in the sequence predicted. While analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element could be found. This SECIs is in the position 14278541-14278615 and was predicted with an A grade. Then, selenoprotein was predicted.
The other members of this family as SelenoT2 can be predicted in the contig KQ557216. The gene is located between 706186 and 708694 position in the forward chain and it contains 210 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 5 exons.
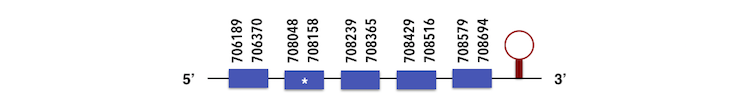
As it can be seen, the first exon in the protein was far from the other so it could be deleted as it might form part of another protein. A selenocysteine can be found in Zebrafish and in the sequence predicted, so while executing Seblastian output a SECIs element could be predicted. The element found with an A grade is a located between 708782-708853 nucleotides, in the forward chain and its grade is A. Then, selenoprotein was predicted.
Selenoprotein U (SELENOU)
This family contains 3 subgroups.SELENOU1a can be predicted in the contig KQ557215. The gene sequence is located between position 14669700 and 14671260 position in the forward chain and it contains 222 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 5 exons.
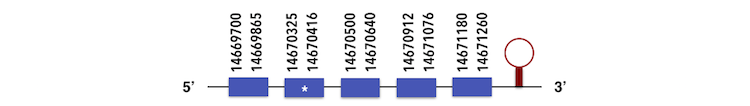
A selenocysteine is present in this Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element (grade A) could be found. This SECIs is located between positions 14671721-14671801. Then, a selenoprotein was predicted.
The other member of this family, SelenoU2 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557204. The gene sequence is located between 22924442 and 22926406 position in the forward chain and it contains 222 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 6 exons.
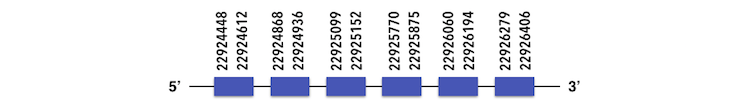
A selenocysteine cannot be found in Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element could be found. This SECIs is located between 23010074-23009995 positions, but it is in the reverse chain. Then, selenoprotein was not predicted.
Finally, SELENOU3, can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557213. The gene is located between position 16879177 and 16876348 in the reverse chain and it contains 179 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 6 exons.
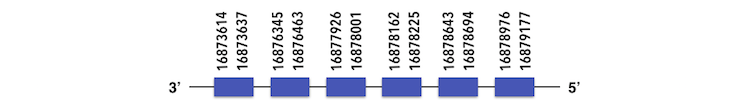
No selenocysteine can be found in Zebrafish gene as well as in Xiphophorus sequence. While analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element was found, but considering that no sec residue could be predicted in the sequence, no selenoprotein could be predicted.
Selenoprotein W (SELENOW)
It is a family containing 3 subgroups. SELENOW1 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557208. The gene sequence is located between position 20256023 and 2025567 in the reverse chain and it contains 95 nucleotides. The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 4 exons.
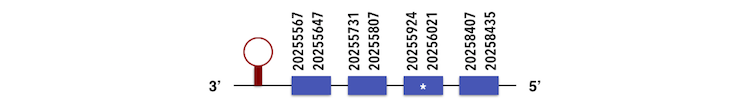
A selenocysteine is present in the Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, two SECIs elements could be found between positions 202553375 - 20255448 and 20257553 - 20257626. It was seen that the second SECIs was located inside the protein sequence. However, as two selenoproteins were predicted, this second SECIs was valid (considering that the second protein was starting at the 57748 nucleotide in the reverse chain).
It was found one only possible scaffold for the other members of this family, SELENOW2 and SELENOW3. Considering that it was the same scaffold which was already used for SELENOW1, analysis of this members could not be done. This event could be due to the presence of a replication event in Zebrafish genome, causing more than one SelenoW protein which has not happened in the studied genome.
Thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD)
This family has two subfamilies.
Thiredoxin reductase 2 (TXNRD2) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557204. The gene is located between positions 6662748 and 6648779 in the reverse chain and it contains 486 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 11 exons.
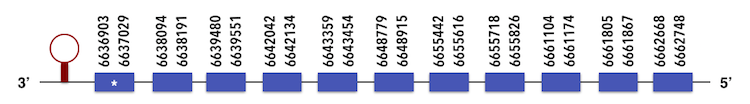
A selenocysteine is present in this Zebrafish gene and while executing Seblastian, a SECIs element located between positions 6634533 and 6634605 could be predicted.
Thiredoxin reductase 3 (TXNRD3) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557213. The gene sequence is located between position 2583705 and 2578121 in the reverse chain and it contains 611 nucleotides..
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 8 exons.
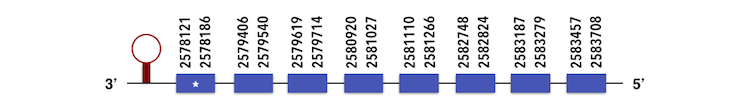
A selenocysteine is present in this Zebrafish gene and while analysing Seblastian output, a SECIs element was found between positions 2577813-2577892. T-Coffe analysis showed a proper alignment so a selenoprotein could be predicted.
Analysis of machinery proteins
Eukaryotic elongation factor (eEFsec)
The Eukaryotic elongation factor (eEFsec) can be predicted in the contig KQ557213.1. The gene is located between 11479958 and 11491648 position in the forward chain and it contains 576 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate is composed by 7 exons as described below.
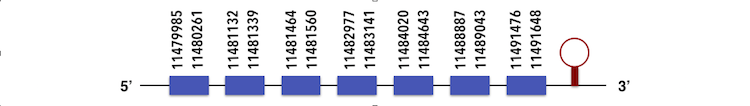
The sequence, which had no Sec residues, was analyzed by Seblastian and no SECIs elements or selenoproteins were predicted, as it could be expected.
Methionine sulfoxide reductases (MsrA)
Methionine sulfoxide reductases A (MsrA) have different contigs. By observing each E-value KQ557211 was chosen for MsrA1 and KQ557207 for MsrA2. The MsrA1 gene is located between 4128965 and 4099551 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 238 nucleotides. The MsrA2 gene is located between 2734208 and 2714593 position in the reverse chain and it contains 232 nucleotides.The exonerate structure of MsrA1 is composed by 6 exons as described below.
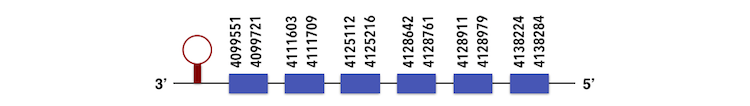
The exonerate structure of MsrA2 is composed by 5 exons as described below.
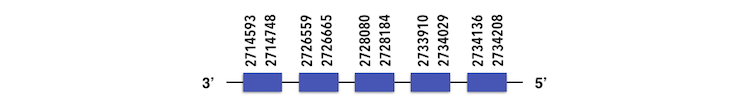
Despite no Sec residues could be found, Seblastian output showed one SECIs element in MsrA. This prediction can be considered a false positive as it was far away from the 3’UTR region (4166337-4166407 position) and no Sec residue could be found.
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase (PSTK)
The Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase protein can be predicted in the contig KQ557202. The gene is located between positions 13454056 and 13455143 in the forward chain and it contains 205 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate is composed by 3 exons as described below.
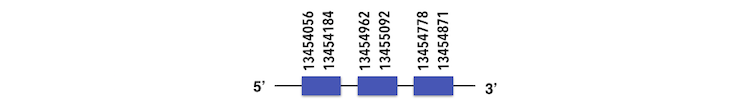
Disorganized exons were found and a reanalysis was needed. It was found that exons were located inside the genome in different queries taking part of the whole gene. A Sec residue could be found in Zebrafish proteasome and while executing Seblastian output, no SECIS elements or selenoproteins could be predicted.
SECIS binding protein 2 (SBP2)
This protein family is composed by SBP21 and SBP21. SBP22 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557219. The gene is located between positions 9645124 and 9637070 in the forward chain and it contains 982 nucleotides.
Exonerate predicted a structure with 12 exons (considering that there is one out of sequence). Even a gap was separating the predicted exons, it could be considered as a large single protein. The final structure is the following:
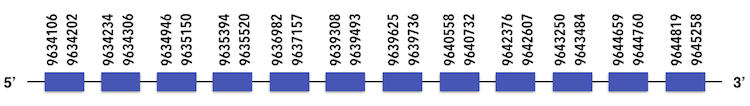
As no Sec residues were found in the predicted sequence, when analysing with Seblastian no SECIs elements or selenoproteins could be found.
SBP22 can be predicted in the scaffold KQ557204. The gene is located between position 26133402 and 26128037 in the forward chain and it contains 362 nucleotides. The exonerate predicted 5 exons, but just 4 of them were inside the gene as described below.
The sequence was analyzed by Seblastian, which predicted a SECIs element in the position 26029263-26029348 as shown in the image, but it could be a false positive as it was too far from the exons.
Selenocysteine synthase (SecS)
The Selenocysteine synthase protein can be predicted in the contig KQ557206. The gene is located between 15802485 and 15792225 in the reverse chain and it contains 490 nucleotides.
The exonerate predicted structure is composed by 11 exons as described below.
The sequence, which had no selenocysteine, was analyzed by Seblastian and no SECIS elements or selenoproteins were predicted.
Selenphosphate synthase (SEPHS)
Selenphosphate synthase family is composed by two proteins, SEPHS1 and SEPHS2, which can be predicted in the contigs KQ557212 and KQ557201 respectively. SEPHS1 gene is located between 13138087 and 13134173 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 392 nucleotides. SEPHS2 gene is located between 4458823 and 4465987 position in the forward chain and it contains 447 nucleotides. The exonerate for SEPHS1 predicted a sequence composed by 9 exons as described below.
The exonerate for SEPHS2 predicted a structure composed by 9 exons as described below.
The sequences, which had no selenocysteine, were analyzed by Seblastian and no SECIS elements or selenoproteins were predicted, as expected.
tRNA Sec 1 associated protein (SECp43)
This family have two subfamilies. tRNA Sec 1 associated protein 11 (SECp43) can be predicted in the scaffold KQ577221. The gene is located between position 8998860 and 8994308 in the reverse chain and it contains 316 nucleotides.
The structure predicted by exonerate analysis is composed by 9 exons.
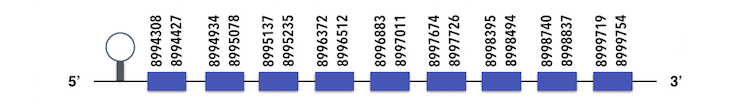
This is a machinery gene so no selenocysteine could be found but surprisingly, a SECIs element was predicted in Seblastian analysis but it was located between 8968986 and 8969064 positions. Thus, it could be considered as a possible false positive.
Different scaffolds could be found in SECp432 subfamily but none of them were working as in the exonerate analysis, exons were not able to be predicted.