DISCUSSION
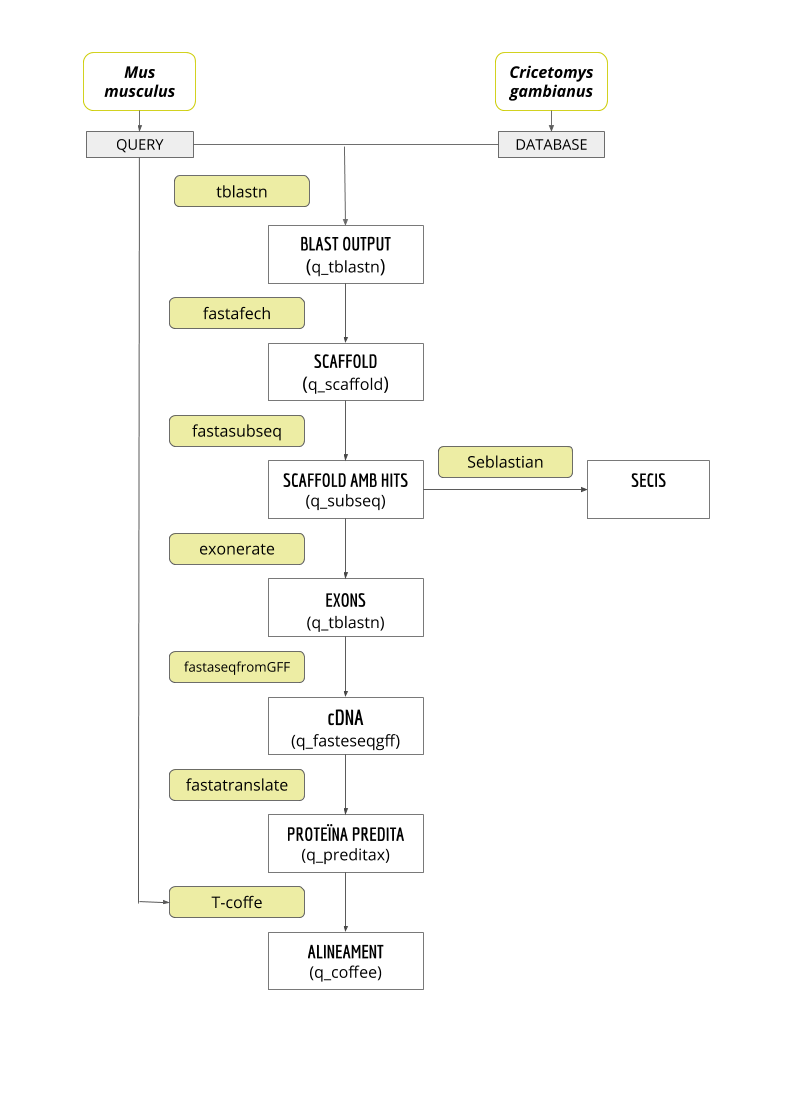
The main goal of this project is to predict and annotate the whole selenoproteome of C. gambianus. The genome of C. gambianus has been recently sequenced. In order to achieve it, a comparison with M. musculus genome was performed. We chose M. musculus because it is the closest specie to Gambian rat with a well annotated genome.
The 27 mouse proteins were obtained from SelenoDB1.0, some of them where selenoproteins or homologous with cysteine, but also machinery related to the processing of selenoproteins. Some of these proteins belong to the same family, having a total of 15 families (1). In order to elaborate the discussion, we took into account some parameters that we will explain in the following paragraphs.
First of all, we looked on the E-value to decide which hit should be aligned. The scaffold corresponding to the lowest E-value was always tried first and then, the rest of the steps were performed. If the final alignment was correct and the results with the Seblastian indicated that we found a selenoprotein, we stopped there. In case that the lower E-value did not get us satisfactory results, we took into account other parameters that we will explain in every particular case.
Then, we also observed some parameters of the results of the T-Coffee: the score, the number of gaps and the number of amino acid changes. In case that the results were good, we moved to the final step.
Finally, we looked for SECIS elements in all the predicted proteins 3’-UTR regions with the SECIS Search3 software. We had one initial screening of the results: all SECIS with an Infernal score lower than 10 were discarded. Then we checked to see if the SECIS element was found in the same strand as the predicted protein and rejected those which did not match. Afterwards, we analysed the Infernal and Covels scores of the remaining SECIS, bearing in mind that most vertebrates have an Infernal score higher than 20 and a Covels score higher than 15. And finally, we checked if the distance between the SECIS element and the selenocysteine (Sec) was biologically coherent (between 2 and 5.2 kb in mammalians) (6). In the discussion, we also mention the grade system developed by the software, assigning grades A, B or C, from best to worst, to each SECIS prediction.
Additionally, for each family of proteins studied we also performed a phylogenetic analysis using the phylogeny.fr website. The tree depiction, with the distances between branches, are represented in the figures throughout the discussion.
Based on all the data we got, we can now discuss our results of the analysis of each protein. There is also a representation of the genes and SECIS elements. It is important to say that the positions of the genes predicted and the positions shown in the schemes correspond to relative positions, which means that the number of nucleotides correspond to the position inside each particular scaffold. In the figures, it is also shown in which exon the hit was found (coloured in green).
In this link you can find a text file with the list of each scaffold and its approximated location in the C. gambianus genome.
We must also mention that the C. gambianus genome was organised in relatively small scaffolds, which has generated an added handicap to our analysis when proteins reached across multiple scaffolds and when searching for SECIS elements in shortened 3’-UTR regions.
GLUTATHIONE PEROXIDASE (GPx) FAMILY
Proteins of the family named Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) are found in the three domains of life and represent the largest protein family in vertebrates. In mammals, we found 8 paralogs (GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4, GPx5, GPx6, GPx7 and GPx8). Not all of them have Sec residue: in some of them this residue is replaced by a Cys. They all have an antioxidant activity and they are involved in many physiological processes (1).
In Mus musculus, our genome of reference, we found that just GPx1, GPx2, GPx4 are selenoproteins, GPx5, GPx6, GPx7 and GPx8 have a Cys residue and GPx3 have none of both. The analysis of selenoproteomes demonstrate a trend towards reduced selenoprotein usage in mammals. Indeed, some selenoproteins appeared in mammals by gene duplication and a replacement from Sec to Cys (GPx5 and GPx6).
In C. gambianus we found that there are four GPx with Sec residues (GPx1-4). GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8 have Cys residues instead. GPx6 can not be found in this species, this will be further discussed.
GPx1
It is the most abundant selenoprotein in mammals (1). When we ran Blast, a huge amount of hits in different scaffolds were found. This was expectable since we knew that there are a lot of proteins in this family and they are very similar to each other. T-Coffee alignment gives us a high score with not many gaps (just in one extreme) or amino acid changes. The residue Sec is conserved as we expected, the position was also the same.
The predicted gene is found between the positions 94403 and 95193 of the scaffold PVKD010000564.1, in the positive strand and it has 790 nucleotides. The scaffold has 2 exons and the hit was found in the second one. Using SECIS Search3, a SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR section of the GPx1 protein, with a good Infernal and Covels score, which defines this SECIS element as correctly predicted. It was found between positions 94808 and 95193 of the genome.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has GPx1.

GPx2
This protein is only present in vertebrates and is mainly found in the epithelium of gastrointestinal tract.
According to all the results obtained with Tblast and T-Coffee it is very likely that this protein is found in the scaffold PVKD010000980.1 between the positions 51940 and 55261 of the forward strand. It has 2 exons and the hit was found in the second one. Moreover, the predicted protein starts with a Met, so it makes sense that this is the beginning of the protein. It contains Sec on the same position as the reference genome. SECIS Search3 detected two possible SECIS elements for this sequence, and one was discarded because it was present in the reverse strand. The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 107425 and 107490 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has GPx2.

GPx3
The results obtained confirmed again that it is very likely to find GPx3 in C. gambianus. Only few amino acid changes and a small gap were found. Although the Sec residue is not present in Mus musculus we did see it in C. gambianus. The predicted gene is located in the scaffold PVKD010003256.1, it has 5 exons between the positions 128652 and 135818 of the forward strand and it has 7166 nucleotides. SECIS Search3 predicted a grade A SECIS element in the positive strand of the protein sequence, between positions 165008 and 165082.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has GPx3.

GPx4
We got really good results in this alignment. This could be explained because this protein is the most conserved in evolution (6). Only four amino acidic changes and no gaps were found when doing the T-Coffee alignment. Both sequences have the Sec residue on the same position. The protein is found on the scaffold PVKD010015909.1 between positions 23844 and 26242 of the forward strand. It has 6 exons and a length of 2398 nucleotides. One grade A SECIS element was found for this sequence. The SECIS element was found on the same strand at the end of the predicted protein, between positions 25198 and 25271 of the scaffold, and thus it was validated.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has GPx4.

GPx5
We had some problems with the alignment of this protein. First of all, we tried with the lowest E-value but we got a really poor score with T-Coffee and almost none of the amino acids were conserved. After that, we also tried with other significant E-values of other scaffold, but the results were the same.
Finally, we changed the reading frameshift (-f 2) and the results were much better. T-Coffee gave us a good score with some amino acid changes and just two gaps on the ends. Moreover, both sequences started with a Met so it is very likely that the protein predicted corresponds to GPx5. In M. musculus, this protein has two Sec residue but none of them is conserved in C. gambianus genome.
The predicted gene is found in the reverse strand on the positions 100514 and 93950 of the genome, corresponding to the scaffold PVKD010003030.1. Its length is 72343 and it has 5 exons. Neither selenoprotein nor SECIS elements could be predicted for the GPx5 of C. gambianus.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has GPx5 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

GPx6
When running the blast and T-Coffee, GPx3 and GPx6 are found in the same scaffold and between the same positions, so it indicates that one is not found in C. gambianus. Knowing that both are part of the same evolutionary group, they may be that similar that the program interpreted them as the same protein. However, when analysing the results in a biological way, it does not make any sense. That is why, even though we got very high results with T-Coffee and blast in both cases, we tried another scaffold with another E-value for GPx6. The results were not satisfactory either, so we decided which protein corresponds to the scaffold using the phylogenetic tree.
The results obtained from the tree suggest that the protein found corresponds to GPx3 because both proteins predicted for C. gambianus are more closely related to the GPx3 of the Mus musculus.
Also, SECIS elements were only found in GPx3, further corroborating our hypothesis that only this predicted protein acts as a selenoprotein in C. gambianus and that the protein GPx6 found in C. gambianus is indeed GPx3.
GPx7
To align this protein, we chose the hit in scaffold PVKD010353829.1 found in the forward strand between the positions 21 and 293. T-Coffee results were good: the alignment presented some gaps in both of the ends but the rest was well conserved and the sequence starts with a Methionine. About Sec residue, it was not found in M. musculus GPx7 and, according to our results, neither in C. gambianus. The sequence is found between the nucleotide 21 and the nucleotide 293 of the scaffold and is 272 nucleotides and it just has one exon. In this case, no SECIS structure was found with SECIS Search3.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has GPx7 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

GPx8
According to the results in T-Coffee, it is very likely that the predicted protein is found in the positions 334 and 3656 of the scaffold PVKD010031108.1. There are a few amino acid changes and quite few gaps. Its length is 3322, it has 3 exons and it is found in the forward strand. We did not find Sec in any of the two proteins, nor did we find any SECIS element.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has GPx8 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

Phylogenetic tree
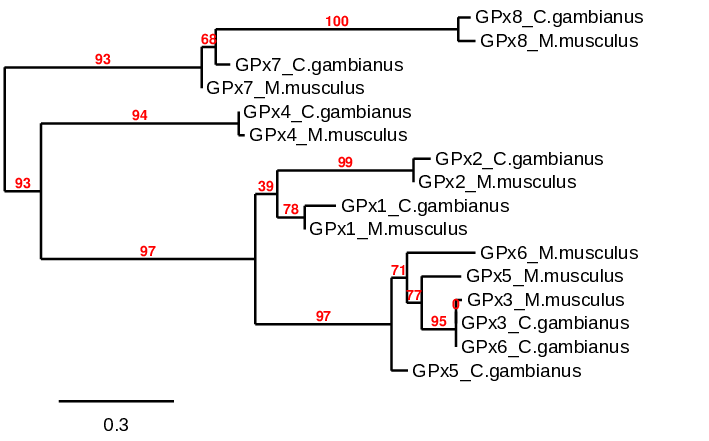
It is known that 3 evolutionary groups are found between GPx family: GPx1/GPx2, GPx3/GPx5/GPx6 and GPx4/GPx7/GPx8 (1). In this phylogenetic tree, 4 evolutionary groups are found correlating quite well with the bibliography. The results showed a cluster conformed by GPx7 and GPx8 for both Mus musculus and C. gambianus> proteins. Even though GPx4 is not in the same cluster, it is the protein closer to them, so all can be considered the same evolutionary group as shown in the paper of Vyacheslav M. et al.. Regarding to GPx1 and GPx2, both of them belong to the same cluster. Finally, the rest of proteins are found in the same group. As we said before, GPx3 and GPx6 of the C. gambianus are the same protein, corresponding to GPx3. We use both proteins to create the tree in order to know which one does not exist. All clusters show the Mus musculus and Cricetomys gambianus homologous porteins together, indicating that the results predicted correlate with the results of the reference genome.
IODOTHYRONINE DEIODINASE (DI) FAMILY
The second family of selenoproteins found in mammals is thyroid hormone deiodinases. This family consists in three paralogous membrane proteins that are involved in activation/inactivation of thyroid hormone. The three of them have different subcellular locations and tissue expression and their function is quite different. While DI1 and DI2 act activating the hormone towards the deiodination of the outer ring (T3), DI3 acts as inactivator in order to regulate levels of this hormone. In some cases, though, DI1 catalyzes the removal of the inner ring iodine leading to the formation of inactive thyroid hormone (1).
Deiodinases possess a thioredoxin-fold and show significant intra-family homology since the three of them share a common ancestor (6).
In some species, such as M. musculus only DI1 and DI2 paralogs are found. The same results were obtained for C. gambianus.
DI1
In this protein, Sec residue is not conserved in any of the two species. T-Coffee results were pretty good. Although there were some gaps on the ends, the middle of the strand was conserved with not many amino acid changes. The hit was found between positions 2734-3063 of the scaffold PVKD010015863.1. It can be found in the reverse strand, it has 1 exon and its length is 329 nucleotides. SECIS Search3 was unable to find any SECIS elements in the 3’-UTR region of the DI1 predicted gene sequence.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has DI1 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

DI2
In this protein, Sec residue is only found in C. gambianus. Actually, in T-Coffee results, which are really good, Sec is aligned with a gap. The scaffold chosen was PVKD010004213.1, and the hit is between positions 65800 and 56999. It is located in the reverse strand and it has a length of 8801 nucleotides and 2 exons. SECIS Search3 was able to find three SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. All three of them were found in the reverse strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the rest. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 52444 and 52370.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has DI2.

Phylogenetic tree

The results observed in this phylogenetic tree are coherent with the ones we extracted from our data. The proteins of the C. gambianus are closely related to their homologues in M. musculus and afterwards they link the whole DI family.
SELENOPROTEINS W1 (SelW1), W2 (SelW2), H (SelH) AND T (SelT)
All these proteins belong to the Rdx family and they all have a thioredoxin-like fold and are characterized by presenting a conserved motif (Cys-x-x-Sec). Based on its structure, it is thought that they act as a thiol-based oxidoreductases, but the exact function is unknown.
SelW is one of the most abundant selenoproteins in mammals. It belongs to the stress-related group and its expression is highly regulated by the availability of Se in the diet.
SelT is thought to have an effect in calcium homeostasis and neuroendocrine function. More recently, it was found that it is also implicated in the regulation of pancreatic cell function and glucose homeostasis.
Finally, SelH specifically binds to sequences that have heat shock and stress response elements and its involved in regulation of transcription of enzymes implicated on GPx de novo synthesis (1).
SelW1
SelW1 was found in the scaffold PVKD010002365.1. The predicted gene was located between positions 85411 and 85888 in the forward strand, containing 3 exons. Its length was 477 nucleotides. In the T-Coffee output, there were some gaps and amino acid changes but the score was very high. This protein contains two Sec residues in C. gambianus. It is remarkable, though, that in M. musculus these two residues have changed to S and W. Two SECIS elements were predicted for this protein, and only one was found in the same strand as the predicted protein, the positive strand. This SECIS element had an overall B grade and was located between positions 177101 and 177181 of the scaffold PVKD010002365.1, at the 3’-UTR region of the gene. However, the distance separating it from the gene was of 90 kb, which is not a valid distance by literature standards (2 to 5.2 kb between SECIS and protein in mammalians) (6). Thus, no viable SECIS elements were predicted for the SelW1 protein.
For all these reasons we can conclude that, although it seems that SelW1 in C. gambianus is still a selenoprotein (as Sec residues are conserved), we cannot conclude it is a functional selenoprotein, as no viable SECIS elements were found. In this case, the UGA codon is probably read as a STOP signal instead of a Sec.

SelW2
According to T-Coffee results, this protein is found in the scaffold PVKD010009993.1 between the positions 46239 and 47120 of the genome and it has a length of 881 nucleotides. The alignment showed almost no amino acid changes nor gaps. It corresponds to the forward strand and it is formed by 4 exons. We did not find Sec residues in any of the two species, they have a Cys instead. No SECIS elements were predicted for the SelW2 protein sequence either.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has SelW2 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

Phylogenetic tree
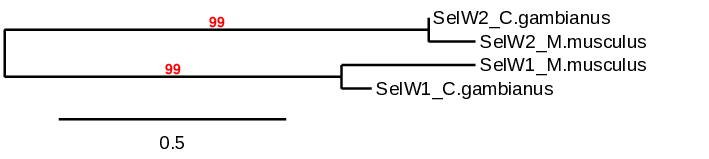
In this phylogenetic tree, both predicted proteins of C. gambianus are closely related to their homologues in M. musculus and then, the whole family is also linked . So the results observed are coherent with the ones we extracted from our data. Both proteins of the C. gambianus are closely related to their homologues in M. musculus and afterwards they link the whole family of proteins.
SelH
It is present in mouse and rat genomes and both proteins conserve the motive Cys-x-x-Sec. We got a high score in the alignment and it only showed 5 amino acid changes and no gaps. This gene is found in the positive strand of the scaffold PVKD010007063.1 between positions 88174-87671. It has 3 exons and its length is 13235 nucleotides. SECIS Search3 found two valid SECIS elements in the 3’ UTR region of the predicted SelH protein, with grades B and A respectively. Both SECIS elements were predicted on the reverse strand and their positions on the scaffold PVKD010015863.1 were 5171-5246 and 86972-87039. We chose the second one (87039-86972), as it was the best scored one. Only the best scoring SECIS element is depicted in the results table.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SelH.

SelT
With the results of T-Coffee output, it is very likely that SelT is found between 24130-37365 of the reverse strand. It corresponds to the scaffold PVKD010015842.1. We got the highest score with the alignment and only few gaps were found in the 5’ region. The sequence starting with a Met and Sec residue was conserved in both species. The length is 503 nucleotides and it has 5 exons. SECIS Search3 predicted one grade A SECIS element for the SelT protein. It was found on the positive strand, between positions 28865 and 28938 of the scaffold PVKD010007042.1.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SelT.

Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MSRA)
MsrA is a selenoprotein which acts as a stereospecific methionine-S-sulfoxide reductase, which means that catalyzes the repair of the S enantiomer of oxidized methionine residues in proteins. It contains the Sec residue in the active site. The Sec-containing MsrA proteins display more than 10-50 times higher activity than MsrA homologues naturally containing Cys, suggesting that Sec provides catalytic advantages in these redox-active enzymes (1).
As we performed for the rest of the proteins, we started analyzing the scaffold with the lowest E-value (PVKD010019530.1). However, the results of the T-Coffee showed an alignment where the first part was full of gaps, while the second part was really good aligned. This fact made us think that maybe the protein was truncated into two different scaffolds. That is why we decided to analyze the scaffold with the second lowest E-value (PVKD010004692.1). This alignment showed exactly the opposite: the first part was really well aligned, while the second one was not. That made us confirm our hypothesis: both scaffolds codify for the same protein and its sequence is truncated. This happened due to the short length of the scaffolds in the reference genome, as we mentioned before.
Scaffold PVKD010019530.1
According to the results obtained with T-Coffee, it is probable that the predicted protein is found in this scaffold, as the score is pretty high (940). No Sec residues are found in either C. gambianus nor M. musculus genome sequences. The predicted gene is located on the reverse strand, from the nucleotide 17092 to the nucleotide 14238, and it has a length of 2854 nucleotides. There are 2 exons in this scaffold sequence.
Scaffold PVKD010004692.1
The score obtained in the T-Coffee output was very high (999), which means that it is probable that the predicted protein is located in this scaffold. No Sec residue has been found in both species’ sequences either. The predicted gene is found between the nucleotide 102269 and the nucleotide 2876 in the reverse strand, and its length is 99393 nucleotides. There are 5 exons in this scaffold sequence.
As we said before, this protein is located in the reverse strand, which means that its 3’ end is located at the beginning. That is why we performed the SECIS Search3 using the scaffold named as PVKD010004692.1.
SECIS Search3 predicted a SECIS element between positions 99675 and 99567 of the scaffold PVKD010004692.1. This SECIS had an overall B grade, with low infernal and covels scores, and it was found in the same strand as the protein.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has MsrA, but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved.

SECIS BINDING PROTEIN 2 (SBP2)
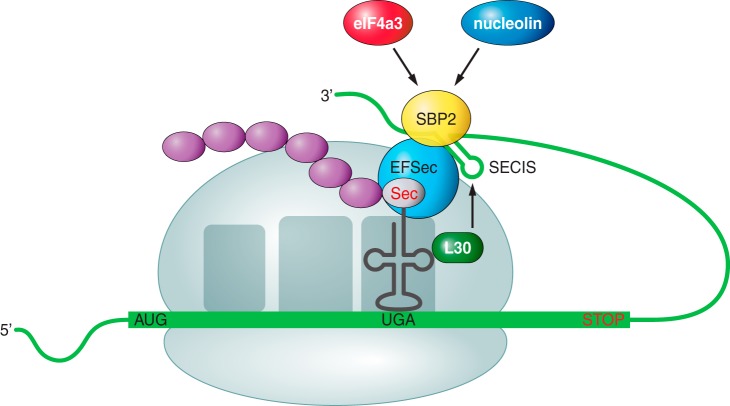
The SBP2 is a protein which takes part on the mechanism and regulation of Sec incorporation into proteins, as it is required for efficient re-coding of UGA as Sec in eukaryotes, together with another protein (eEFSec) (1).
We first started analyzing the scaffold with the lowest E-value, but we realized the score obtained by the T-Coffee was too low and it showed a lot of gaps and changes of amino acids, and just a few random alignments. We then tried to do the same for the second scaffold with the lowest E-value, but something similar happened. Then, we realized that the exonerate results showed a protein with too many exons, and even some of them were superposed. We thought that this could be due to an alternative exon of the protein, so we tried just with exons corresponding to one protein.
Results with T-Coffee were also bad, but then we decided to repeat the process changing the reading frameshift (-f 2). Finally, we obtained a very good result by using the first scaffold with the best E-value ( PVKD010006502.1) and the new reading frameshift.
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output is 998, with almost no gaps and just some amino acid changes. No Sec residues found in any of the two species. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 112116 and the nucleotide 35680 of the forward strand, and its length is 23564 nucleotides. It has 17 exons, which is quite a lot, but since this protein has three domains it makes sense that the coding region is large (1). SECIS Search3 was not able to predict SECIS elements in the 3’ UTR region of the SBPS2 predicted protein sequence, that makes sense since we did not found Sec.
For all these reasons we can conclude that SBP2 is not a selenoprotein. This result make sense since this protein belongs to the group of machinery related to the processing of selenoproteins (1).

SELENOPHOSPHATE SYNTHETASE (SPS) FAMILY
In this family we find two proteins: SPS1 and SPS2. Initially, they were grouped because it was thought they both have the SPS function. However, it has been shown that SPS2 can generate selenophosphate, whereas SPS1 can not. Several findings suggest that SPS2 is required for de novo synthesis of selenophosphate, while SPS1 may have a possible role in Sec recycling through a Se salvage system. In addition, since SPS2 is a selenoprotein itself, it possibly serves as an autoregulator of selenoprotein synthesis (1).
SPS1
The obtained score from the T-Coffee is so high (1000) we can almost confirm that the SPS1 protein is found in the scaffold PVKD010000387.1. Also, the alignment is perfect, with the exception of one single change of amino acid. No Sec residue is found in either of the compared sequences. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 390929 and the nucleotide 411306 of the forward strand, and it is 20377 nucleotides long. It has 8 exons. No SECIS elements were found in this sequence.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has SPS2 but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved and no SECIS elements were found.

SPS2
Analyzing the results from the T-Coffee output, we can say it is probable that the protein is located in the scaffold PVKD010013165.1, as the score is very high (999). The alignment shows one single gap in the 5’ end and small amino acid changes. Also, our predicted protein starts with a methionine, so we think it is a good prediction. We also found a Sec residue in both genome sequences, the M. musculus and the C. gambianus. This gene has one single exon and is located between the nucleotide 10245 and 11588 of the forward strand, and it has a length of 1343 nucleotides. SECIS Search3 detected one grade A SECIS element for the SPS2 protein, between positions 12115 and 12191 of the PVKD010013165.1 scaffold, a the 3’ UTR region of this protein.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SPS2.

Phylogenetic tree
The results observed in this phylogenetic tree are coherent with the ones we extracted from our data. Both proteins of the C. gambianus are closely related to their homologues in M. musculus and afterwards they link the whole SPS family of proteins.
SELENOPROTEIN I (SelI)
The transmembrane protein SelI is a recently evolved selenoprotein which is found only in vertebrates. The physiological function of the Sec-containing SelI has to be further examined (1).
The highest score (1000) of the T-coffee was obtained, meaning that it is probable that the predicted protein is located in the scaffold named as PVKD010011778.1. The alignment was almost perfect, even though there were a few changes of amino acids and small gaps. We found the Sec residue in both sequences, C. gambianus and M. musculus. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 1782 and the nucleotide 39026 of the forward strand, and it is 37244 nucleotides long. It has 10 exons. The SECIS element found in the predicted SelI gene sequence was located in a 3’ position to the selenocysteine, on the forward strand and between positions 13706 and 13783 of the scaffold PVKD010011778.1. It had an overall A grade, with a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SelI.

SELENOPROTEIN 15 (Sel15) AND SELENOPROTEIN M (SelM)
Both Sel15 and SelM are thioredoxin-like fold ER-resident proteins that form a distinct selenoprotein family. On the one hand, Sel15 is thought to mediate the cancer prevention effect of dietary Se and regulation of redox homeostasis in the ER. On the other hand, SelM is a distant homolog of Sel15, which was identified by bioinformatics approaches. The presence of redox-active motifs and structural similarities to other thioredoxin-fold oxidoreductases suggest that Sel15 and SelM may catalyze the reduction or rearrangement of disulfide bonds in the ER-localized or secretory proteins (1).
Sel15
As we performed for the other proteins, we started analyzing the scaffold with the lowest E-value. However, the results obtained with T-Coffee were not really good. That is why we decided to work with the second lowest E-value, corresponding to the scaffold named as PVKD010011498.1. The score obtained from the T-Coffee was really good (1000), so we can be almost sure our predicted protein fits in this scaffold. The alignment was absolute, even though there were some changes of amino acids and one gap. We also found the Sec residue in both of the studied sequences. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 10111 and the nucleotide 41086, on the forward strand and it has a length of 30975 nucleotides. It has 5 exons. One grade A SECIS element was predicted for the Sel15 protein. It was found between the 10795 and 10873 positions of the scaffold PVKD010011498.1, on the 3’ region of the predicted selenocysteine and on the same strand as the predicted gene.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has Sel15.

SelM
According to the results obtained with T-Coffee, we can be pretty sure the protein predicted is found in the scaffold PVKD010014587.1, as the score is the highest possible (1000). The alignment is almost perfect, although some changes of amino acids can be found. We found the Sec residue conserved in both sequences, C. gambianus and M. musculus. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 3785 and the nucleotide 5927 on the reverse strand, and it is 2142 nucleotides long. It has 5 exons. SECIS Search3 found a grade A SECIS element at the reverse strand of the predicted protein gene sequence. It was found in a 3’ position to the selenocysteine, between positions 3672 and 3743 of the scaffold PVKD010014587.1, and had good infernal and covels scores.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SelM.

SELENOPROTEIN K (SelK) AND SELENOPROTEIN S (SelS)
Even though SelK and SelS have no similarities on their sequences, they could be assigned to a single SelK/SelS family of related selenoproteins based on their topology, the presence of a glycine-rich segment and a characteristic location of Sec residues in the COOH-terminal end of the protein. This family is the most widespread eukaryotic selenoprotein family, whose members are present in nearly all known Se-utilizing organisms. They have been both implicated in ER-associated degradation of misfolded proteins (1).
SelK
The score obtained from T-Coffee indicates that it is probable that this protein is located in the scaffold PVKD010007843.1, as the value is high (997). There are some changes of amino acids and a few little gaps, but the fact that it starts with a methionine makes us think it is a good prediction. We found the Sec residues in both of the studied sequences. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 63806 and the nucleotide 64090, in the forward strand and it is 284 nucleotides long. It has 1 exon. Regarding SECIS element prediction, no SECIS elements were found in this genome sequence.
For all these reasons we can conclude that, although it seems that SelK in C. gambianus is still a selenoprotein (as Sec residues are conserved), we cannot conclude it is a functional selenoprotein, as no SECIS elements were found. The UGA codon is probably read as a STOP codon in C. gambianus.

SelS
In the T-Coffee output we obtained a really high score (999), indicating that it is probable that the predicted protein is located in the scaffold PVKD010001728.1. Although there are some changes of amino acids and little gaps, the alignment is really good. We found the Sec residue in the M. musculus sequence, but not in the C. gambianus one. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 134279 and the nucleotide 142479, in the forward strand and it has a length of 8200 nucleotides. It has 6 exons. Regarding the SECIS, three SECIS were predicted for SelS, but one was discarded for being in the incorrect strand. From the remaining two, only one is considered a valid SECIS, because of the low infernal and covels scores presented by the third predicted SECIS elements. Thus, the valid SECIS element, which we can see in the results table, is found in the positive strand between positions 177085 and 177172 of the scaffold PVKD010001728.1, and has an overall A grade.
For all these reasons we can conclude that C. gambianus has SelS but it is no longer a selenoprotein as its Sec is not conserved even if viable SECIS elements were found.

SELENOPROTEIN N (SelN)
SelN was one of the first proteins identified through bioinformatic approaches. It is an ER-resident transmembrane glycoprotein and it plays an important role in the maintenance of satellite cells and it is required for regeneration of skeletal muscle tissue following stress or injury (1).
The result obtained from the T-Coffee was pretty high (998), meaning that it is probable that the predicted protein is located in the scaffold PVKD010009337.1. There are some amino acid changes and one single gap, but generally the alignment is really conserved. The Sec residue is also conserved in both sequences, M. musculus and C. gambianus. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 35198 and the nucleotide 46051, in the reverse strand and it has a length of 10853 nucleotides. It has 12 exons. One SECIS element was found on the 3’ UTR region of this protein. It had good infernal and covels scores, and an overall A grade. It was found in the same strand as the predicted protein, the reverse strand, between positions 34061 and 34151 of the scaffold PVKD010009337.1.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has SelN.

THIOREDOXIN REDUCTASE (TR) FAMILY
This family of selenoproteins together with the thioredoxin represent the biggest reduction system of the cell. In mammals, we found three isoforms (TR1, TR2, TR3) which all contain selenocysteine.
TR1 is involved in NADPH-dependent reduction of Trx1. This protein takes part in the control of many physiological processes such as antioxidant defense, apoptosis, transcription regulation and so on. It also acts as an electron donor for enzymes activated by redox reactions. The second member of the family, TR3, is involved in reduction of mitochondrial thioredoxin. Finally, the third isoform is TR2. This protein differs a little bit from the two above regarding to its structure. It has a glutaredoxin (Grx) domain that gives to this protein a Grx activity apart from the Txr one. However, its function still remains unknown.
When we analyzed the exon distribution in TR1 and TR2, we realized they were almost the same, just differing in one exon. In our opinion, this might be because of an alternative splicing which allows the existence of these two isoenzymes (1).
TR1
Taking into account the results obtained from the T-Coffee, it is probable that the predicted protein is found in the scaffold PVKD010006181.1, as the score is really high (999). At the beginning of the sequence, there are some changes of amino acids, but the rest is really well conserved. Also, the protein gets started with a methionine, which makes us think that it is a good prediction. The Sec residue is conserved in both of the studied sequences. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 53709 and the nucleotide 72789, in the forward strand and it is 22659 nucleotides long. It has 14 exons. SECIS Search3 predicted a grade A SECIS element for this protein. It was found in the same strand as the predicted TR1 protein, the positive strand, between positions 66841 and 66918 of the scaffold PVKD010006181.1, positioned 3’ to the selenocysteine.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has TR1.

TR2
To study this protein, we had to choose the scaffold with the second lowest E-value, as the first one was not good enough. The T-Coffee output shows a quite high score (997), which means that it is probable that the predicted protein is found in the scaffold called PVKD010006181.1. The alignment showed a few changes of amino acids and a single little gap. The Sec residue is conserved in both M. musculus and C. gambianus sequences. The predicted gene is located between the nucleotide 24690 and the nucleotide 76368, in the forward strand and it has a length of 51613 nucleotides. It has 13 exons. One grade A SECIS element was predicted for TR2, at the positive strand and between positions 37828 and 37905 of the scaffold PVKD010006181.1. It had good infernal and good covels scores.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has TR2.

TR3
In this alignment we obtained the highest score (1000), no gaps and few amino acid changes. So it is very likely that the protein is found between the positions 5981-35538 in the positive strand of the scaffold PVKD010012172.1. Sec residue is conserved in both M. musculus and C. gambianus genomes. It has 16 exons and 29557 nucleotides. SECIS Search3 predicted one SECIS element for the TR3 predicted protein, on the forward strand between positions 11127 and 11202 of the scaffold PVKD010012172.1. It was found in a 3’ position to the selenocysteine and had an overall A grade.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that C. gambianus has TR3.

Phylogenetic tree
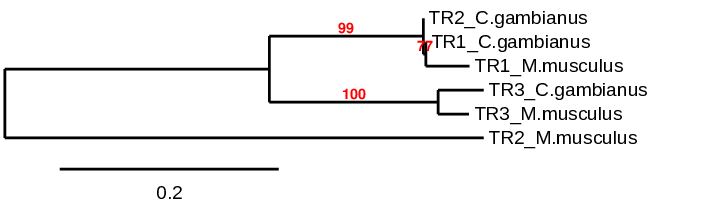
In literature, it was seen that TR2 differs a bit from the other two isoforms (TR1 and TR3) (1). In this phylogenetic analysis, we see that indeed TR1 and TR2 are closely related to their homologues in each species. However, the results for TR2 are surprising, as the TR2 from Mus musculus seems to follow the pattern observed in literature, but the TR2 from Cricetomys gambianus does not. If we look at the scaffolds form which the proteins were extracted, we see that TR1 and TR2 both come from the same scaffold, and in our analysis both these proteins are nearly the same, just deferring in one exon. In our opinion, this might be because of an alternative splicing which allows the existence of these two isoenzymes in Cricetomys gambianus. It could also be due to the fact that our predicted protein does not include the GRx domain which normally makes it more different to the other TR family isoforms, as this domain could have disappeared from the TR2 Cricetomys gambianus gene.