Results
The results of the analysis of Monopterus albus in comparison to Danio rerio are shown in the following table. Different M. albus selenoproteins and proteins involved in their synthesis can be found in the table (see first column). In the second column it is annotated the specie which has been used to compare the genome of Monopterus albus; in our case, Danio rerio. The Scaffold and the exact Gene location of each protein are presented in third and fourth columns as well as the type of alignment (using a thumb symbol in the fifth column). Moreover, the results of T-blastn, Exonerate, Exons, t-coffee and Predicted protein are attached in the sixth, seventh, eighth, ninth and tenth columns respectively and presented as an eel symbol. SECIS information and images can also be found in the eleventh and twelfth columns of most of the proteins. To easily interprete the table we have used some symbols:
 |
Good alignment |  |
Available file |
 |
Bad alignment |  |
Not available file |
Selenoproteins
| Protein | Species | Scaffold | Gene location | Alignment | Tblastn | Exonerate | Exons | T-coffee | Predicted protein | SECIS | SECIS image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sel15 | Danio rerio | KV884860.1 | 46845-50137(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOE | Danio rerio | KV884725.1 | 49878-72805(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx1a | Danio rerio | KV884777.1 | 49662-51143(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
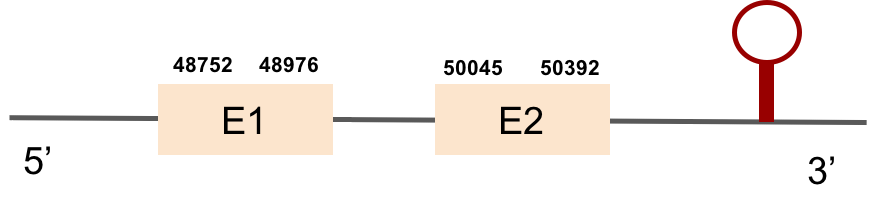
| GPx1b | Danio rerio | KV884724.1 | 48752-50392(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
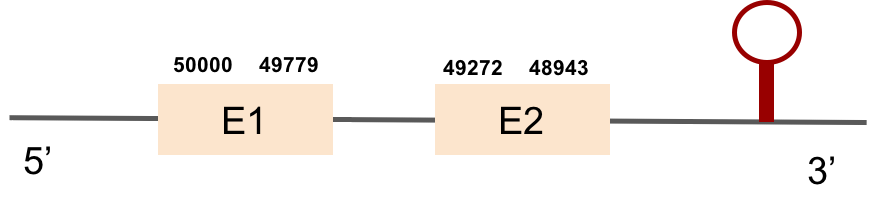
| GPx2 | Danio rerio | KV884828.1 | 48943-50000(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx3a | Danio rerio | KV884690.1 | 49755-90093(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx3b | Danio rerio | KV884757.1 | 1449-50738(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx4a | Danio rerio | KV884810.1 | 49723-50372(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx4b | Danio rerio | KV884860.1 | 40633-51128(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx7 | Danio rerio | KV885045.1 | 1048-2346(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| GPx8 | Danio rerio | KV884708.1 | 49770-51413(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| DIO1 | Danio rerio | KV884771.1 | 50000-51307(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
| DIO3a | Danio rerio | KV884750.1 | 50021-50791(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| DIO3b | Danio rerio | KV884701.1 | 50000-50740(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SEPHS | Danio rerio | KV884693.1 | 48771-51999(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SEPHS2 | Danio rerio | KV884875.1 | 36363-51219(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOH | Danio rerio | KV884690.1 | 49905-59163(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOI | Danio rerio | KV884750.1 | 49009-54715(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOJ1 | Danio rerio | KV884754.1 | 48578-52162(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOK | Danio rerio | KV884694.1 | 47588-50577(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOL | Danio rerio | KV884852.1 | 48146-79351(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOM | Danio rerio | KV884744.1 | 49863-52292(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENON | Danio rerio | KV884701.1 | 48105-57297(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
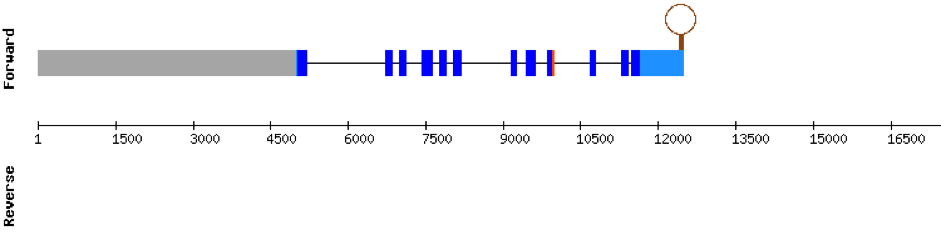
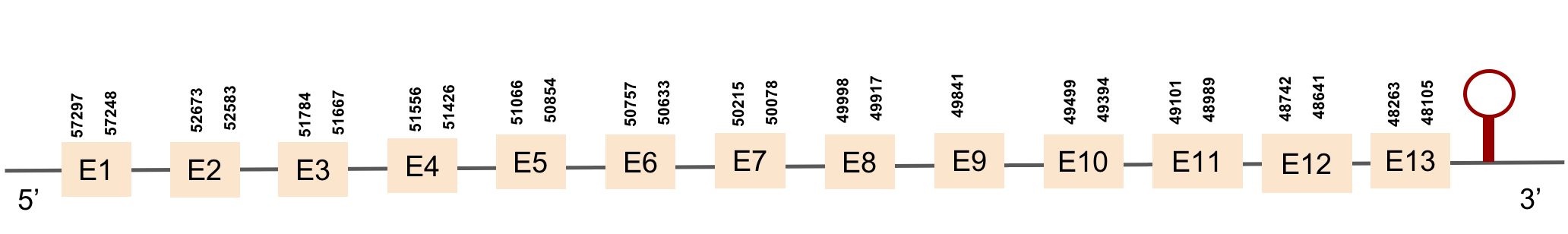
| SELENOO1 | Danio rerio | KV884747.1 | 44623-50000(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOP(1) | Danio rerio | KV884754.1 | 3900-95063(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOP(2) | Danio rerio | KV884708.1 | 19921-50563(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
| MSRB1a | Danio rerio | KV884862.1 | 49506-50497(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
| MSRB1b | Danio rerio | KV884859.1 | 49332-50417(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| MSRB2 | Danio rerio | KV884788.1 | 35898-37817(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| MSRB3 | Danio rerio | KV884739.1 | 47006-51820(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOS | Danio rerio | KV884994.1 | 44043-62483(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
| SELENOT1 | Danio rerio | KV884716.1 | 45129-51707(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SELENOT2 | Danio rerio | KV885052.1 | 37306-58707(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |

|  |
 |
 |
| SELENOU1a | Danio rerio | KV884748.1 | 49645-51035(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
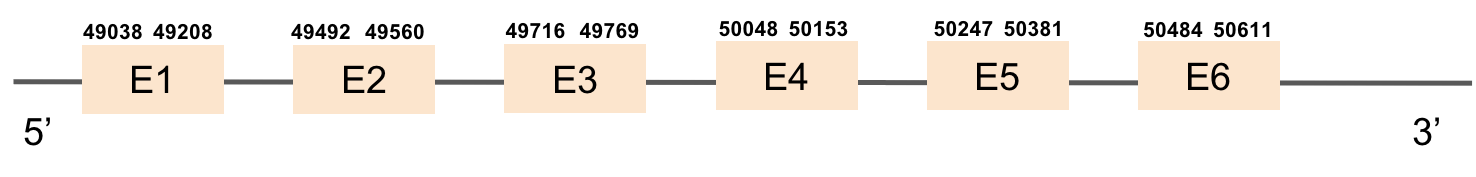
| SELENOU2 | Danio rerio | KV884708.1 | 49038-50611(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
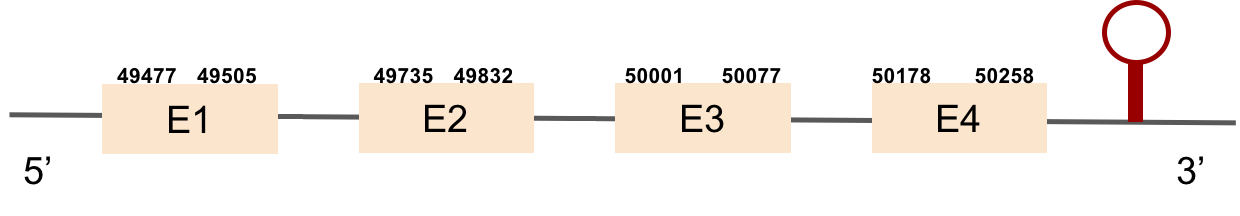
| SELENOW | Danio rerio | KV884758.1 | 49477-50258(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| TXNRD2 | Danio rerio | KV884700.1 | 61214-56173(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| TXNRD3 | Danio rerio | KV884706.1 | 39705-54311(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Selenoprotein machinery
| Protein | Species | Scaffold | Gene location | Alignment | Tblastn | Exonerate | Exons | t-coffee | Predicted protein | SECIS | SECIS image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
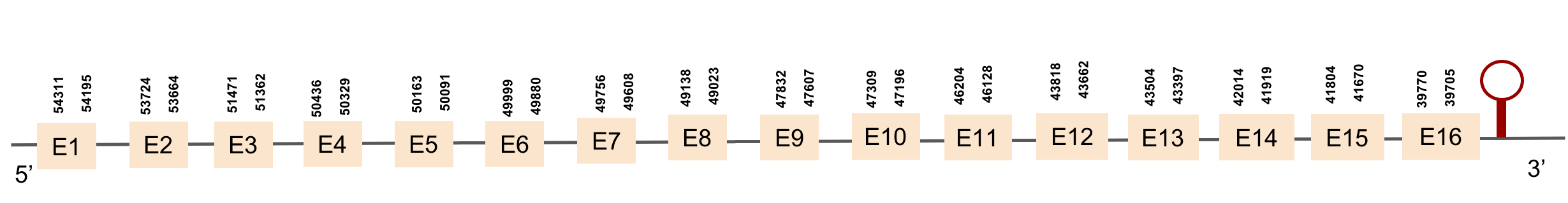
| eEFsec | Danio rerio | KV884777.1 | 45614-55367(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| MsrA(1) | Danio rerio | KV884701.1 | 49833-77839(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| MsrA(2) | Danio rerio | KV884890.1 | 49839-82460(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
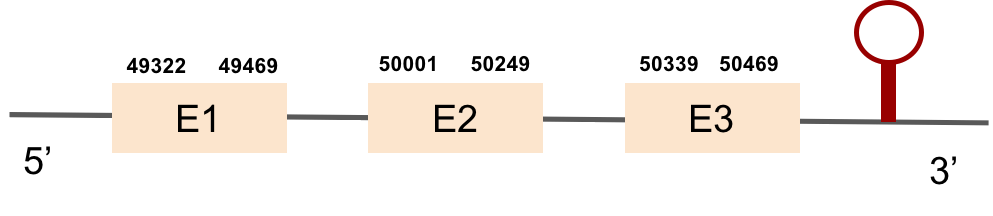
| PSTK | Danio rerio | KV884757.1 | 49322-50469(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
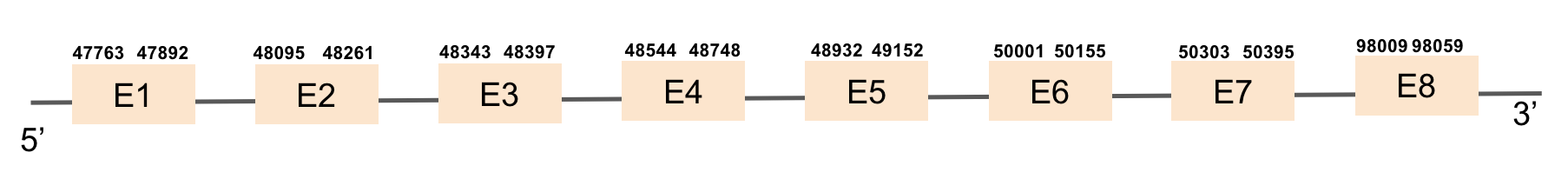
| SBP2(1) | Danio rerio | KV884725.1 | 47763-98059(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SecS | Danio rerio | KV885014.1 | 50000-58155(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| SECp43(1) | Danio rerio | KV884842.1 | 41097-50799(-) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
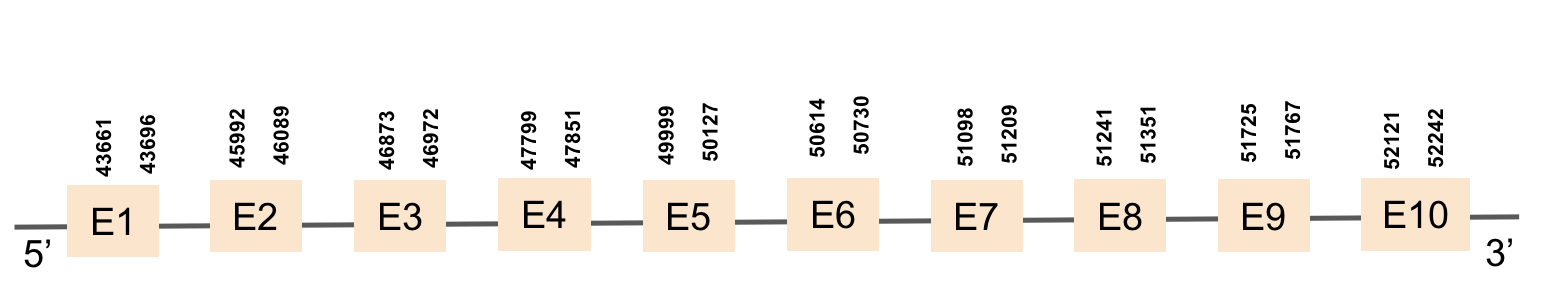
| SECp43(2) | Danio rerio | KV884821.1 | 43661-52242(+) |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Analysis of Selenoproteins
All first images of the sequences are taken from SelenoDB database and refer to zebrafish genome. They do not always coincide with our results because the methods used for the obtention of the proteins are not the same. Nevertheless, we rely on our results when the result of t-coffee comprises the whole protein. The second images are made by us and refer to M. albus genome.
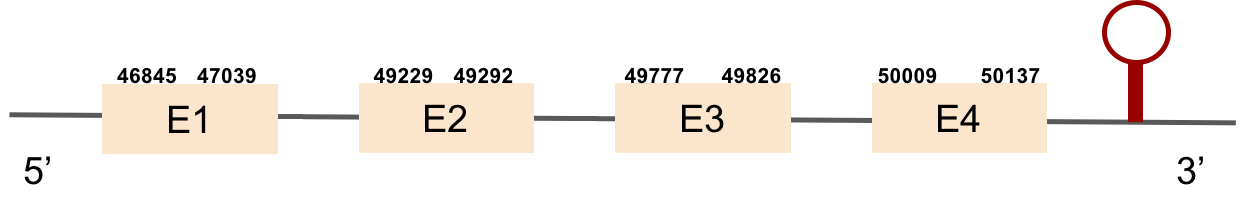
Sel15Sel15 was found in the KV884860.1 scaffold. We have found 4 different exons. t-coffee results showed an almost perfect correlation with its homolog in zebrafish. We found a conserved selenocysteine residue, that aligned perfectly with that of zebrafish. There was one SECIS structure predicted in the same strand as Sel15 and placed in 3’ UTR.
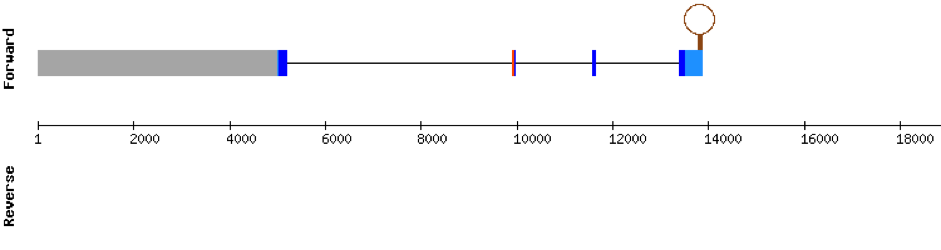
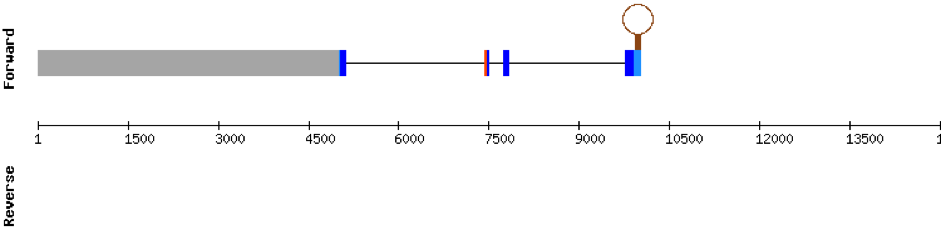
We found 3 different hits of SELENOE in M. albus genome located in KV884725.1 scaffold. This protein had 5 different exons in the negative strand. The t-coffee result showed a very good alignment. Moreover, the selenocysteine residue was conserved and well aligned with the residue of zebrafish. One SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR.
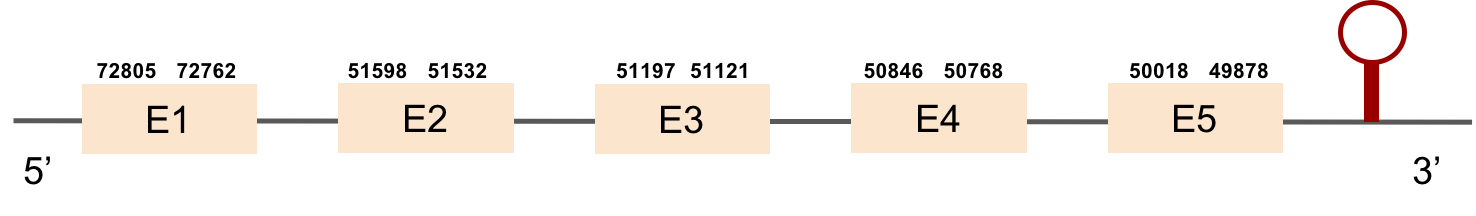
GPx1a
The scaffold where we found the most significant hit for GPx1a was KV884777.1. We found 2 different exons in the negative strand. The alignment obtained from t-coffee was really good. Furthermore, selenocysteine residue was conserved in M. albus, and aligned with the selenocysteine of Danio rerio. When searched in seblastian, one SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR.
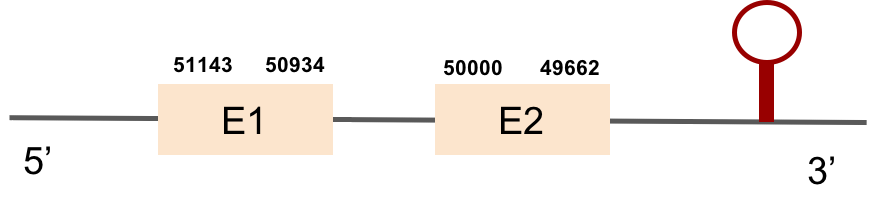
GPx1b protein was found in scaffold KV884724.1 with two exons in the positive strand. It had a good alignment, as the selenocysteine was conserved. One SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR.
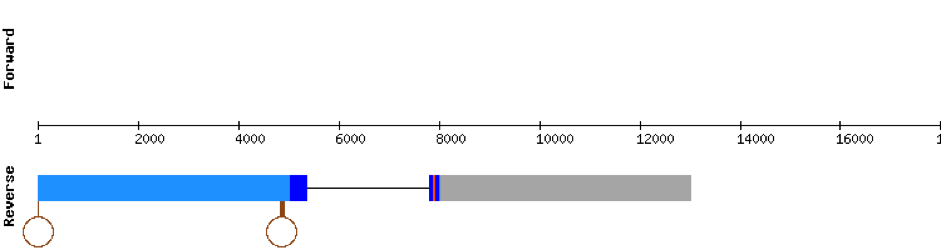
This protein was found in scaffold KV884828.1 and it had two exons in the negative strand. GPx2 had a good alignment and the selenocysteine was aligned and conserved. We noticed that in this case the protein that we predicted had a lot of Xs and gaps. Our program automatically assigned to this unread position the value of X. As we can see, that region of the scaffold is full of Ns, meaning that it is not well annotated. Finally, one SECIS structure was predicted by Seblastian in 3’ UTR of the negative strand.
This protein was found in scaffold KV884690.1. It has 7 exons and is located on the negative strand. GPx3a had a good alignment with zebrafish protein and the selenocysteine was conserved and aligned with the one of zebrafish. Seblastian predicted one SECIS structure that was found in 3’ UTR.
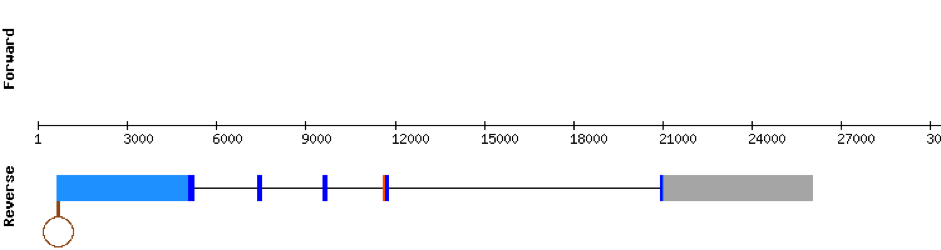
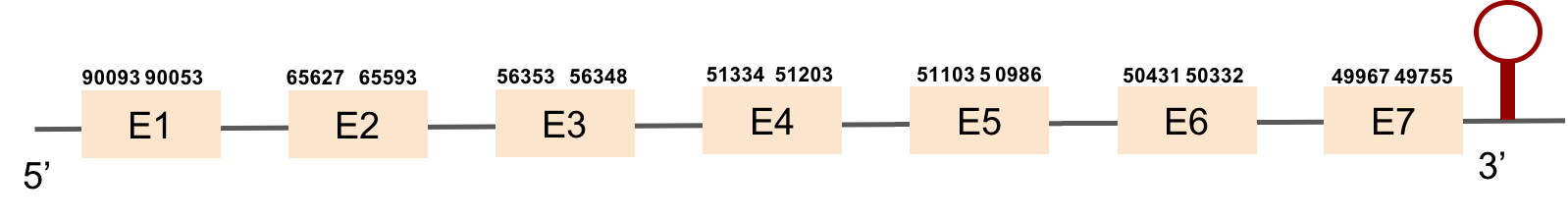
GPx3b protein was found in scaffold KV884757.1 and it is constituted by 5 exons located on the negative strand. The t-coffee alignment was good, the selenocysteine is conserved as it is also aligned with the zebrafish protein. No selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence with Seblastian but one SECIS structure was found in the opposite strand, meaning that it is not part of the protein.
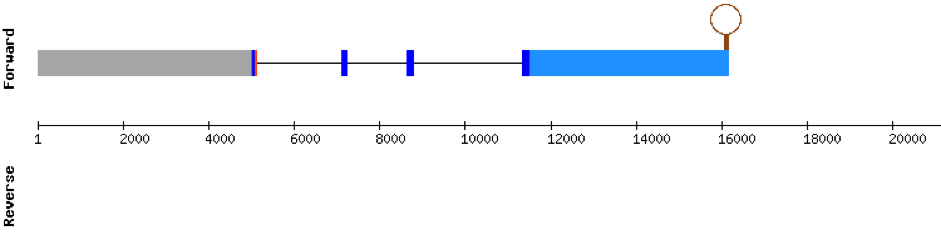
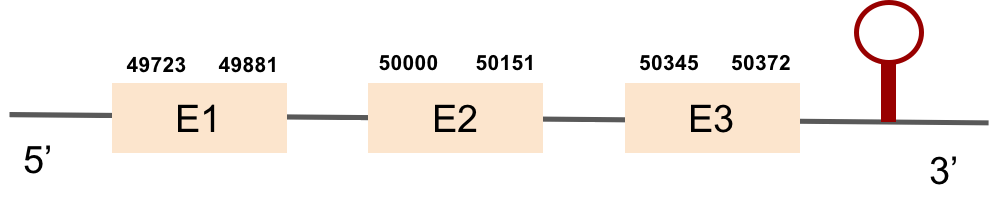
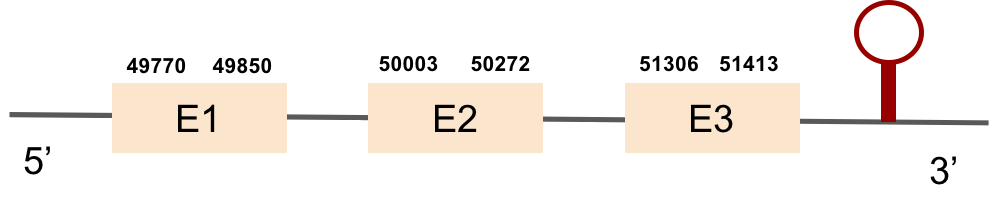
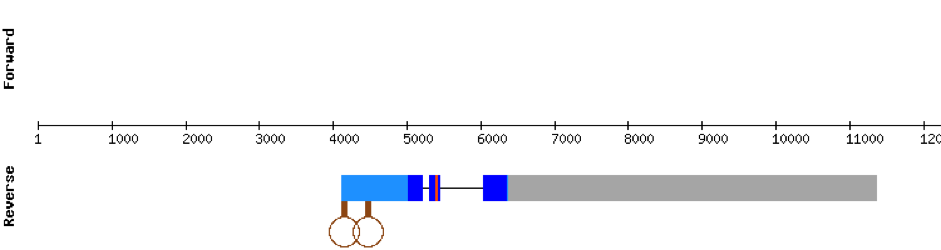
This protein was found in KV884810.1 scaffold and it has 3 exons located on the positive strand. The t-coffee results showed a good alignment with the zebrafish protein and the selenocysteine was also conserved. Finally, one SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR position with Seblastian.
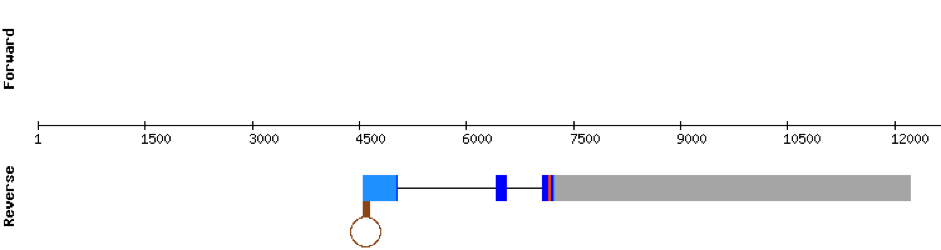
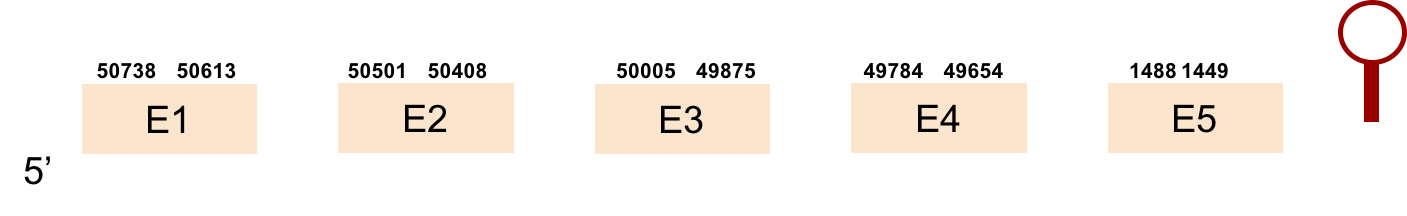
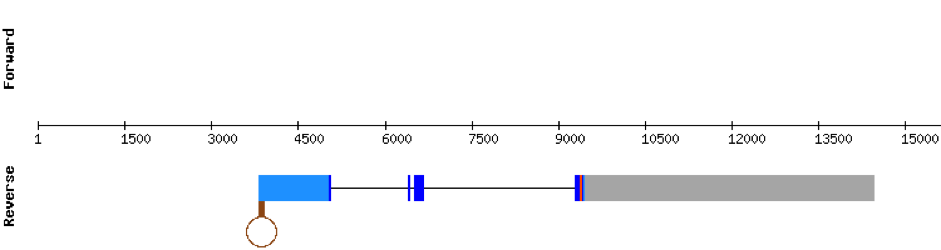
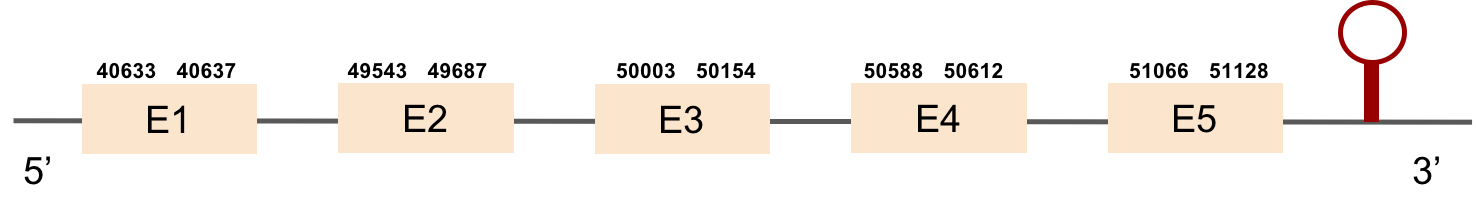
This protein was found in KV884860.1 scaffold and it had 5 exons that were located on the positive strand. t-coffee results showed also a great alignment, selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned with the protein from zebrafish. Seblastian predicted one SECIS structure that was found in 3’ UTR.
GPx5 and GPx6 are not found in the genome of zebrafish. However, in order to make sure that M. albus did not have these two selenoproteins, we compared GPx5 and GPx6 from Homo Sapiens genome to M. albus genome. We saw that there were some scaffolds where these two proteins were found although these ones were already found in other selenoproteins at the same position with better scores than in GPx5 and GPx6.
GPx7This protein was found in scaffold KV885045.1 and it consists in 3 exons that are located on the negative strand. GPx7 had a good alignment as we can see in the results of t-coffee and there is no selenocysteine neither in zebrafish nor in M.albus as expected. Moreover, no SECIS could be predicted for this sequence with Seblastian, as also expected.
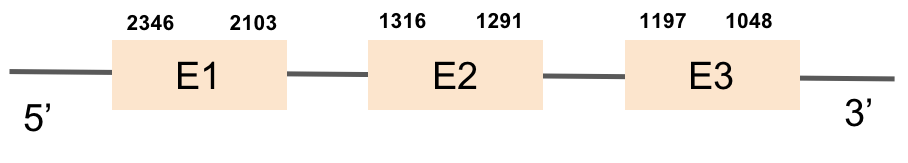
This protein was found in scaffold KV884708.1 and is constituted by 3 exons located on the positive strand. The alignment with zebrafish protein was good but there was no selenocysteine neither in zebrafish nor in M. albus, as it was expected. No selenoprotein could be predicted in this sequence with Seblastian although one SECIS structure was predicted but it was located in the opposite strand of the protein.
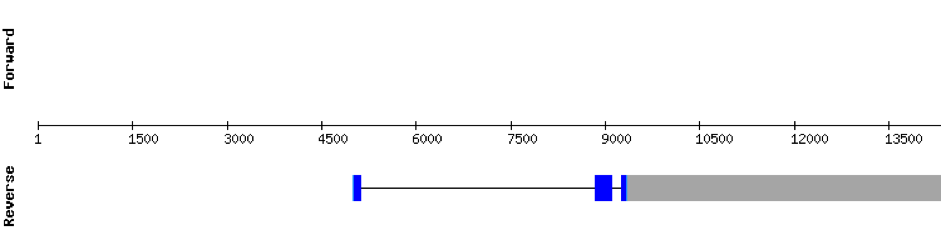
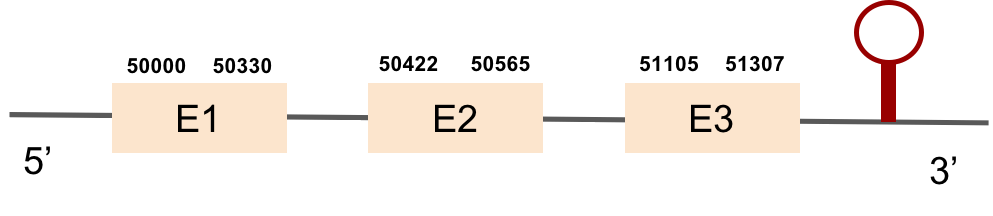
DIO1
DIO1 was found in scaffold KV884771.1 with 3 hits although it was also found in two other scaffolds that had only one hit. We interpreted that it had 3 exons as its homolog. It had one selenocysteine that was conserved as it aligned perfectly with the one of zebrafish protein although the first exon alignment was not very optimate. There were 2 SECIS structures found of grade A that were on the same strand as our protein. Both SECIS structures were in 3’ UTR extreme, being part of the protein.
This protein was not found in Monoperus albus genome. It was found in some scaffolds but the e-value was high and the alignment that resulted from the t-coffee matched a very small fraction of the protein.
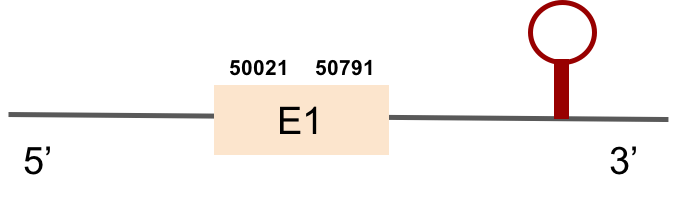
DIO3aThis protein was found in KV884750.1 scaffold and it is constituted by only one exon. t-coffee results showed that DIO3a was well aligned and has a selenocysteine conserved as it aligns with the zebrafish one. When predicted with Seblastian 1 SECIS structure was located at 3’ UTR.

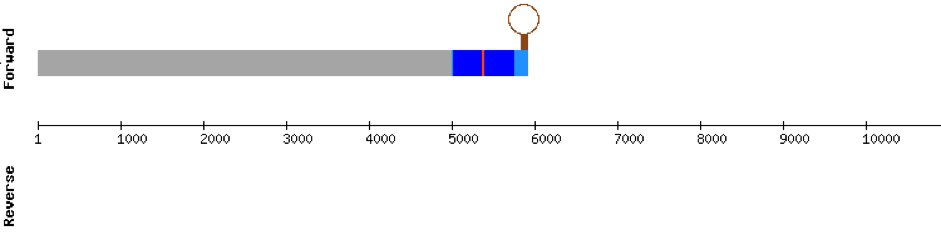
SEPHS
This protein was found in scaffold KV884693.1 and it has 9 exons located in the positive strand. SEPHS had a perfect alignment with its homolog in zebrafish, but with no selenocysteine as it is a machinery protein. Therefore, no selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence with Seblastian but one SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR 4.000 bases away from the last exon.
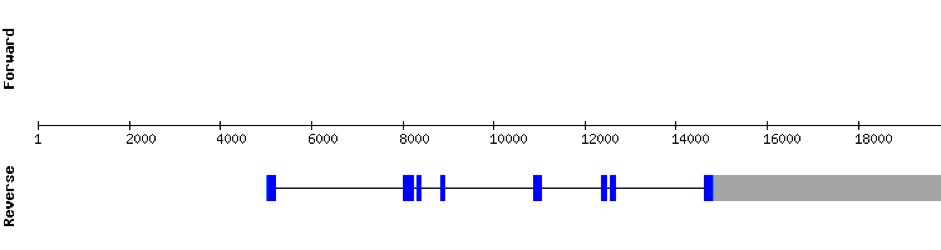
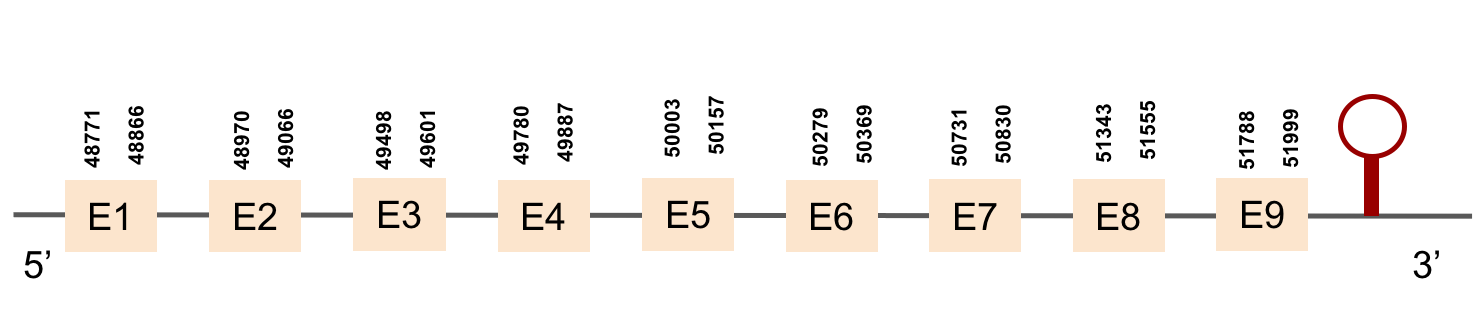
This protein was found in scaffold KV884875.1 and it has 9 exons that are also located in the positive strand. The alignment made with t-coffee was good. The selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned with the one of zebrafish. Moreover, Seblastian preducted one SECIS structure in 3’ UTR. Even though it is a machinery protein it contains a selenocysteine.
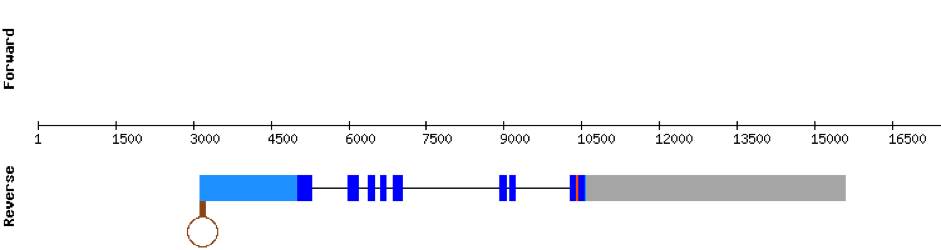
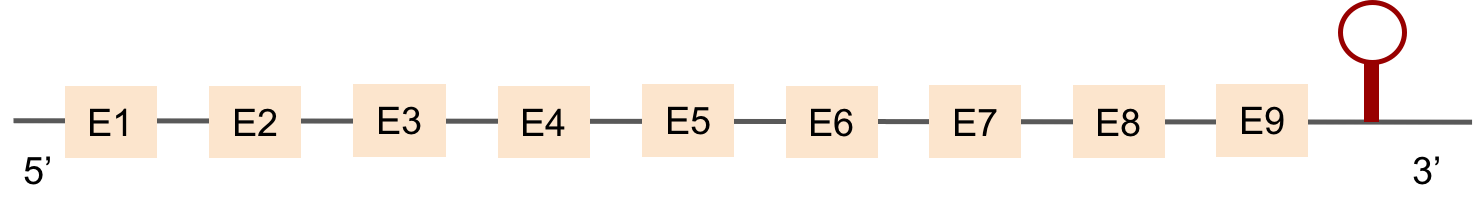
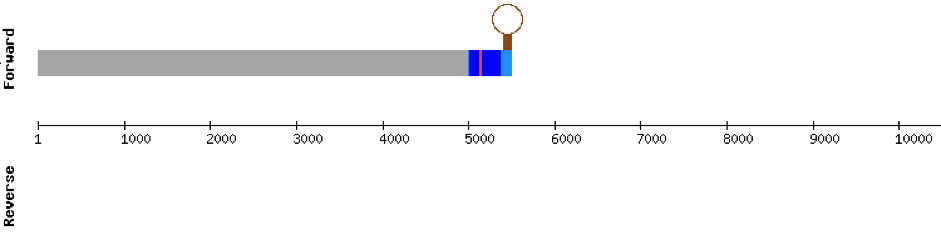
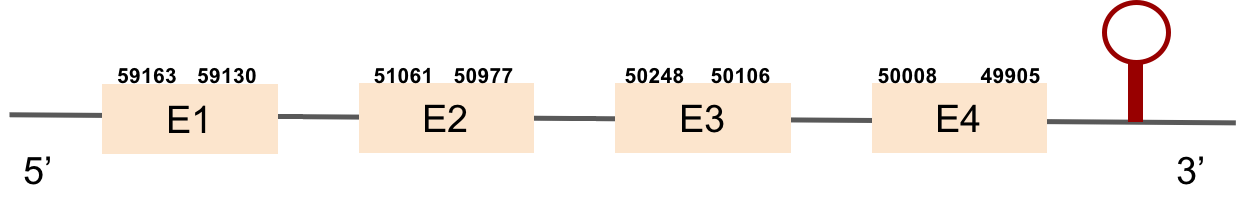
SELENOH protein was found in KV884690.1 and it is constituted by 4 exons located in the negative strand. It did not have a very good alignment with zebrafish protein but the selenocysteine residue was aligned and conserved .We predicted an alignment covering the positions 41 to 127 of the query protein.The SECIS structure was found with Seblastian in the 3’ UTR position of the negative strand in M. albus while in Zebrafish is found in the positive strand.
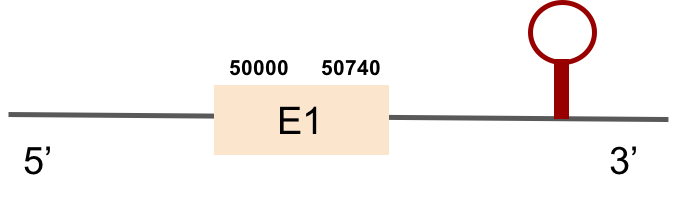
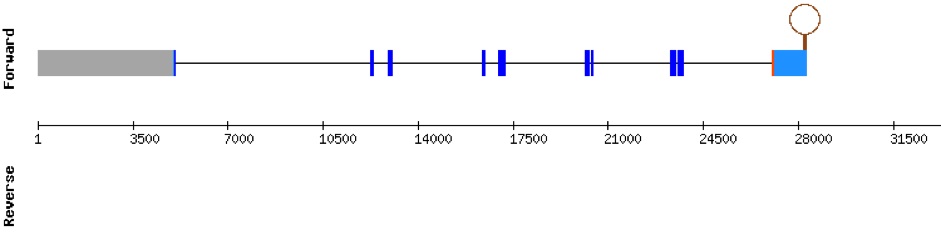
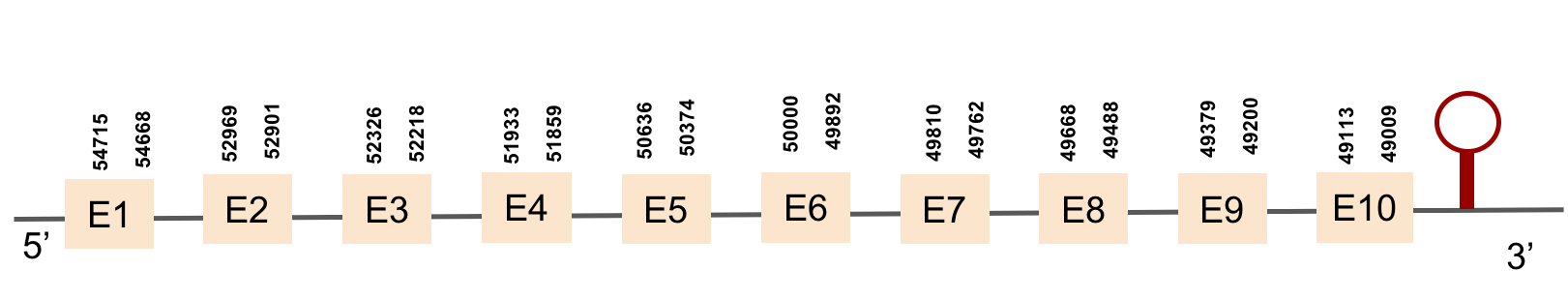
This protein was found in scaffold KV884750.1 and it has 10 exons located in the negative strand. The selenocysteine residue was conserved and well aligned when looking at the t-coffee alignment. Moreover, a SECIS structure was found with Seblastian in 3’ UTR in the negative strand.
Nine exons constitute this protein that was found in scaffold KV884754.1. The alignment with zebrafish protein was really god and the selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned. When predicted with Seblastian, one SECIS structure was found in 3’ UTR in the positive strand although no SECIS structure had been found in zebrafish.
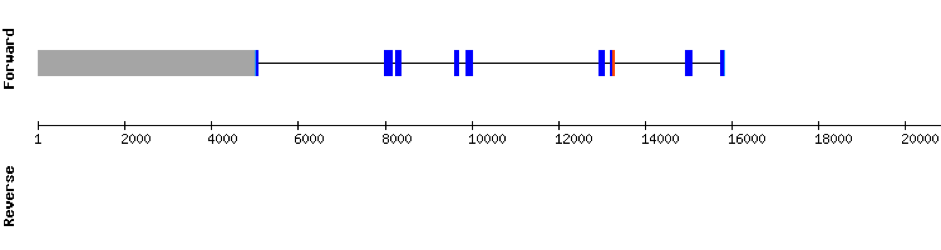
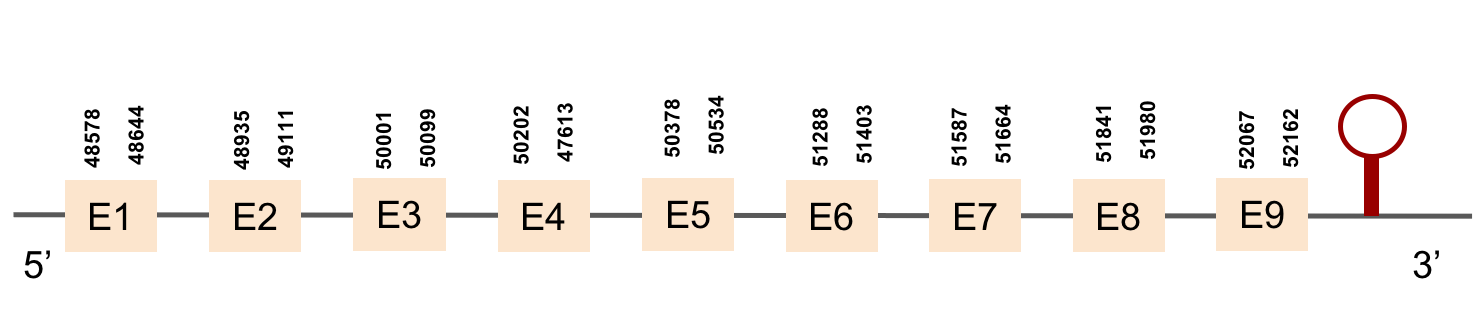
This protein was found in scaffold KV884694.1 and it has 4 exons that are located in the negative strand. The t-coffee results showed that the selenocysteine residue was conserved and well aligned with the one of zebrafish. Two SECIS structures were found with Seblastian although only one was found in 3’ UTR (grade A).
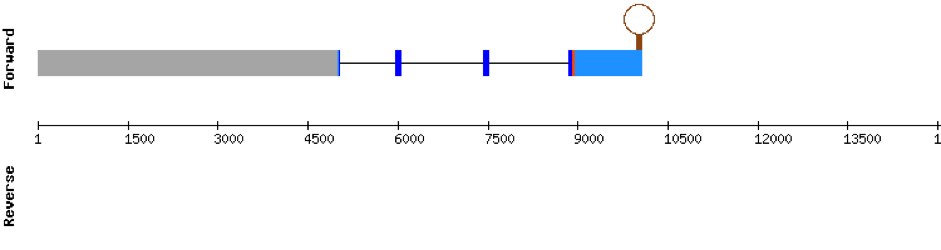
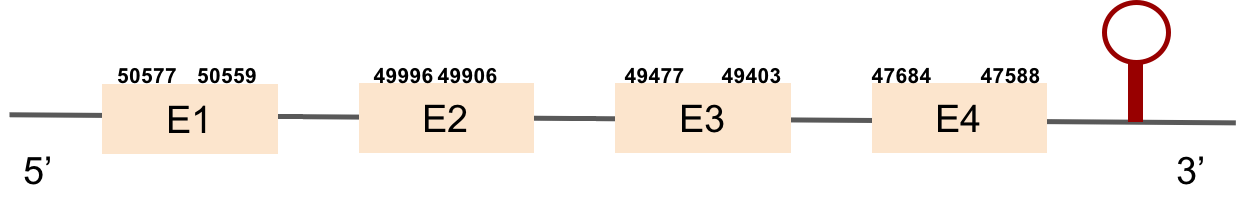
Nine exons constitute this protein which was found in scaffold KV884852.1. The results from t-coffee showed that the second half of the protein was well aligned, but the first half is absent. Despite that, the selenocysteine is well aligned and conserved. However, the predicted alignment only covered the positions 177 to 298 of the query protein. No selenoprotein could be predicted with Seblastian but 3 SECIS structures were found for this protein and only one was located in 3’ UTR (grade B).
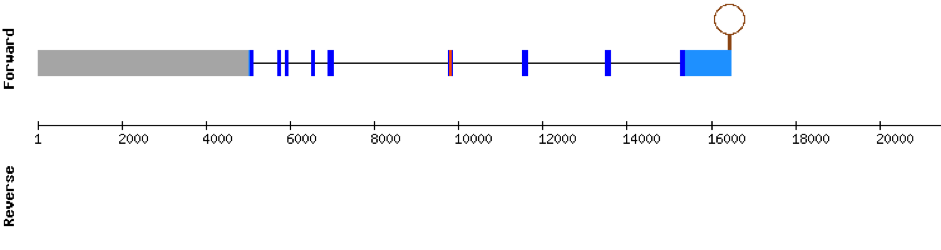
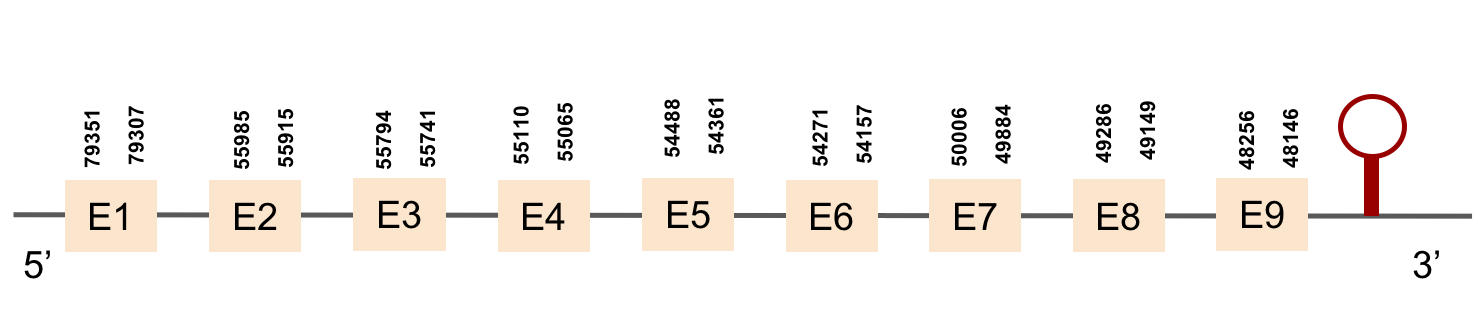
This protein was found in scaffold KV884744.1 and it had 5 exons which are located in the negative strand. When looking at t-coffee results we saw that the selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned. Furthermore, one SECIS structure was predicted with Seblastian in 3’ UTR.
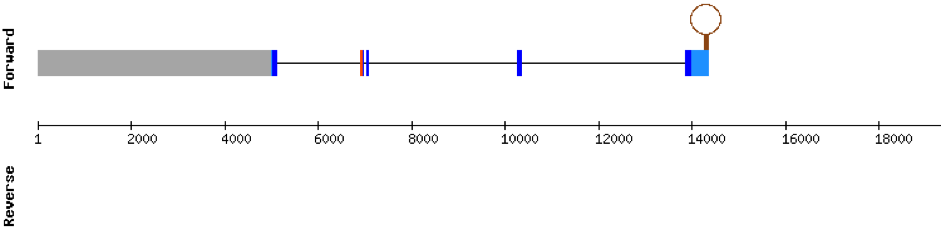
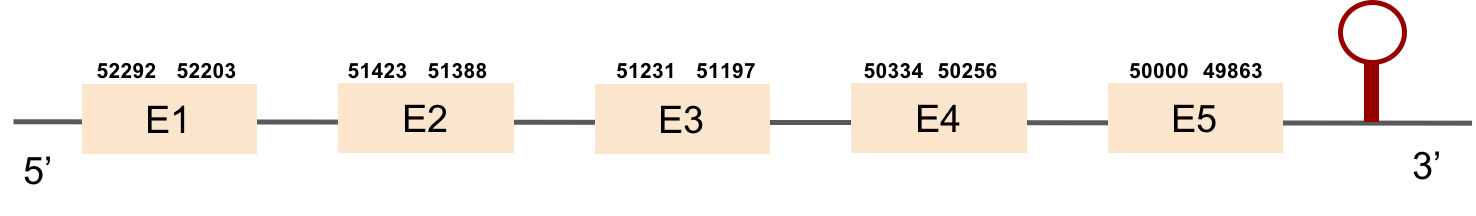
This protein was found in scaffold KV884701.1 and it has 13 exons that are located in the negative strand. The alignment made with t-coffee was good and the selenocysteine was conserved and aligned.However, the predicted alignment covered the positions from 64 to 555 of the query protein. Finally, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
SELENOO1
In M. albus, SELENOO1 was found in KV884747.1 scaffold, this protein is composed by 9 exons and is located in the negative strand. When looking at t-coffee results, the selenocysteine was well aligned and conserved with the one of zebrafish. Finally, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
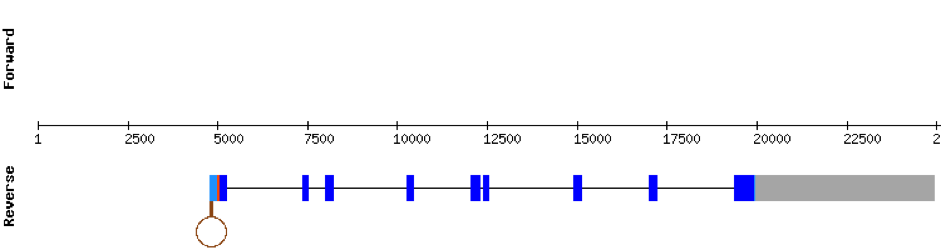
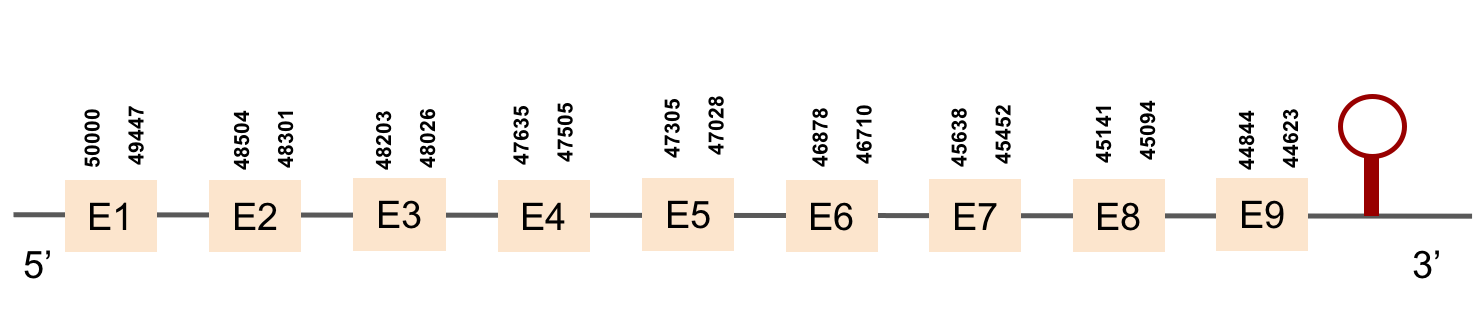
This protein aligned the same region of the same scaffold as SELENOO1 with a much worse alignment. Therefore, we interpreted that it is not found in M. albus.
SELENOP familySELENOP (1)
This protein has 10 exons located in the negative strand and was predicted in scaffold KV884754.1.The t-coffee results showed a bad alignment with the zebrafish protein but the selenocysteine residue was conserved. One SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
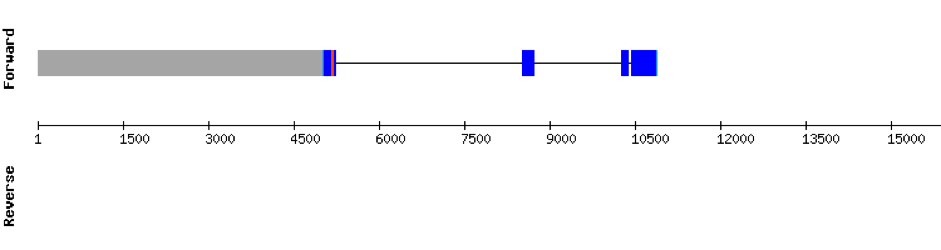
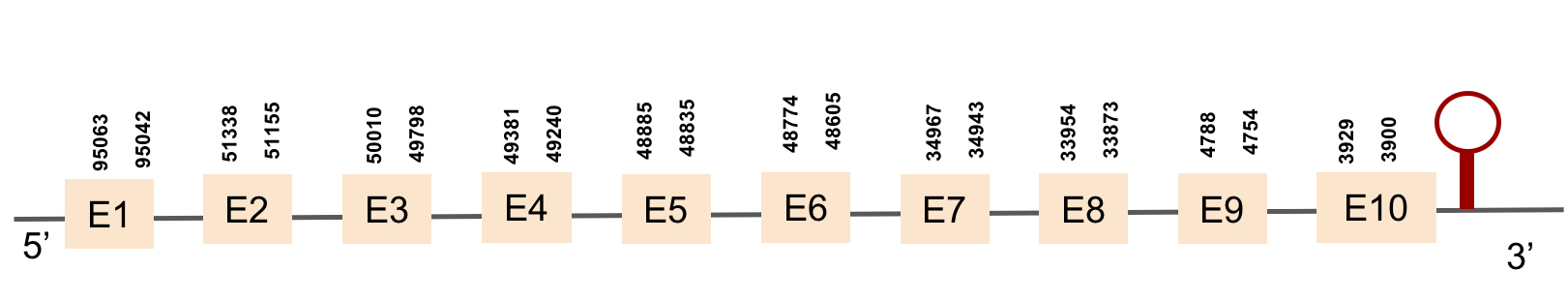
This protein has 6 exons located in the negative strand and was found in scaffold KV884708.1. When looking at t-coffee results we saw that SELENOP had a cysteine instead of a selenocysteine aligned with the selenocysteine of zebrafish protein. Moreover, in this protein we found a lot of selenocysteines and some of them were aligned but some others did not match as there was a one position shift. It looks like we do not have an optimal alignment for this protein, because the Xs are always moved 1 position, as if a gap had been opened in a wrong position. Finally, two SECIS structures were predicted in 3’ UTR.
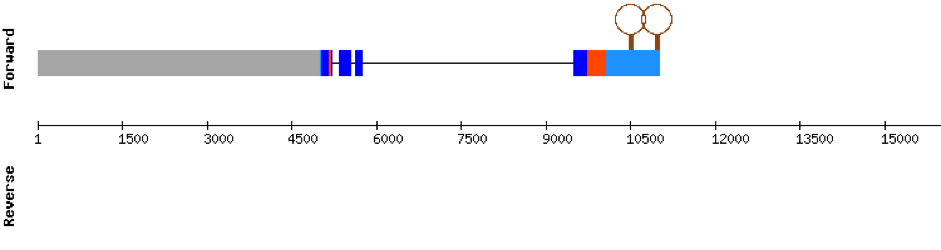
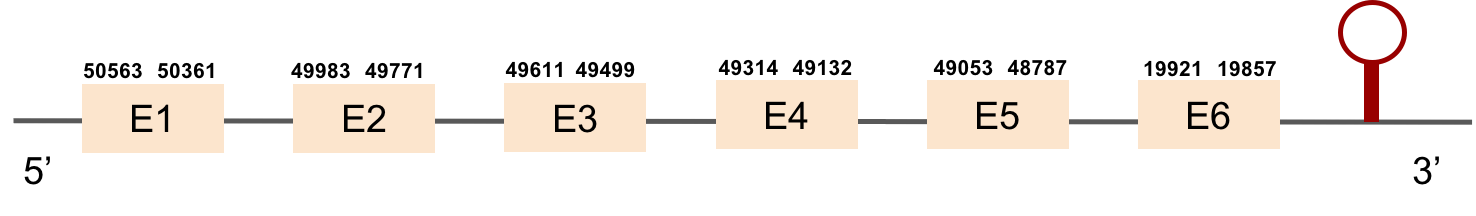
MSRB1a
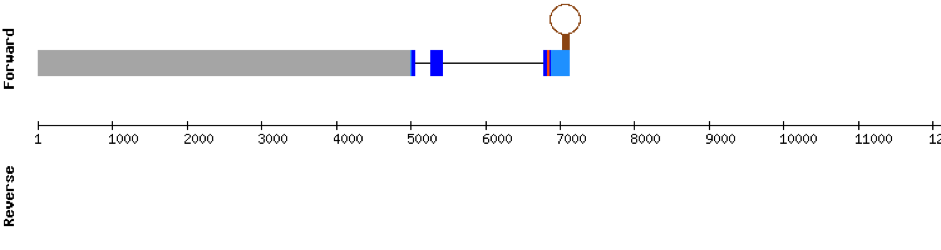
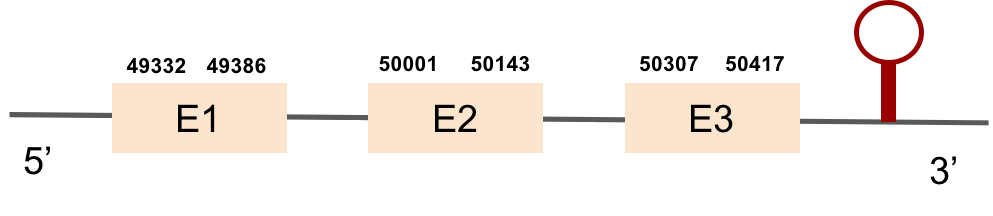
This protein is constituted by 3 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884862.1. Its selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned with the one of zebrafish. When searched in Seblastian, two SECIS structures were predicted in 3’ UTR, both of grade B.
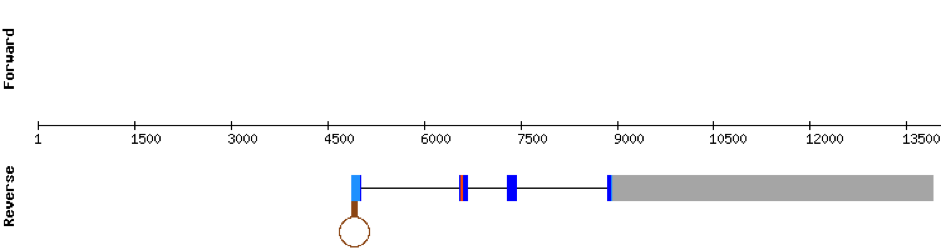
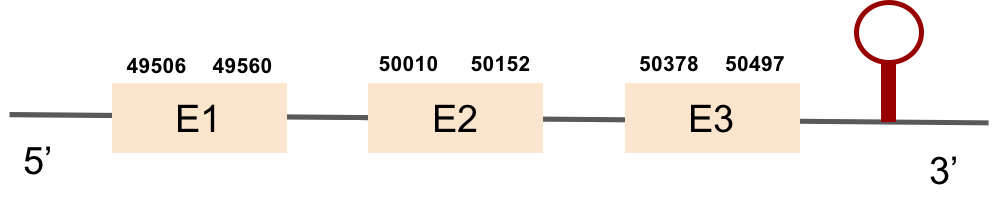
This protein is constituted by 3 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884859.1. The alignment was good for this protein and the selenocysteine was conserved and aligned with the one of zebrafish. Finally, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR, of grade A.
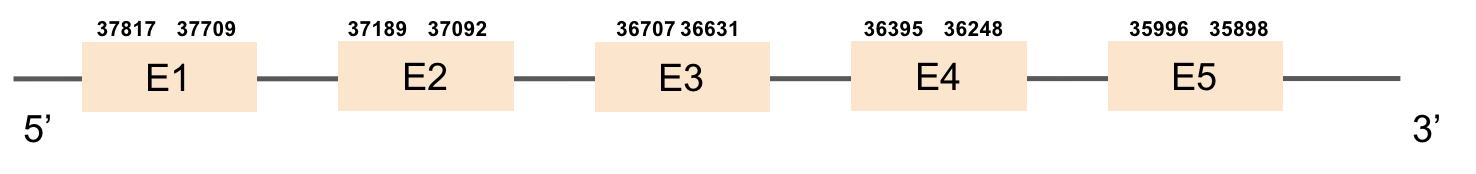
This protein has 5 exons located in the negative strand. It was found in KV884788.1. The first part of the protein is not well aligned and there is no selenocysteine. Moreover, no SECIS structure could be predicted for this protein, as expected.
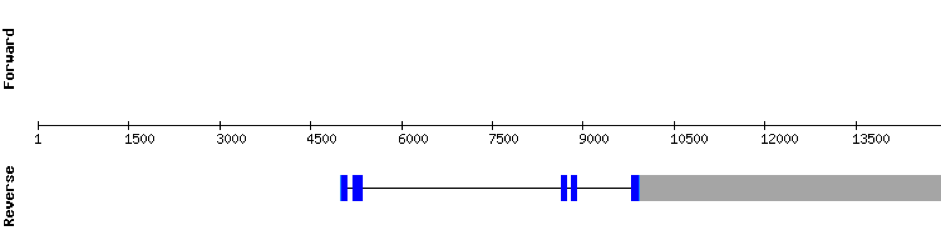
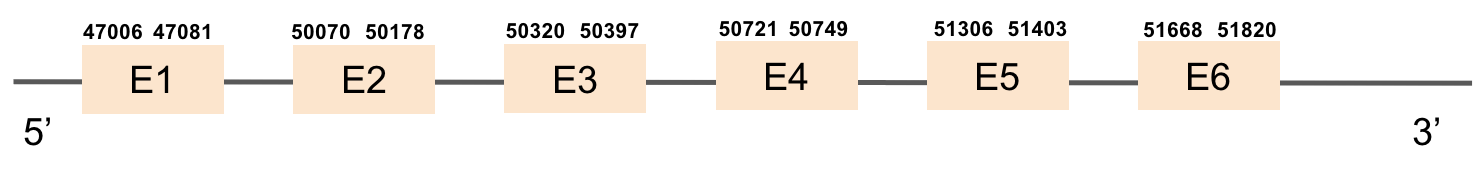
This protein is constituted by 6 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884739.1. The results of t-coffee showed a good alignment with zebrafish protein, with no selenocysteine. No SECIS structure could be predicted for this protein, as also expected.

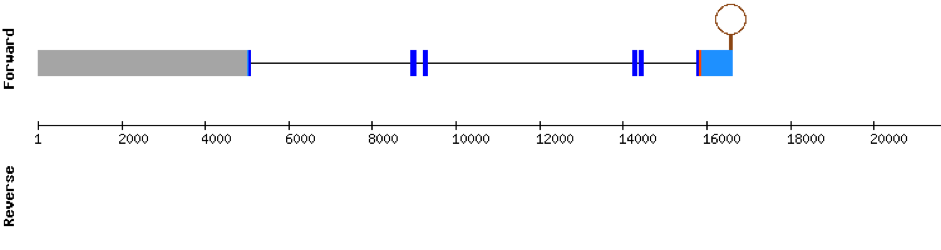
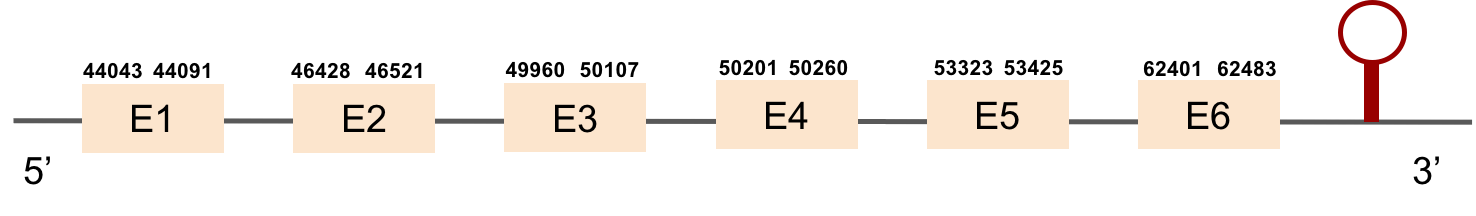
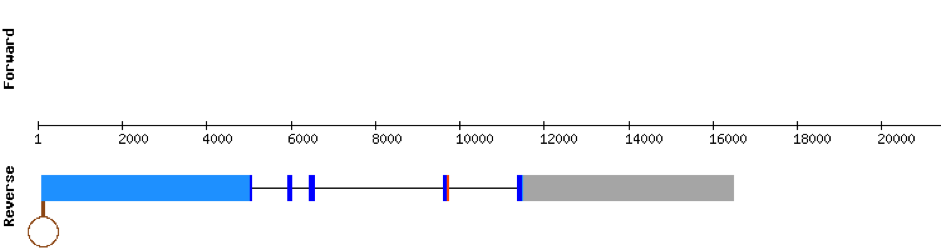
This protein is constituted by 6 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884994.1. With the tBLASTn we only got one hit, with a relatively high e-value and a low percentage identity. The t-coffee result gave us an average good alignment, but we got an X where we did not expect one, aligned with a Valine. We then performed an exhaustive exonerate and repeated the t-coffee. Our results were the same, but we found out that the X in our result was not caused by a UGA codon, but for a UAA codon. This information had to be contrasted with Genewise, where no selenocysteine residue was detected, and it was a bad alignment. No selenoprotein could be predicted for this protein but 2 SECIS structures were predicted in 3’: the first one was grade A and the second one grade B.
SELENOT1
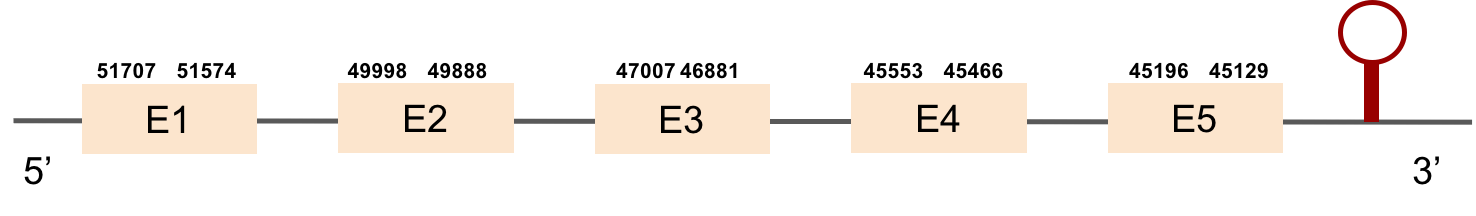
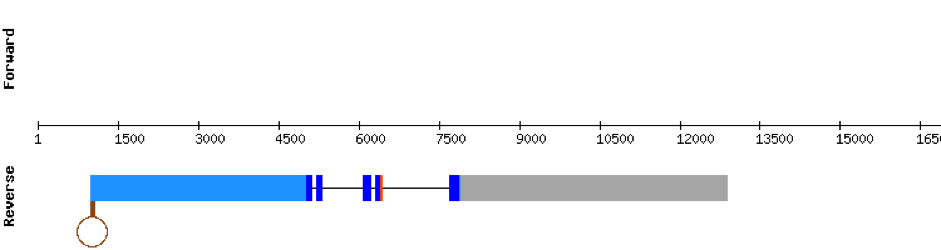
This protein was found in scaffold KV884716.1, it has 5 exons which are located in the negative strand. t-coffee results showed a good alignment and the selenocysteine was conserved and well aligned. When searched in Seblastian, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
This protein is not found in M. albus as it had a very bad alignment with the one of zebrafish.
SELENOT2This protein has 6 exons which are located in the negative strand. It was found in scaffold KV885052.1. It had a bad alignment with the zebrafish protein but the selenocysteine was aligned and conserved: there was a gap of 39 amino acids in the middle of the protein sequence. We then performed a manual exhaustive exonerate and our new prediction covered all the gap and matched in an almost perfect alignment. Finally, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
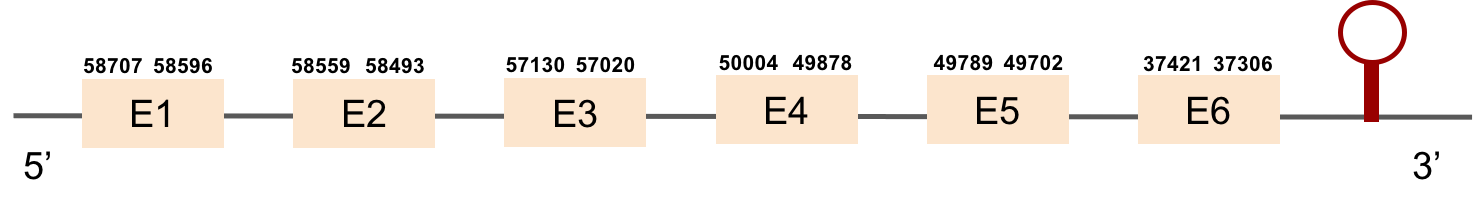
SELENOU1a
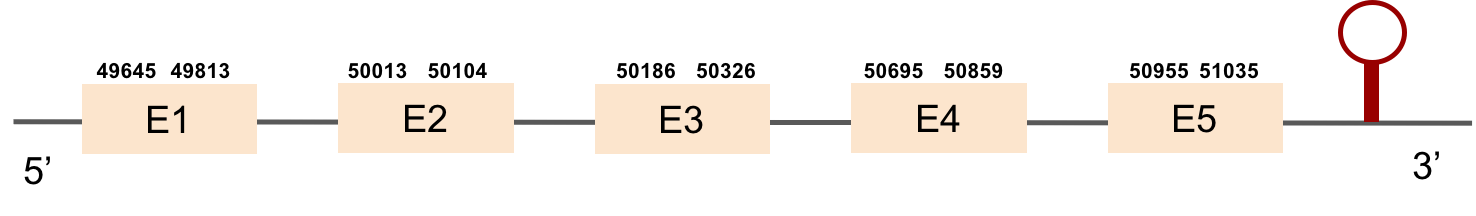
This protein is constituted by 5 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884748.1. The selenocysteine was conserved and aligned with the one of zebrafish. When searched in Seblastian, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
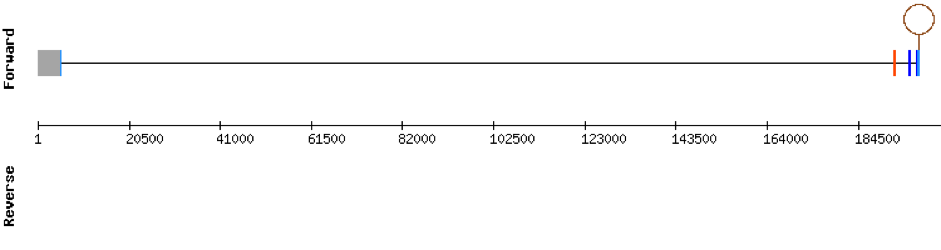
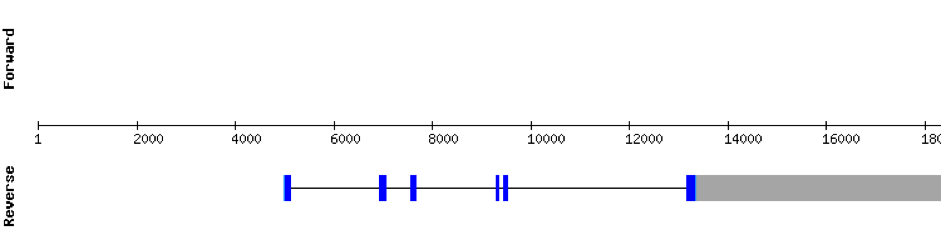
This protein is constituted by 6 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in KV884708.1 scaffold. t-coffee results showed a good alignment and no selenocysteine was found. Moreover, no SECIS structure could be predicted for this protein.
This protein had 0 hits in Monoperus albus genome.
SELENOW familySELENOW (1)
This protein has 4 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884758.1. When looking at t-coffee results we saw that it had a great alignment and a selenocysteine was aligned and conserved. However, no selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence but 2 SECIS elements were found and only one was located in 3’ UTR
This protein was not found in Monoperus albus as it was predicted in the same region of the scaffold as SELENOW (1) with a higher e-value.
SELENOW (3)This protein had 0 hits in Monoperus albus genome.
TXNRD familyTXNRD2
This protein has 15 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884700.1. t-coffee results showed a perfect alignment with zebrafish protein and the selenocysteine was aligned and conserved between species. Finally, when searched in Seblastian, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
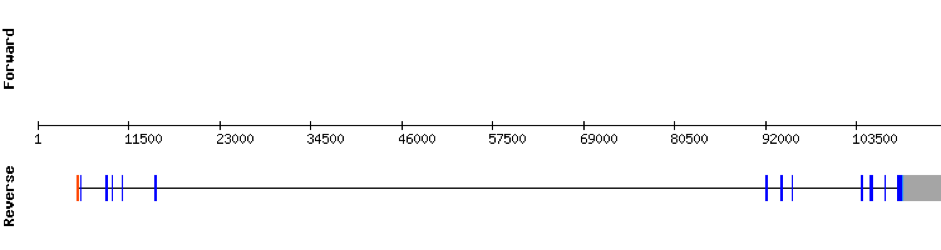
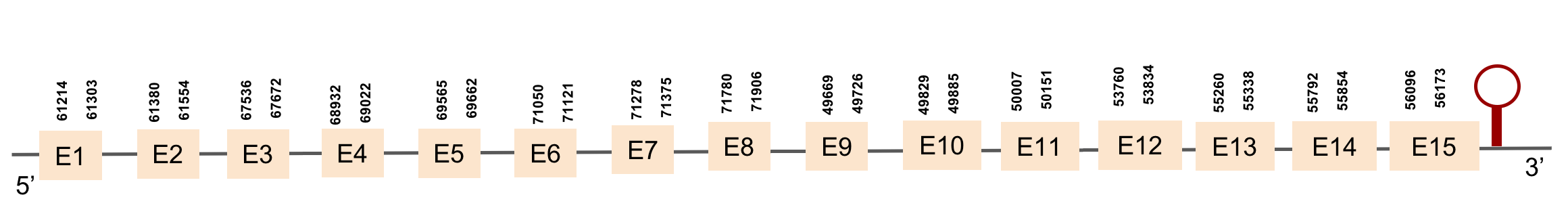
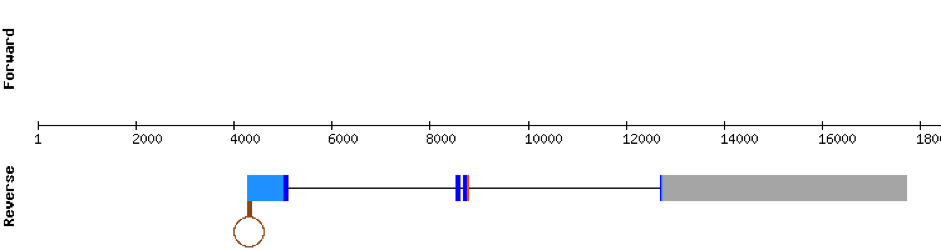
This protein is constituted by 16 exons which are located in the negative strand. It was found in scaffold KV884706.1. Results from t-coffee showed a good alignment with selenocysteine well aligned and conserved. When searched in Seblastian, no selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence but one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR.
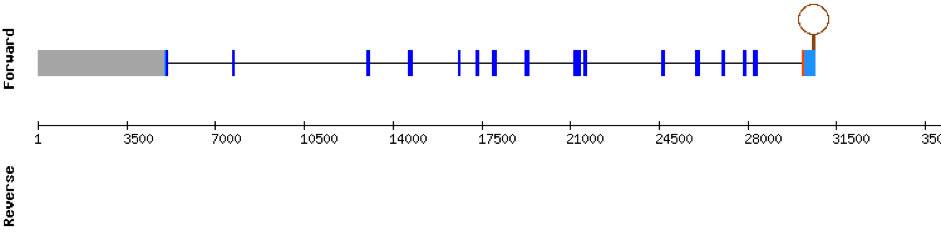
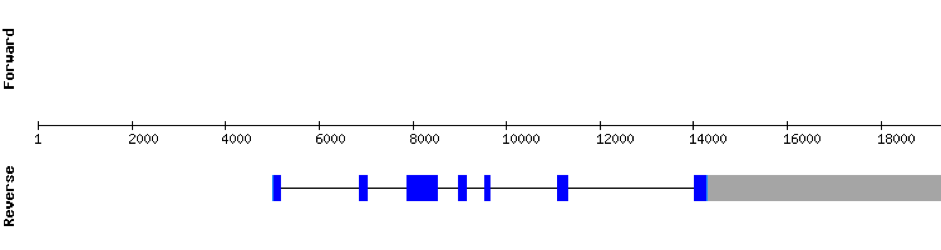
Analysis of Selenoprotein machinery
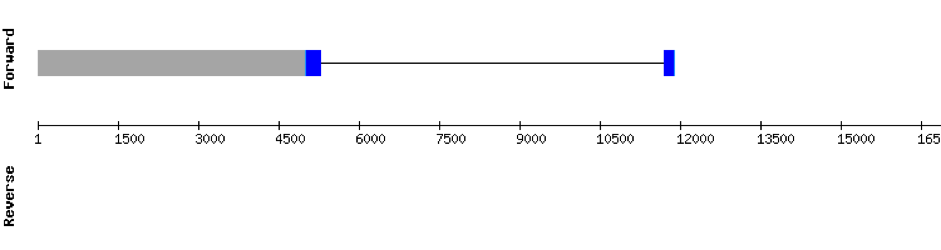
eEFsecThis protein had a lot of significant hits. It was found in the scaffold KV884777.1 with 7 hits, all located in the same scaffold. eEFsec had 7 exons found with exonerate command, like its homolog in zebrafish. As it is a machinery protein, we didn’t find any selenocysteine as expected and there was no SECIS structure predicted as also expected. The result of the alignment shows that this protein is very conserved and has a length of 585 amino acids.
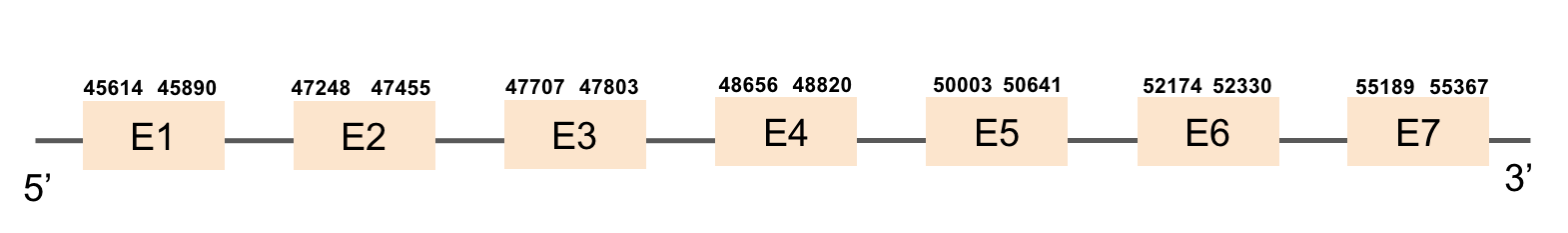
MsrA (1)
The first MsrA protein was found in scaffold KV884701.1 and it is constituted by 6 exons that are located in the negative strand. As we can see in the results from t-coffee MsrA has a good alignment with its homolog in zebrafish. When predicted with Seblastian no selenoprotein sequence could be found. However, 2 SECIS structures were predicted in the opposite strand, not being part of the protein.

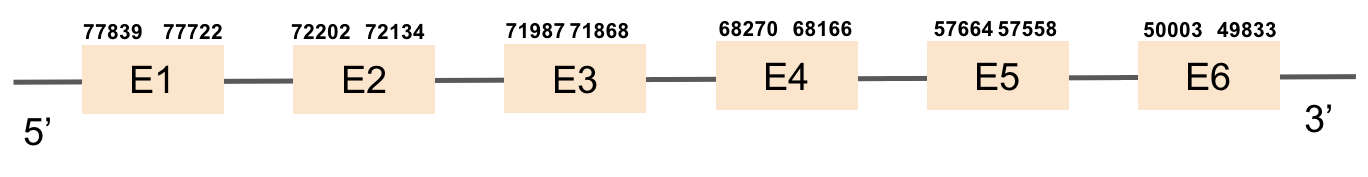
The second MsrA protein was found in KV884890.1 scaffold with 6 exons that were located in the negative strand. t-coffee results from this protein showed a good alignment with zebrafish protein. There is no selenocysteine neither in zebrafish nor in Monoperus albus as it is a machinery protein and hence no SECIS elements could be predicted for this sequence.
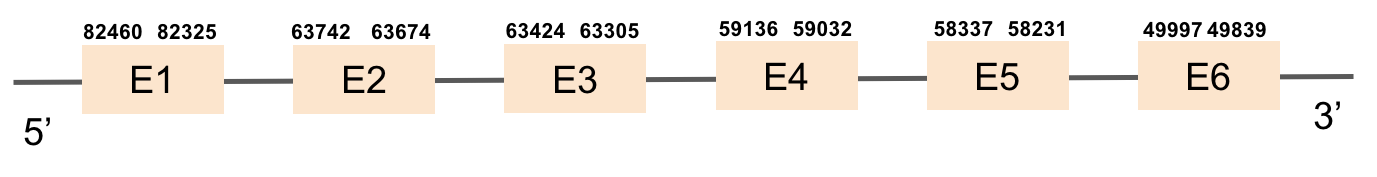
This protein was found in scaffold KV884757.1 and it has 3 exons located in the positive strand. PSTK had a regular alignment with its homolog in zebrafish as we can see in the results from t-coffee. There are not selenocysteins in the sequence as it is a machinery protein. In spite of that, one SECIS structure was predicted in 3’ UTR with Seblastian.
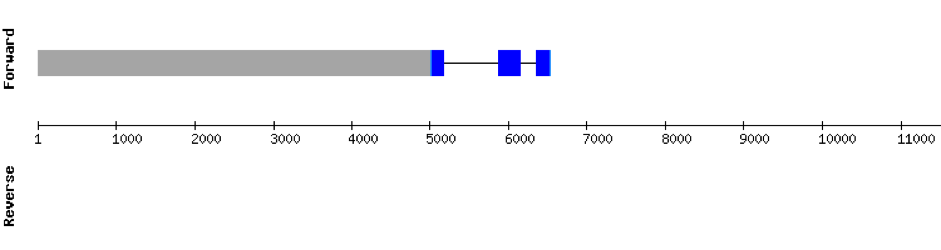
SBP2 (1)
SBP2 protein was found in scaffold KV884725.1 and it is constituted by 8 exons that are located in the positive strand. The alignment with zebrafish protein was not very good as it had a region with 2 different gaps: one in the middle of the protein and the other one at the end. We repeated the prediction using exhaustive exonerate and the gaps were filled and the alignment was much more consistent and reasonable. Selenocysteine was not found, as expected. However, Seblastian predicted one SECIS structure but it was in the opposite strand so it had no SECIS structure.
z.png)
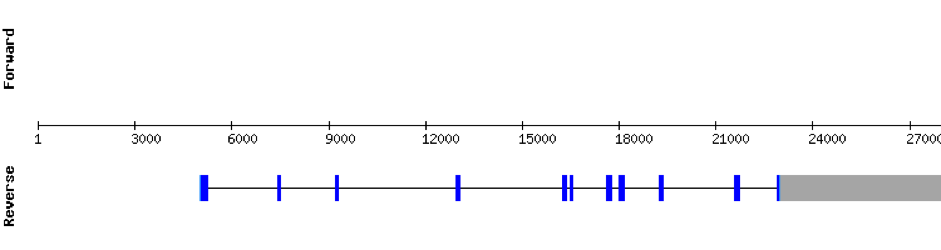
This protein was not found in M. albus genome as the sequence predicted had a very bad alignment with zebrafish protein.
SecSThis protein was found in scaffold KV885014.1 and it had 11 exons, all found in the positive strand. t-coffee results showed a good alignment with zebrafish protein. There was no selenocysteine residue found in the sequence, neither in zebrafish nor in M. albus.No selenoprotein could be predicted with Seblastian but one SECIS element was predicted at 3’ UTR.
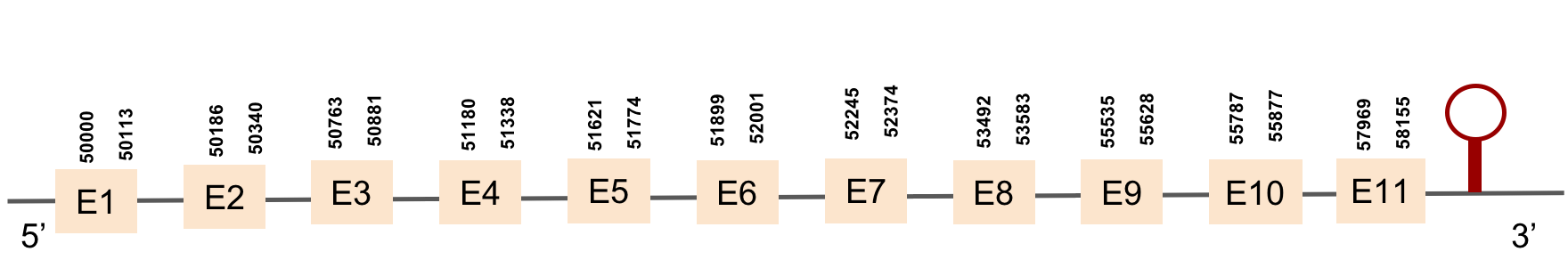
SECp43 (1)
This protein has 7 exons, which are located in the negative strand. It was found in KV884842.1 scaffold. This protein had a good alignment with the one from zebrafish but no selenocysteine was found as we expected, due to its function as a machinery protein. No selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence although 2 SECIS structure were predicted but both were located in 5’ UTR.
z.png)
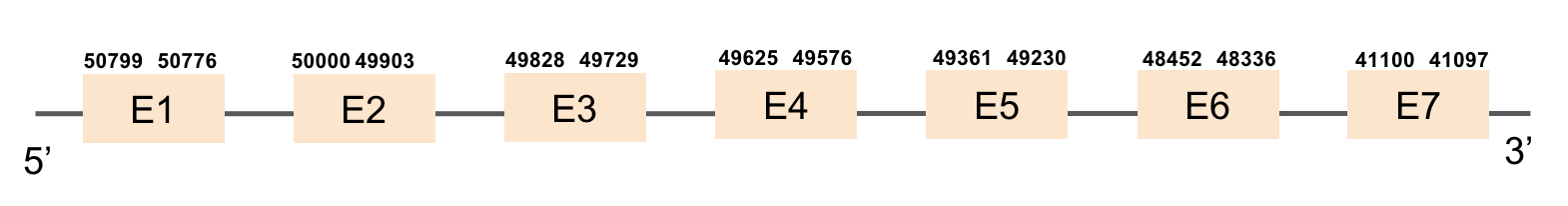
This protein is constituted by 10 exons which are located in the positive strand. It was found in scaffold KV884821.1. When looking at the results from t-coffee we saw that it had a bad alignment because there was a region that had a lot of gaps. No selenocysteine was found as it is a machinery protein. No selenoprotein could be predicted for this sequence when searched in Seblastian. However, two SECIS structures were predicted but were not in the 3’ UTR extreme of the protein.
z.png)