

DIO1
A prediction in the scaffold VONY01000009.1 was selected using the DIO1 chicken protein as a query based on our criteria. The predicted gene is located in the reverse strand and contains 4 exons, (this document shows where U is found in DIO1 sequence). We obtained a good alignment with tcoffee, with the protein starting with a Met and a score of 1000. We also obtained a good prediction with Seblastian, which used Coturnix japonica's genome to compare. Regarding the SECIS, a grade A SECIS was found in the positions 4528883-4528950 (-), so we can accept it. The structure of the gene can be found hereunder:
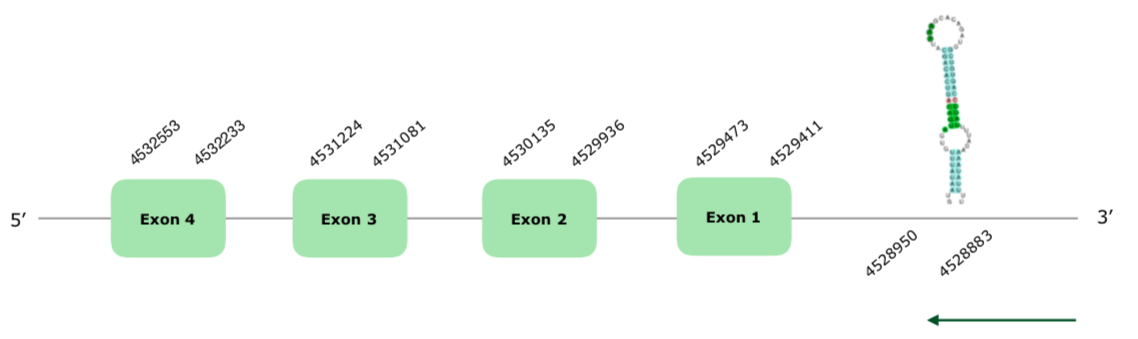
Therefore, we can conclude that this protein is present in the Colinus virginianus in the explained position..
DIO2
The gene in Colinus scaffold VONY01001224.1 was the only one selected from Tblastn based on our criteria. 3 hits were found in this scaffold, but one was very far away and had a significantly lower percentage of identity, so we only took the other 2. In this case, the gene is in the reverse strand and has two exons (this document shows where U is found in DIO2 sequence). Tcoffee's alignment was very good, with a Met at its beginning and a score of 1000. Two SECIS were obtained with SECISearch3, one being grade A in the positions 38099828-38099754 (-), so we accepted this prediction. The other one was much further and only grade C, so we ignored it. In spite of that, Seblastian was not able to predict a protein, maybe because it does not have a right protein in its database.The predicted structure of the gene can be found hereunder:
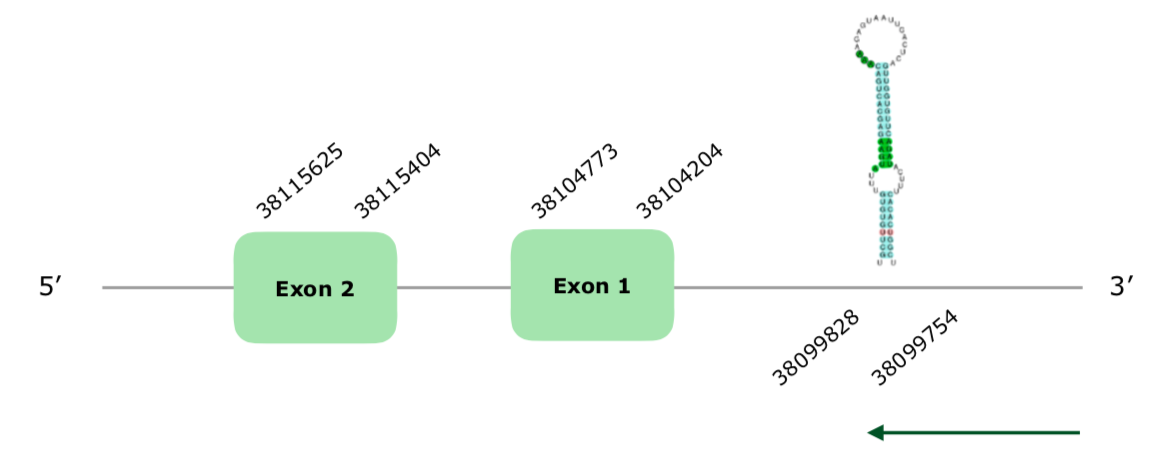
Therefore, and despite not finding it with Seblastian, we consider that DIO2 is present in the Colinus virgnianus' genome.
DIO3
Two hits were found in the scaffold VONY01001224.1, but only one had a significant % of identity according to our criteria. Also, the other hit was the one used in DIO2 tcoffee. The predicted protein has 1 exon (this document shows where U is found in DIO3 sequence) and it is localized in the reverse strand. The tcoffee has a very good alignment, with a 1000 score, even though the protein does not start with a Met; but Gallus gallus DIO3 fasta does not start with a Met neither. Maybe this is because the protein is uncomplete and it lacks the first amino acid. Similarly to DIO2, Seblastian was not able to predict a selenoprotein, and neither did SECISearch3 predict a good SECIS element, since both were grade B and far away from the selenoprotein.Hereunder you will find the structure of the predicted protein according to Exonerate:
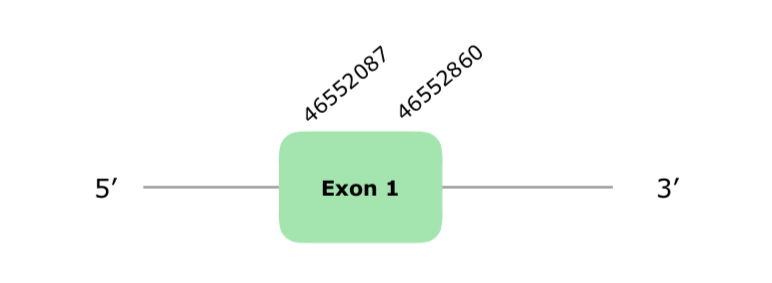
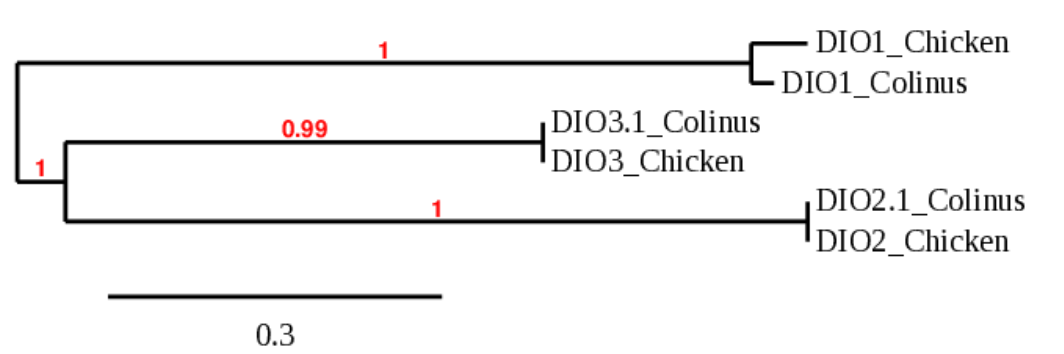
All in all, and after checking the phylogenetic tree, it all points out towards the protein being conserved and present in the Collinus, even though Seblastian did not succeed predicting it.
GPx1
In this case, GPX1 human protein was studied, for the reasons above mentioned. When analysed, the tblastn showed two different scaffolds and, in order to choose one of them we made a phylogenetic tree, which we can see below. Based on this tree, we decided to choose the first scaffold.

This gene has 2 exons (this document shows where U is found in GPx1 sequence) and it is localized in the reverse strand. The Tcoffee showed an alignment quite good with a 984 score. On the other hand, Seblastian did a good prediction and three SECIS were predicted, with one SECIS on grade A between positions 18155557-18155621 (-). Nevertheless, as the Tcoffee and the Seblastian made a good prediction, we can say that this selenoprotein is present and conserved in Colinus.
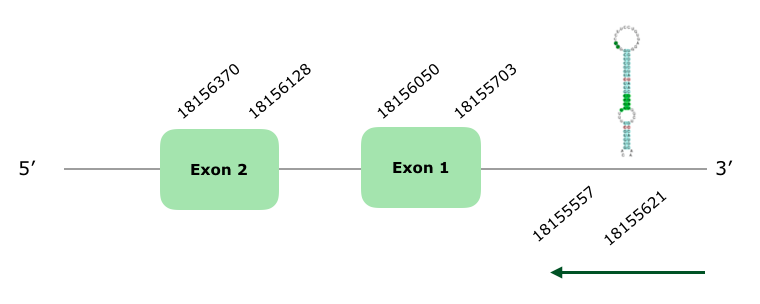
GPx2
Since, according to Li et al. 2018, GPx2 was used, one hit that accomplished our criteria was found in VONY01001224.1 using Turkey GPx2 as a query.
This gene has 2 exons (this document shows where U is found in GPx2 sequence) and it is localized in the reverse strand. The Tcoffee made a good alignment with a high score (1000) although in the end it presents many gaps. No selenoprotein is predicted in seblastian, and the SECIS prediction is not very good, since it is grade C and is far away from our predicted protein. However, based on the Tcoffee alignment, we can conclude this protein is present and conserved in Colinus.
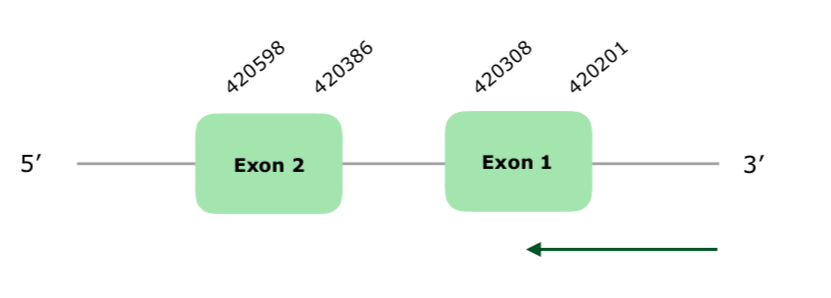
GPx3
Two genes in different scaffolds were predicted that fulfilled our criteria; in spite of this, the one with a lower percentage of identity and a higher e-value did not produce a satisfying alignment with Tcoffee, so we discarded it. The other one was in the VONY01000288.1 and had 5 hits, but only 3 of them accomplished our criteria. This gene contains 4 exons (this document shows where U is found in GPx3 sequence) and it is localized in the reverse strand. The Tcoffee shows a score of 1000 and an overall good alignment, even though there are some gaps in the beginning and it does not start with a Met. Seblastian showed a good prediction, even though not as good as the Tcoffee, likely because it used the GPx3 of a monkey (Cebus capucinus imitator) as a query. A grade A SECIS is predicted at the end of our protein in the reverse strand, in the positions 12038260-12038337. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted protein:
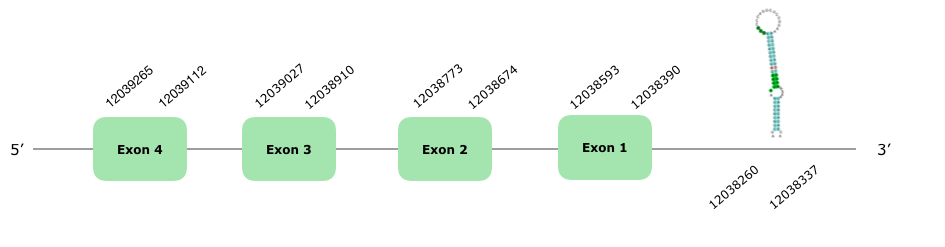
In spite of the SECIS prediction, since the Tcoffee and the Seblastian predictions are very good, we can conclude that the selenoprotein is present and conserved in Colinus virginianus.
GPx7
Two hits located in the scaffold VONY01000009.1 were selected from the Tblastn prediction based on our criteria. The obtained protein is encoded by 2 exons, in the reverse strand. The Tcoffee shows a very good alignment, with a 998 score (even though the protein does not start with a Met). GPx7 is a Cys-containing homolog, i. e. the Selenocysteine was substituted by a Cysteine, and we find this Cysteine in both the Gallus gallus query protein and the predicted one. As expected Seblastian did not find any Selenoprotein. A SECIS element was found, however it was grade B so we did not accept it. Hereunder we can see the structure of the protein predicted by exonerate:
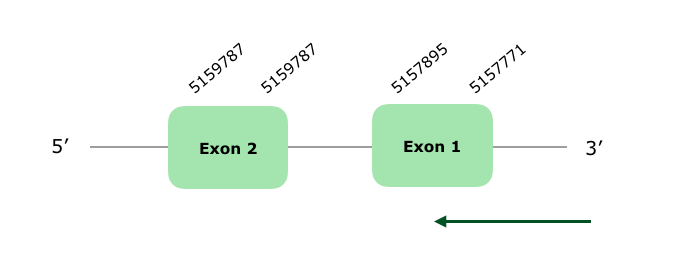
For these reasons, we can accept our prediction, concluding that, GPx7 is present in Colinus virginianus' genome.
GPx8
Any prediction with an identity higher than 70% was found after doing the Tblastn. Just to make sure that any of them was actually correct, we decided to align the predicted hits and analyze the three of them.
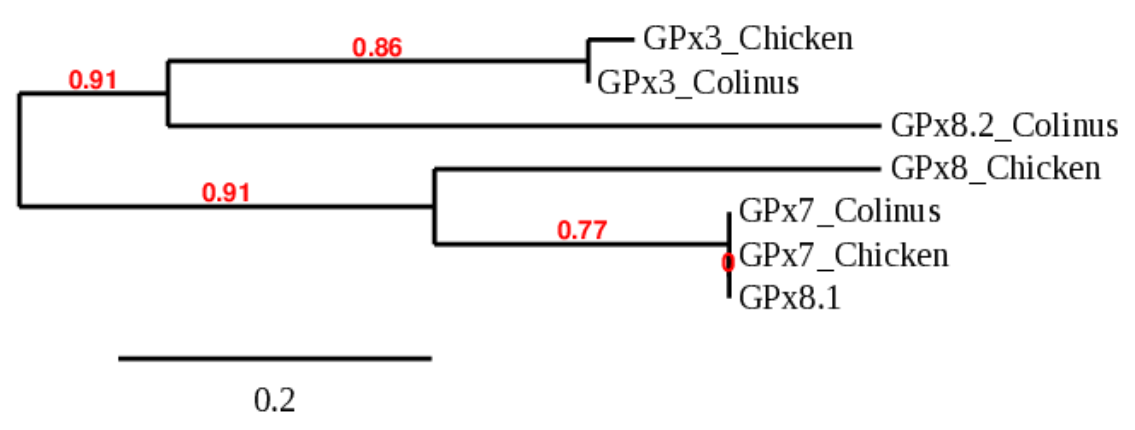
After performing a phylogenetic tree of these proteins, we corroborated that any of them was encoding the protein we were searching for. The hit of the first scaffold (GPx8.1) was actually the same one we used for GPx7, as we can see in the tree (they appear as related). In GPx7, this scaffold had a 100% of identity, whereas in GPx8 it only had a 56% and a higher e-value. Also, the alignment was extremely better for GPx7 than with GPx8, supporting our theory that it was actually correspond to GPx7. This confusion of the program may come from the fact that both GPx7 and GPx8 evolved from a common GPx4 ancestor, so it is logical that they keep ressemblances. The hit of the second scaffold (GPx8.2) resulted in a pretty weak Tcoffee unrelated to the GPx8 of the chicken, our query. Finally, the third scaffold did not even give an alignment, so we could not include it in the tree. We decided to analyse this protein on Turkey, in order to study if in this organism the alignment was better. However, we found that in Meleagris gallopavo (turkey) this protein does not exist either. Therefore, we can think that whether this protein was lost in Colinus, as it did in Turkey, or that it has changed so much that it cannot be found.
MsrA
The Tblastn found three hits in the scaffold VONY01000317.1 that fulfilled our criteria. The predicted gene contained 3 exons. The Tcoffee showed alignment, with a 1000 score, even though it does not start with a Met. As commented before, this could be due to a lack in the alignment of the first nucleotides or some other reason. As in the chicken, this protein does not contain a Selenocysteine but rather a Cysteine, so it most likely has become a Cys-containing homolog. This was confirmed when any selenoproteins nor SECIS elements were predicted using Seblastian and SECISearch3. The structure of the gene can be found hereby:
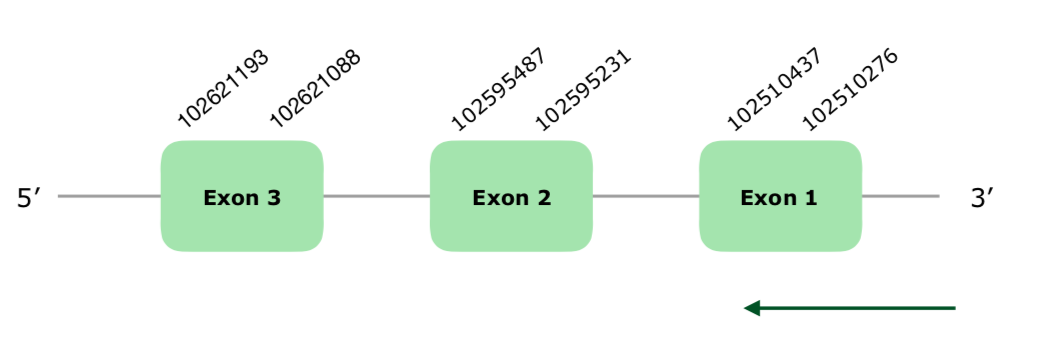
For all of these, we can say that this protein is present and conserved in Colinus as a Cys-containing homolog, as it is in the Gallus gallus.
MsrB1
The tblastn found two hits in the scaffold VONY01001437.1. The gene contained 3 exons (this document shows where U is found in MsrB1 sequence) and was encountered in the reverse strain. The Tcoffee shows a good alignment with a 1000 score and a Met at the beginning of the protein. Seblastian also offers a good prediction, also using Gallus gallus' MsrB1 as query protein. SECISearch3 offers 4 SECIS prediction, 2 of them grade A, and one being in the reverse strain. Specifically, this SECIS was in the positions 5687061-5687133 (-), so this one is quite a good prediction. The structure predicted by Exonerate can be found hereby:
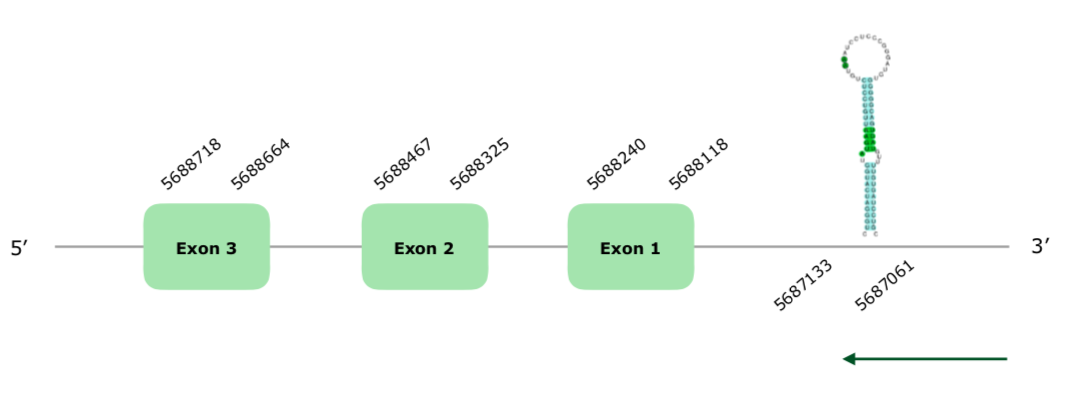
Therefore, we can conclude that MsrB is conserved in Collinus virginianus.
MsrB3
Tblastn showed 4 hits in the scaffold VONY01001511.1 even though only 3 fulfilled our criteria. Nevertheless, the other hit was extremely close to the others so it was taken at the moment of setting the boundaries. The predicted gene has 5 exons and is located in the reverse strand. Tcoffee prediction was very good, with a 1000 score, even though some gaps were present at the beginning of the protein. Since it is a Cys-containing homolog, Seblastian and SECISearch 3 failed to predict a selenoprotein or SECIS elements. The gene structure can be found hereby:
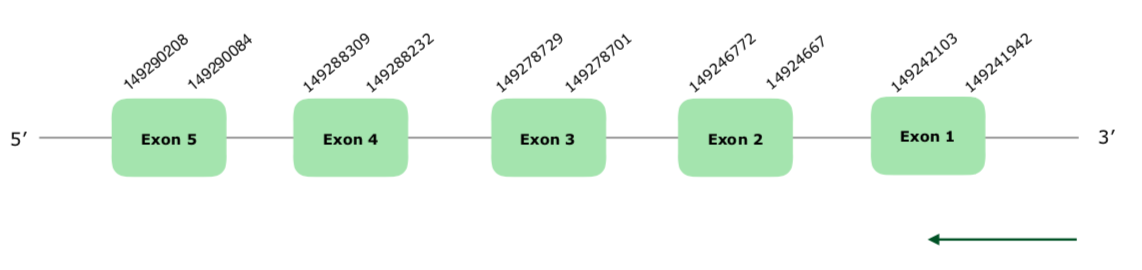
All of this points that this protein is conserved, such as in Gallus gallus, as a Cys-containing homolog.
A gene was predicted in the scaffold VONY01000009.1. It contained 4 exons in the reverse strand (this document shows where U is found in Sel15 sequence). Tcoffee is excellent, with an almost perfect alignment and a score of 1000. Seblastian's prediction is also very good, using Anas platyrhynchos Sel15 as a query, and it even extends the prediction for 12 nucleotides more in the first exon. One SECIS element was predicted 550 nucleotides away in the right strand, in the positions 13352209 - 13352279 (-), so it was accepted. The structure of the predicted gene can be found hereunder:
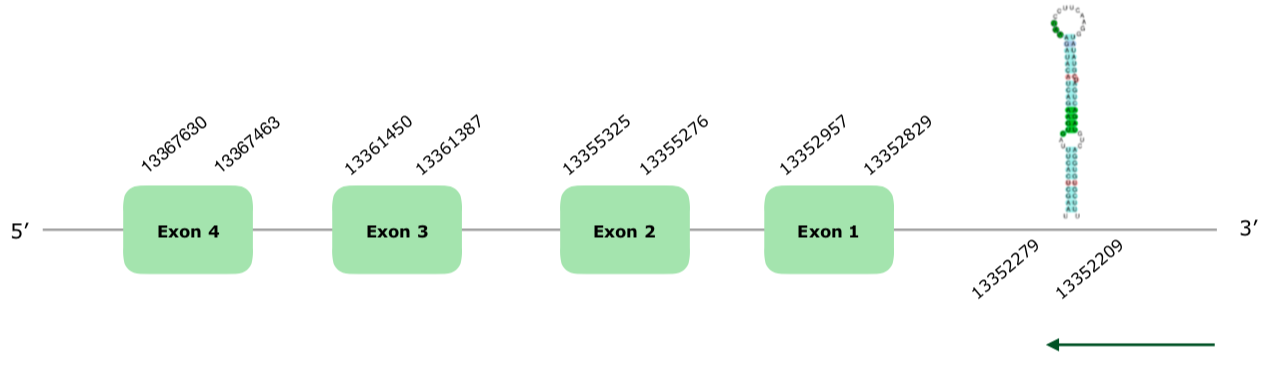
Therefore, we can conclude that this protein is present in the Colinus virginianus in the explained position. For all of this, we can say that Sel15 is preserved and present in Colinus' genome.
One hit on the scaffold VONY01000045.1 was selected acording to our criteria. The gene has 2 exons in the forward strand. The Tcoffee shows a perfect alignment with a 1000 score. On the other hand, Seblastian was not able to predict a protein, as expected. The SECIS prediction was also failed. The structure of the predicted gene can be found hereunder:
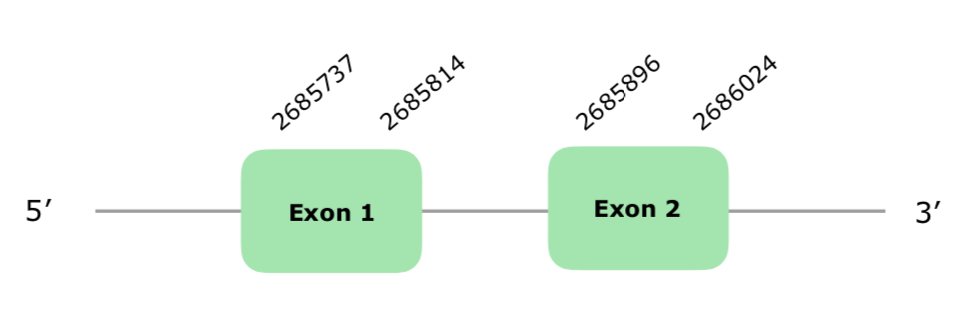
Taking into account all of the mentiones, we can conclude that this protein is present in Colinus in the explained position.
SelenoT
The gene in the scaffold VONY01001093.1 was selected from the Tblastn prediction based on our criteria. The predicted gene contains 5 exons in the reverse strand (this document shows where U is found in SelenoT sequence). Regarding the Tcoffee alignment, it is very good overall, with a score of 999, with the only exception of a number of gaps at the beginning of the protein. This could be due to a partial deletion at the beginning. Seblastian used found a similar selenoprotein using Python bivittatus' SelenoT as a query, starting with almost the same sequence that our prediction showed. Regarding the SECIS structure, a grade A SECIS was predicted in the positions 22072590-22072671 (-), so we accepted it. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted gene:
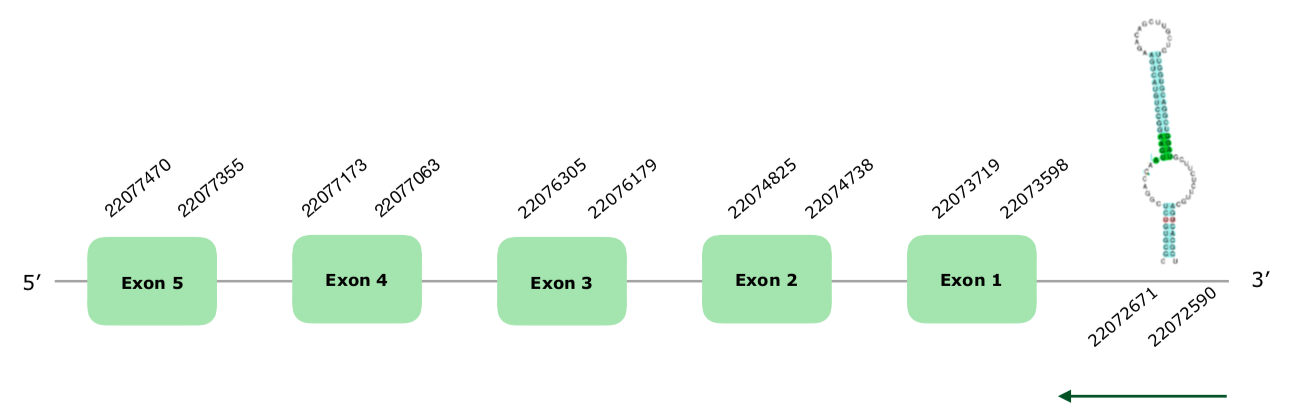
We can conclude that this selenoprotein is conserved and present in Colinus' genome.
SelenoH
This protein belongs to the machinery in our query (chicken). However, when we tried to search it in the Colinus virginianus' genome with the tblastn, this program was not able to find any hit with an e-value minor or equal to 0.001. Therefore, we decided to search this protein using the Turkey (Meleagris gallopavo) as our query, and in this case we did find a predicted protein. Nevertheless, SelenoH is a selenoprotein in Turkey, which is different from the Chicken, where it belongs to a machinery protein.
The gene in the scaffold VONY01001224.1 was the only one selected based on our criteria. Exonerate predicted a gene with 2 exons in the reverse strand (this document shows where U is found in Sel15 sequence). Tcoffee showed a very good alignment, with few mismatches and a score of 1000. However, Seblastian was not able to predict any protein, and the analysis performed by SECISearch3 was not very good, because it predicted 2 grade B SECIS that were very far away from the predicted protein, so we did not accept them. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted gene:
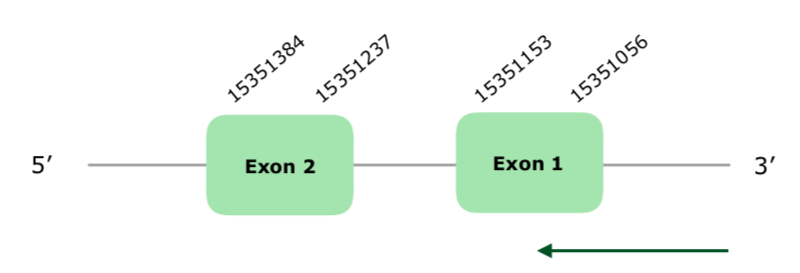
Having all of these reasons into account, we consider that this protein is present and preserved in Colinus.
Tblastn showed many hits but only the alignments in the scaffold VONY01000317.1 fulfilled our criteria. The predicted gene contained 10 exons in the reverse strand. Tcoffee of this prediction is really good, with an almost perfect alignment, a score of 1000 and the first amino acid being a Met. Seblastian, however, predicted another protein, with only 5 exons, using Meleagris gallopavo SelenoI as a query. The alignment is good, but not as good as the one we predicted, and it does not start with a Met. This may be because Seblastian did not have Gallus gallus SelenoI in its database, or because it failed to extend the protein as much as our Tcoffee did. Anyways, we consider our prediction better than Seblastian's, and you can find it hereunder:
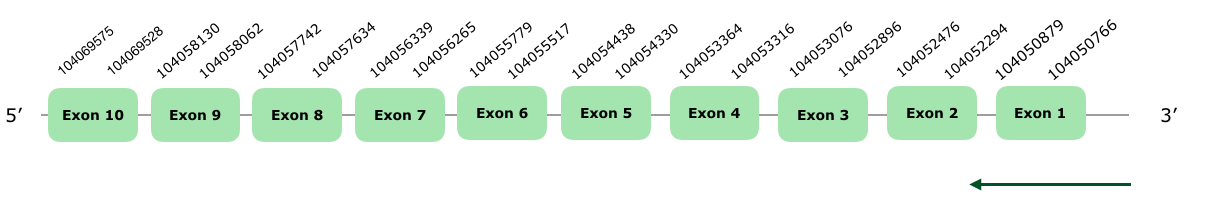
As for SECIS element, one grade A was predicted in the positions 104049571-104049496, so we can not accept it because it is too far. Taking all of this into account, we consider SelenoI to be conserved and present in Colinus' genome.
SelenoK
One hit in scaffold VONY01000200.1 was selected according to our criteria. The predicted gene contains 4 exons in the forward strand (this document shows where U is found in SelenoK sequence). Regarding the Tcoffee, we have a good alignment with a score of 993, with only two or three mismatches and starting with a Met. Seblastian predicted also a 4 exon protein very good aligned, using Coturnix japonica's SelenoK as a query, and two SECIS elements were predicted, one being grade A SECIS in the forward strand, in the positions 5671194-5671270 (+), so we can also accept it. The structure of the Exonerate predicted gene can be found hereby:
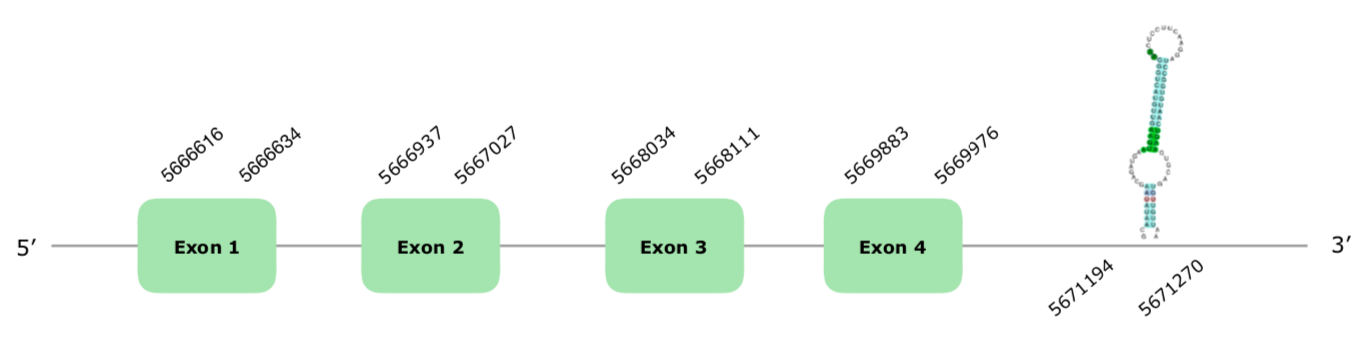
All in all, we can conclude that SelenoK is present and conserved in Colinus.
SelenoS
The gene in the scaffold VONY01000010.1 was the only one selected based on our criteria. Exonerate predicted a gene with 6 exons in the reverse strand (this document shows where U is found in SelenoS sequence). Tcoffee was very good, with a great alignment, starting with a Met and a score of 1000. Seblastian also offered a great prediction Gallus gallus as we did. A SECIS grade A element was predicted in the positions 16370327-16370404 (-), so we accepted it as good. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted gene:
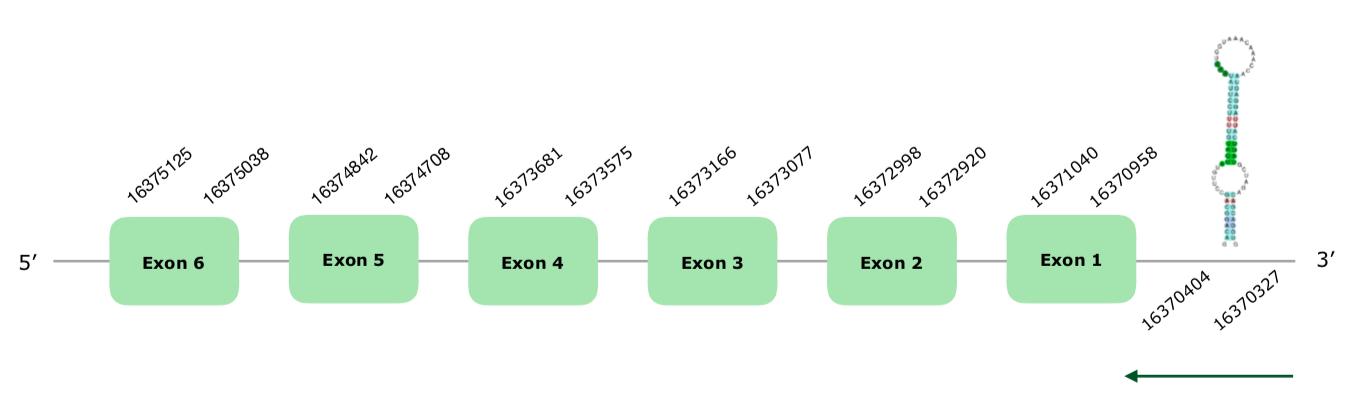
Having all of these reasons into account, we consider that this protein is present and conserved in Colinus.
Meleagris gallopavo's SelenoN as a query, and we saw the the 4 first exons of our predicted alignment did not appear here. Therefore, we consider our prediction better (this document shows where U is found in SelenoK sequence). Out of the 5 predicted SECIS, we accepted a grade A in the forward strand, in the positions 3278190-3278262 (+).The predicted structure we accepted can be found hereunder:
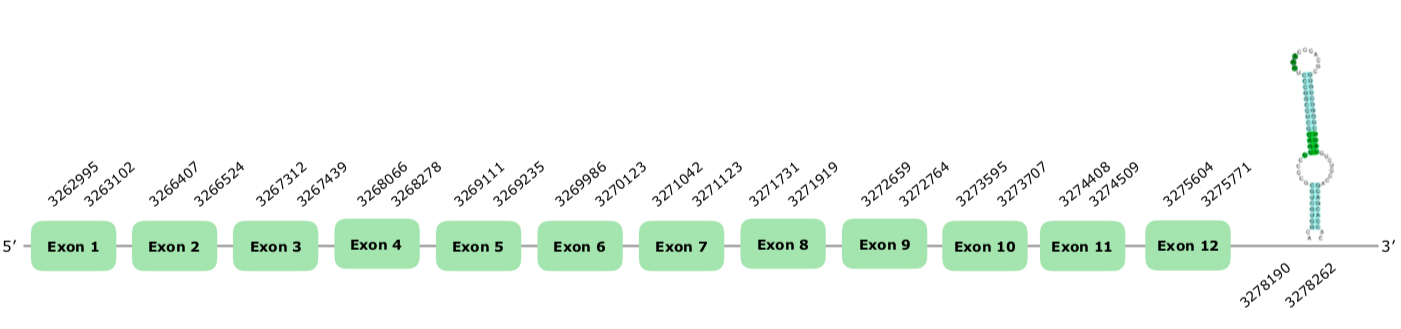
For all of these reasons we can conclude that SelenoN is conserved and present in Colinus.
In this case more than one isoform was present in SelenoDB, and again we took the longest one. Hits on the scaffold VONY01001511.1 were selected according to our criteria. 9 exons were predicted in the reverse strand with exonerate (this document shows where U is found in SelenoO sequence). Tcoffee alignment was very good, with a score of 998 and very few mismatches. Seblastian predicted an 8 exons protein, using Meleagris gallopavo's SelenoO as a query. Again, our prediction contains one exon more than Seblastian's prediction, so we take ours as better. Other than that, Seblastian's prediction is good aligned. More than one SECIS were predicted, but we accepted as good one grade A SECIS in the positions 162162793 - 162162867 (-).The structure of the gene predicted by exonerate can be found hereunder:
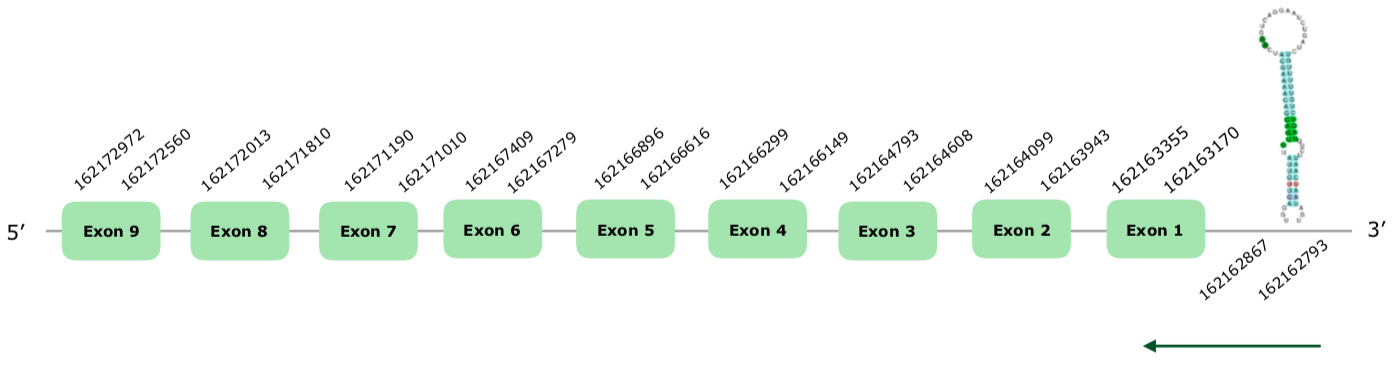
Taking into account all of this, we conclude that SelenoO is present and conserved in Colinus.
The gene in the scaffold VONY01000599.1 was the one selected according to our criteria. The predicted gene has 5 exones and it is localized in the forward strand, (this document shows where U is found in SelenoT sequence). Tcoffee produced a very good alignment, with a score of 1000 and almost no mismatches. Seblastian, however, failed to predict a selenoprotein, maybe because it did not have any similar SelenoU examples loaded. However, it did predict a grade A SECIS in the positions 23234319-23234385 (+) in the right strand, therefore we accepted it as possible. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted gene:
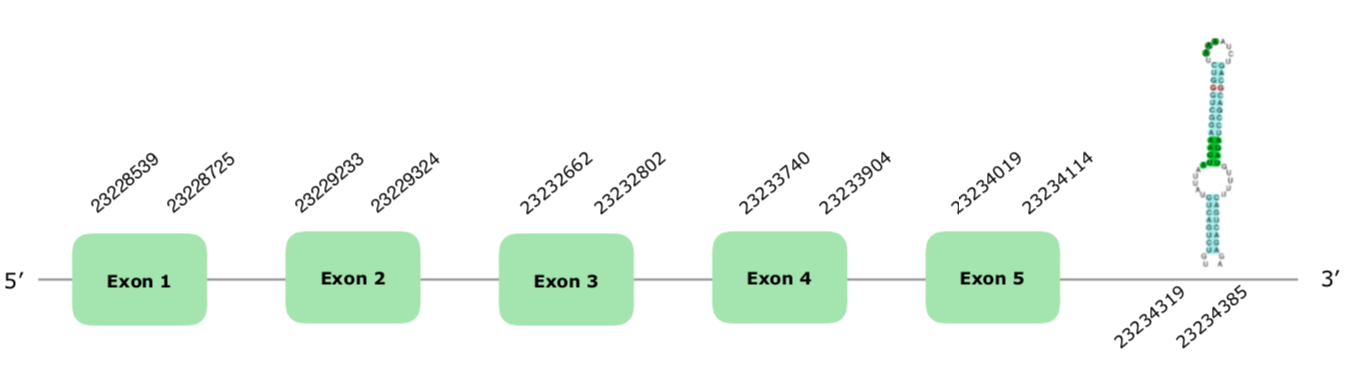
Despite Seblastian did not predict a Selenoprotein, we can consider that SelenoU is present and conserved in Colinus' genome.
Before discussing the results for this protein family, it is necessary to explain why we chose the scaffolds for each protein. To select them, we built a phylogenetic tree from a multifasta file where we included all the possible scaffolds for all three proteins.
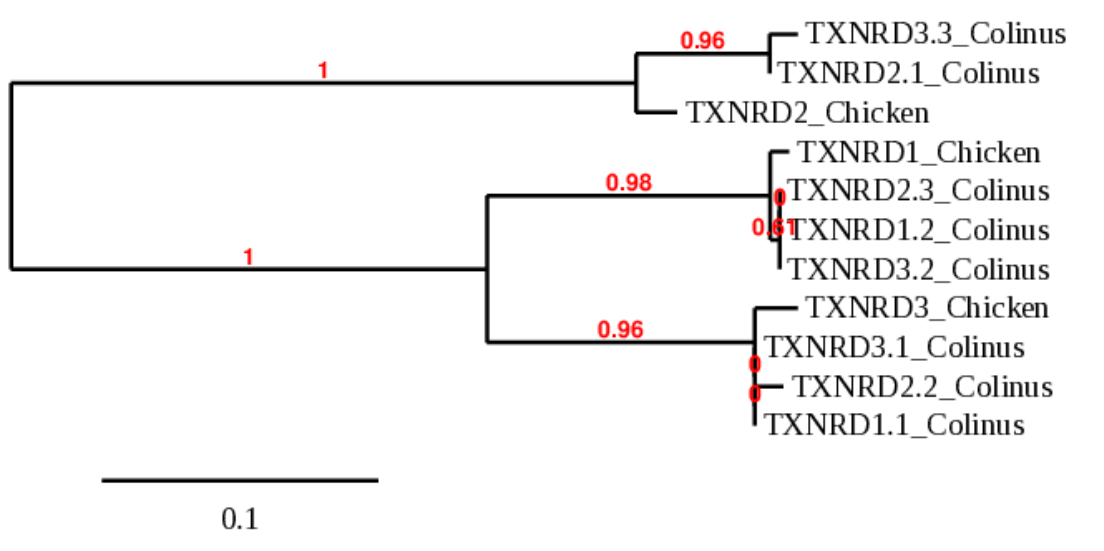
TXNRD 1.2
The gene in the scaffold VONY01001511.1 was the one selected following the criteria explained above. The predicted gene has 13 exons in the forward strand; however, the Seblastian is only capable of predicting 9 exons. If we take a look at the positions, we realize that Seblastian was not able to extend the first 4 exons. We will consider our exonerate prediction as the veridic one, therefore considering the protein has 13 exons (this document shows where U is found in TXNRD_1 sequence).
If we analyse the Tcoffee we see that it has a very good alignment, with a score of 1000 and almost no mismatches. Moreover, the Seblastian did a very good prediction but without the first 4 exons, as stated above. Finally, the predicted SECIS has a grade A and it is found at the positions 129752974-129753050 (+) so we accepted it.
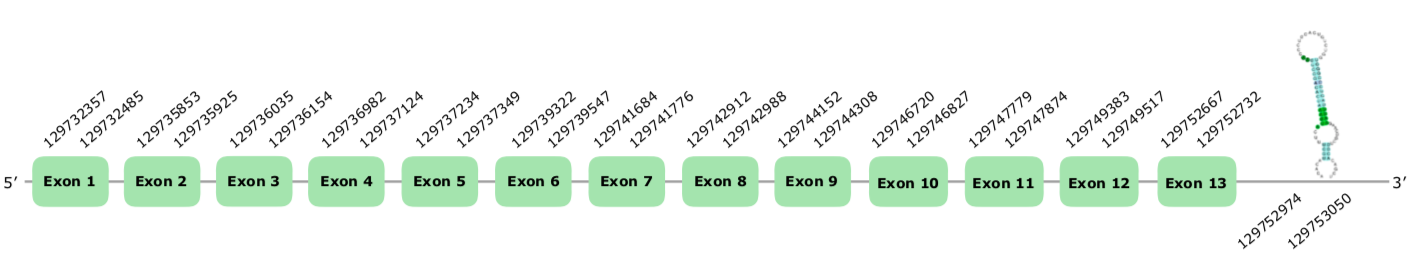
We conclude that this selenoprotein is present and preseved in Colinus.
TXNRD 2.1
The gene in the scaffold VONY01000045.1 was the one selected following the phylogenetic tree explained above. The predicted gene has 16 exons in the reverse strand; however, the Seblastian only predicts 13 exons. This is the same as with TXNRD_1.2, Seblastian was not capable of extending the first 3 exons. Therefore, we will consider our exonerate prediction as the veridic one, considering the protein has 16 exons (this document shows where U is found in TXNRD 2 sequence).
The Tcoffee shows a good alignment, with a score of 998, but with some mismatches and a four nucleotide gap in the middle of the protein. Moreover, the Seblastian did a very good prediction but without the first 3 exons, as stated above. Finally, the predicted SECIS has a grade A and it is found at the positions 5850096-5850173 (-), which makes sense and we accepted it.
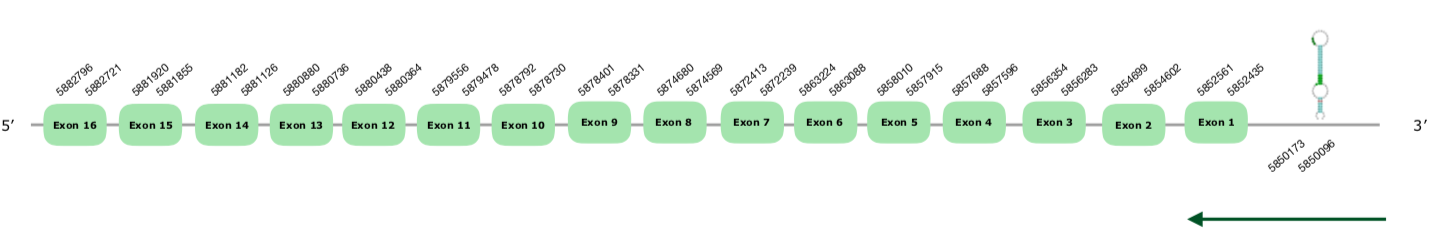
We conclude that this selenoprotein is present and preserved in the Colinus.
TXNRD 3.1
The gene in the scaffold VONY01000200.1 was the one selected following the phylogenetic tree explained above. The predicted gene has 16 exons in the reverse strand, and Seblastian this time predicts all of them too (this document shows where U is found in TXNRD 3 sequence).
If we study the tcoffee, we see that it shows a very good alignment, with a score of 1000, with a few mismatches. Moreover, the Seblastian did a very good prediction. Finally, the predicted SECIS has a grade A and it is found at the positions 2703025-2703116 (-), or in other words, which is normal and thus we accepted it.
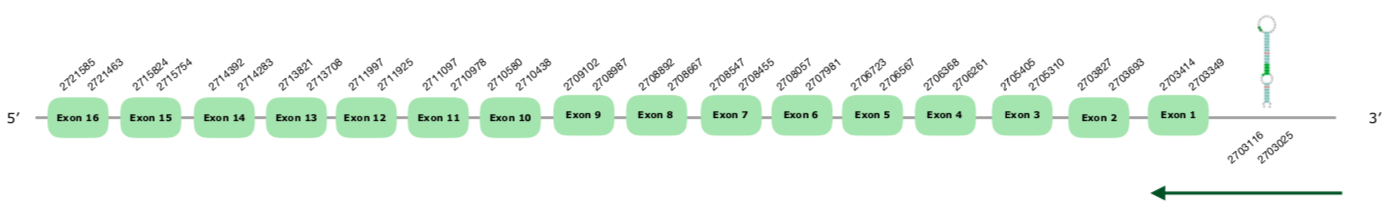
We conclude that this selenoprotein is present and preserved in the Colinus.
eEFsec
The gene in the VONY01000200.1 scaffold was the only one selected from the Tblastn prediction according to our criteria. This gene contains 6 exons and is located in the forward strand. It does not contain a Selenocysteine, since it is not a selenoprotein itself but part of the machinery. As expected, we do not get a prediction with Seblastian, and neither SECIS elements predictions. Although it presents some gaps and amino acid changes, the Tcoffee alignment is quite good, with a high score (995). You can find the structure of the predicted protein by exonerate hereunder:
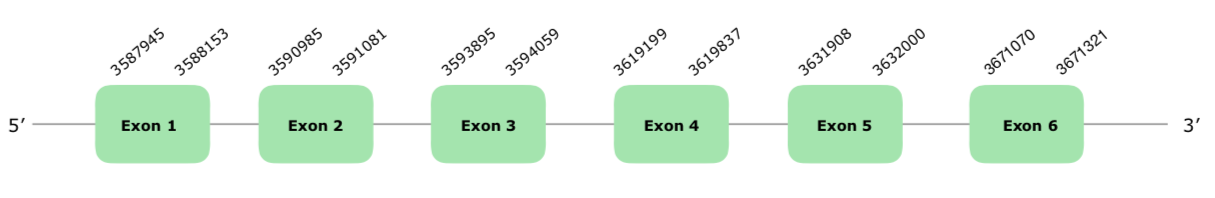
For this reason, we can say that the protein is conserved and present in Colinus, and that it is a machinery protein necessary for the selenoprotein synthesis process.
PSTK
Tblastn obtained 4 significant hits in the scaffold VONY01000599.1. The predicted gene contains 5 exons and is located in the reverse strain. Tcoffee shows a good alignment, with a score of 993, even though the Met start does not seem conserved. Since PSTK is a machinery protein, Seblastian failed to predict a selenoprotein. One SECIS element was predicted, but since it was far away from the protein (more than 8000 nucleotides away) it was not accepted. The gene structure can be found hereunder:
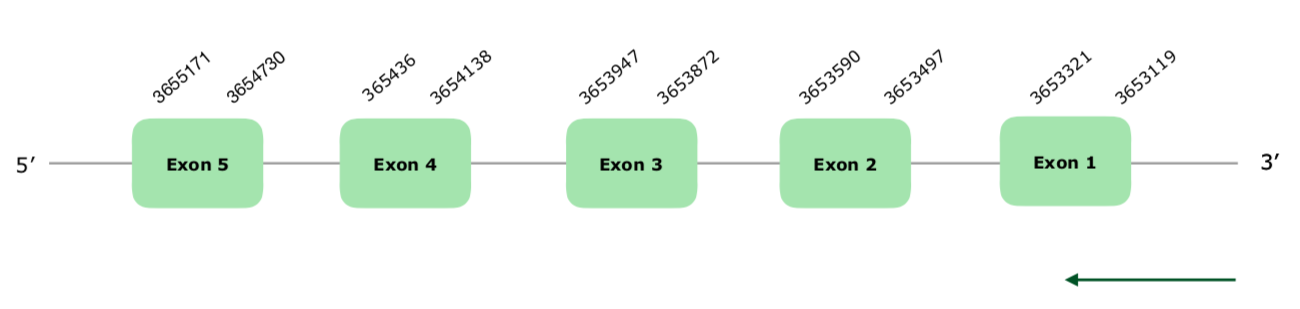
Collinus.
SBP2 (SECIS binding protein 2)
First thing we want to highlight is that we used the second isoform that SelenoDB had registered, since it was the longest one. We consider that, given this, a bigger part of the protein could be covered and the prediction could be better and more accurate.
Many good hits were predicted in the scaffold VONY01000010.1, all of them very close to each other. Gene prediction showed 16 exons in the reverse strand. Tcoffee's alignment was very good, with a score of 1000. No selenoprotein nor SECIS element were predicted using Seblastian and SECISearch3, as expected, since SBP2 is a selenomachinery protein entitled for incorporating the Selenocysteine to the selenoproteins. Exonerate prediction of the SPB2 gene can be found hereunder
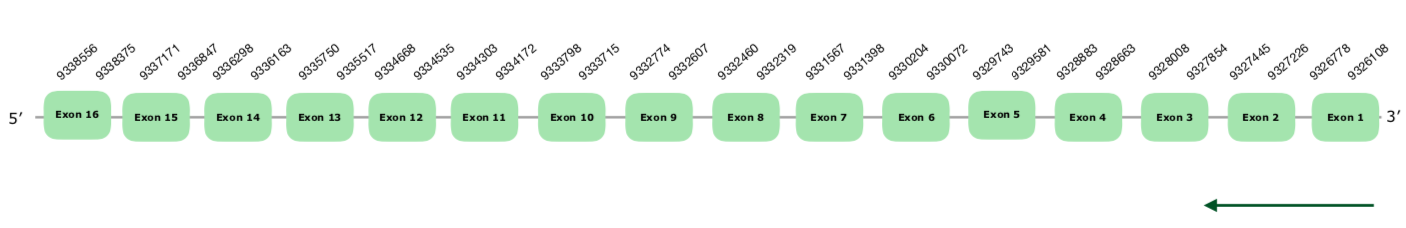
Given the good alignment of the Tcoffee and the expected lack of Selenoprotein and SECIS finding, we can conclude that this protein is present and conserved in Colinus as part of the machinery.
SECp43
Two hits of different scaffolds fulfilled our criteria HACER FILOGENIA VONY01000726.1 was the one finally selected. The predicted gene contains 7 exons in the direct strand. Tcoffee has a very good alignment and a score of 1000. As expected, since SECp43 is a machinery protein, Seblastian did not predict any Selenoprotein. In addition, only one grade B, far away SECIS was found, but it was not taken into account. The structure of the predicted gene is hereunder attached:
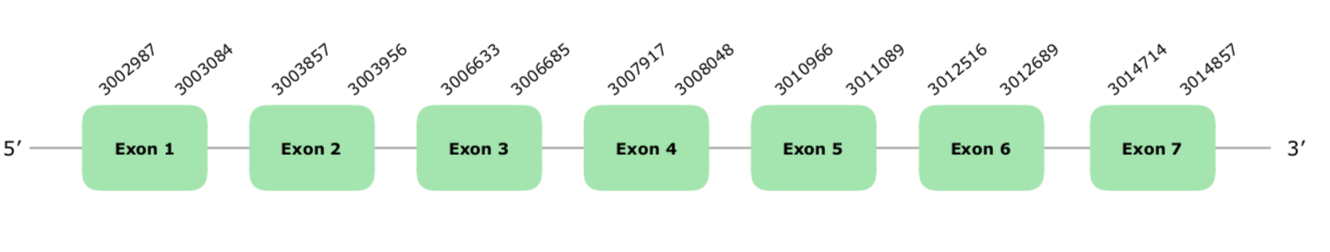
Due to the good of our Tcoffee, we can conclude that this protein is conserved and present in Colinus' genome.
SecS_2
A prediction in the scaffold VONY01000009.1 was selected using the DIO2 chicken protein as a query based on our criteria. As happened in SBP2, more than one isoform was noted in SelenoDB. We also selected the second one because it was the longest one, based on the same criteria we used with SBP2. The only hit accomplishing our criteria was in the scaffold VONY01000583.1. Exonerate showed 11 exons in the direct strand. Tcoffee showed a good alignment, with a score of 1000 and a Met in the first position. As expected, Seblastian did not predict a selenoprotein and SECIS elements were far away from the Sec. Since SecS is a machinery protein, no selenoprotein was expected. The structure of the predicted gene is hereunder attached:
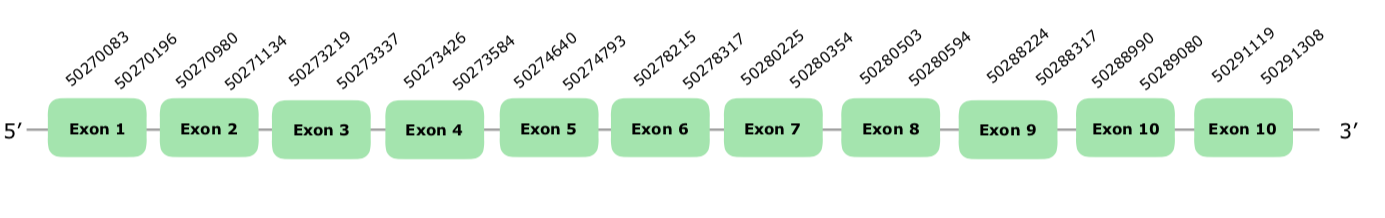
We can conclude that this protein is conserved and present in Colinus' genome.
SepHS (Selenophosphate syntethase)
The gene in the scaffold VONY01001511.1 was the one selected according to our criteria. The predicted gene has 8 exons and is in the forward strand. Tcoffee produced a very good alignment, starting with Met and it showed a score of 1000 and only a few mismatches. Since SEPHS is a machinery protein, Seblastian was not able to predict any selenprotein. However, we found 2 SECIS, both of them grade B. Despite this founding, as both SECIS were far away from the protein, they were not taken into account. Hereunder you can find the structure of the predicted gene:

Having all these information in mind, we conclude that this protein is present and conserved in the Colinus genome although it is not a selenoprotein but a protein of the machinery, as seen in chicken.