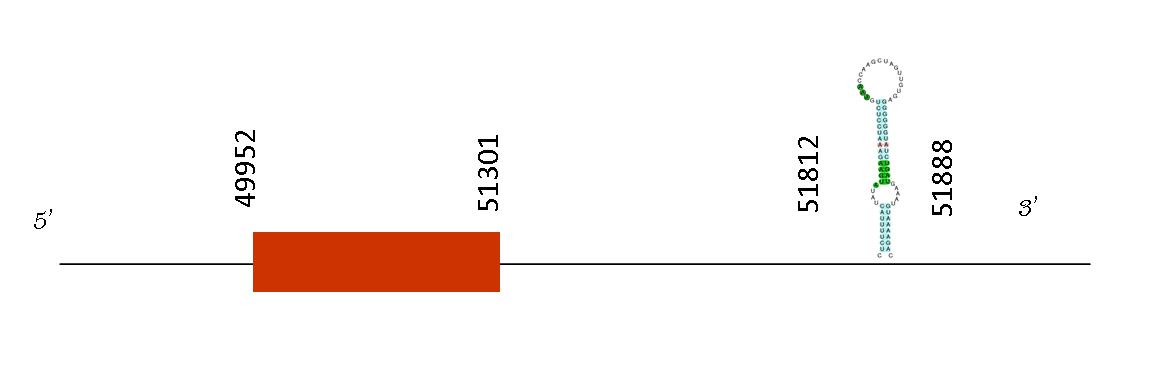We have characterised selenoproteins in Mus spicilegus by studying its homology with Mus musculus, due to the closer phylogenetic relation between these two species. We also used this species because it is a model animal and it has a good anotated genome.
We would expect a pretty similar selenoproteome between this two species. However, we found several differences explained in detail below.
The selenoproteins found by Seblastian in the genome we analysed are: GPx1,2,3,4, Sel15, SelH, SelI, SelM, SelN, SelS, SelW1, TR1,2,3.
We could not find the following selenoproteins: GPx5,6,7,8, MsrA, SelK, SelW2. These proteins have not been predicted by Seblastian, but they present SECIS elements.
There were several proteins that were not found in SelenoDB 1.0. For this reason, we decided to look for them in SelenoDB 2.0. The proteins that were analysed are: DIO1, DIO2, DIO3, SelenoO, SelenoP, SelenoU1, SelenoU2, SelenoU3, eEFsec, PSTK, SecS, SEPHS2, MSRB1, MSRB2, MSR3, Secp43.
There are several reasons why we were not able to predict a selenoprotein in a given sequence.
As we used a well annotated genome (Mus musculus), we expected to find plenty of selenoproteins. However, there were a high amount of sequences starting with an amino acid different than methionine. In these cases, we analysed the protein comparing it with Homo sapiens's genome. The result has not been any better.
In this next table we can see the proteins expected to be found in the different groups, we will focus on the mammalial placental ones and compare them with our findings7.
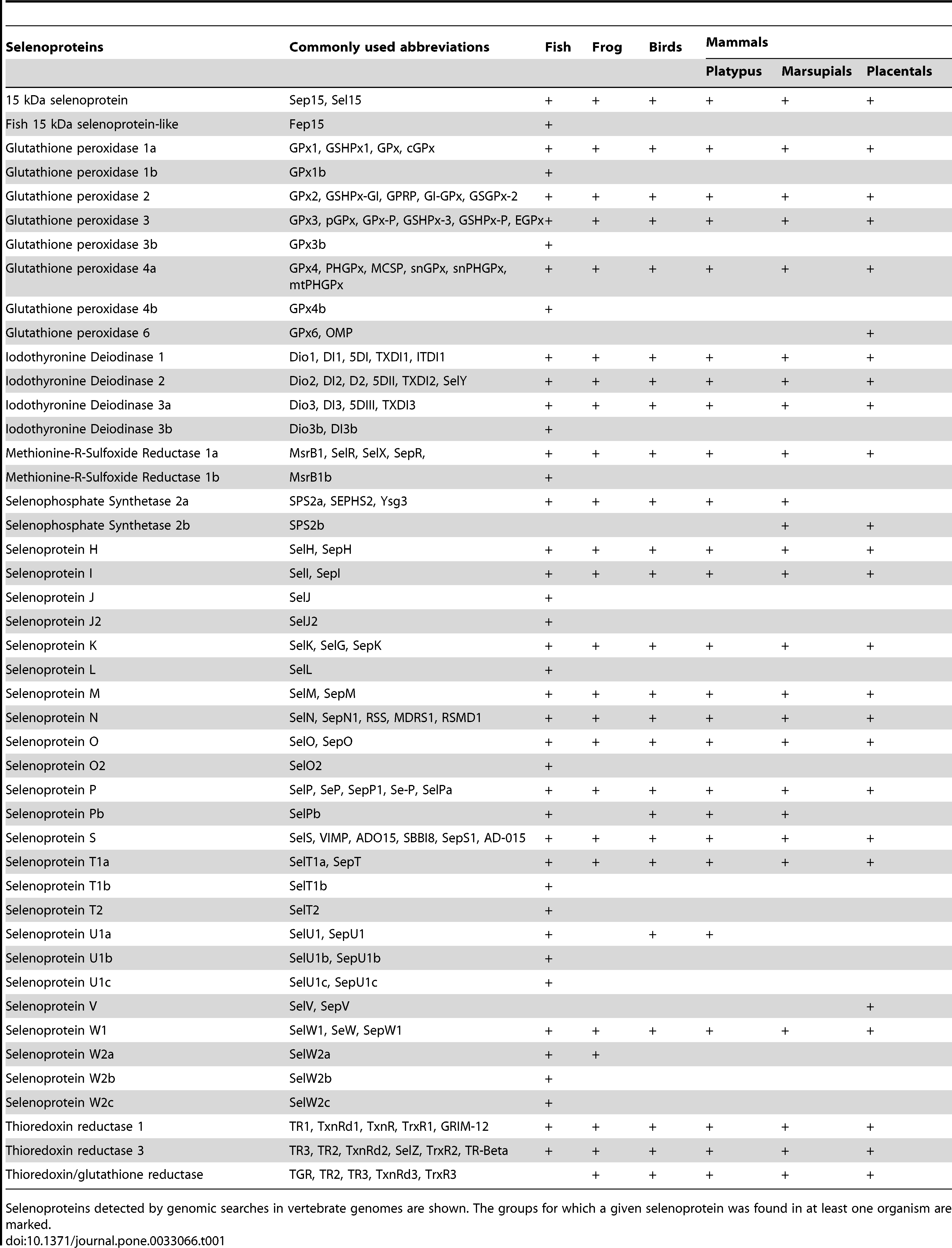
Image 7. Selenoproteins expected in different animal groups.
Glutathione peroxidase family (GPx)
GPx are selenoenzymes that play a key role in catalyzing harmful hydroperoxides with thiol cofactors. It is an excellent antioxidant defense mechanism to avoid reactive species of oxygen (ROS). Several isozymes of this gene family exist in vertebrates, which vary in cellular location and substrate specificity.
The selenocysteine residue at the active site forms a “catalytic triad” with tryptophan and glutamine which activates the selenium fraction and achieves an efficient reduction of peroxides.
For this reason, as it has an important function in the body we would expect to see this family of proteins.
Glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPx1)
Among the 10 scaffolds presented, the scaffold chosen was QGOO01037041.1, which has the best score, it showed an average identity of 94,09 and the lowest e-value. They were two fragment alignments in this scaffold.
This protein presented several scaffolds, but we selected the one with the best score, QGOO01037198.1. This scaffold contained two fragment of alignments with an average identity of 98,65 and it had the lowest e-value.
The scaffold selected was QGOO01037355.1, among all the eight different scaffolds presented, this was the one with the best score. It had an average identity of 89,45 and the lowest e-value. This scaffold had 4 different fragment of alignments.
The blast showed 8 different possible scaffolds but we chose QGOO01000322.1 because it had an identity of 90.116 and also the e-value was 3.59e-100 which is very low. This scaffold only had 1 fragment.
Within the 8 scaffolds that appeared in the blast sequence, QGOO01037229.1 was the one chosen due to its characteristics. It has 9 fragments of alignment, the average identity was 79.97 and the e-value was the lowest in comparison to the other scaffolds.
We chose the QGOO01037229.1 scaffold from the 8 scaffolds that the blast presented. This one had 9 fragments of alignment and showed an average identity of 75,04 and the lowest e-value.
The scaffold selected was QGOO01037308.1. In this case, the blast presented 9 different scaffold possibilities. The one chosen has 3 fragments of alignment and an average identity of 95,50, it as had the lowest e-value.
This protein did not appear in the list of selenoproteins in SelenoDB from Mus musculus. For this reason, we decided to searched it in Homo sapiens.
Iodothyronine Deiodinases catalyzes the activation and the inactivation of thyroid hormone by outer and inner ring deiodination
We selected the scaffold QGOO01037358.1 from the three scaffolds that Blast presented. This scaffold has 4 fragments and showed the best e-value and an average identity of 90,413.
The blast showed three scaffolds and we selected the QGOO01037505.1, that presented two fragments of alignment. The e-value was the lowest one and the average identity was 98,214.
Among all the 4 possible scaffolds that appeared in the blast file, we chose QGOO01037276.1. It shows just one fragment with an identity percentage of 99.620, and the e-value was the lowest.
In this case, just the scaffold QGOO01037280.1 was showed in the blast. This scaffold has 6 different fragments of alignment, an average identity percentage of 89,34 and a very low e-value.
Just one scaffold has been found for Sel15: QGOO01036624.1. This scaffold has identity percentage of 86,08 and a low e-value. This scaffold was composed by 3 different fragments of alignment.
One scaffold has been found on SelH protein, QGOO01037024.1. This scaffold contained just one fragment of alignment with a identity percentage of 59.474.
Three scaffolds have been found on SelI protein. However, we have selected just one, QGOO01000252.1, because the identity percentage average is of 90.04 and the e-value was the lowest. This scaffold had 9 different fragments of alginment.
SelK had 10 different scaffolds. However, we have selected just one, QGOO01037347.1, because was the longest, the identity percentage average was 91 and the e-value was really low. This scaffold had 9 different fragments of alignment.
Just one scaffold was found on SelM, QGOO01036943.1. This scaffold consisted on 3 fragments of alignment. The average of identity percentage was of 87,755 and it presented the lower e-value.
A single scaffold was found on SelN, QGOO01037443.1. This scaffold contains on 9 fragments of alignment. The average of the identity percentage was 93,6 and it presented the lower e-value.
A single scaffold was found on SECIS protein, the QGOO01037411.1 scaffold, and it contained 5 fragments of alignment. The average of identity percentage was of 96,4 and it presented a low e-value.
The semi-automatic program did not obtain an output file from FASTAsubseq. For this reason, we decided to realize the procedure with an Homo sapiens query, which starts with the amino acid Methionin like in the Mus Musculus.
Four scaffolds were found on SelT protein. However, just one was selected, QGOO01011872.1, because it was the one with the lowest e-value and a really good identity value of 98.851. This scaffold consisted on a single fragment of alignment.
We think this protein may not be well annotated in SelenoDB1 because in Pubmed it does not appear either for Mus musculus or Homo sapiens species. Furthermore, in the amino acid sequence from SelenoDB1 it does not start with methionine, instead it has a leucine at the beginning. Seblastian prediction showed the SelH prediction when introduced the subsequence file of SelW1, supporting our hypothesis that this selenoprotein does not exist in Mus musculus.
However, another explanation could be that as Mus spicilegus genome evolves quickly, SelW1 may have been lost in Mus spicilegus genome and the alignment tries to be the more accurate possible and has aligned the sequence to SelH and for that reason Seblastian shows SelH alignment.
Two scaffolds were found on SelW2 protein but we chose one, QGOO01036902.1. Its average of identity percentage was of 86,42, is the longer and has the best e-value.
Four scaffolds were found on TR1 but the one we chose was QGOO01036908.1 that contained 13 fragments of alignment. Its average of identity percentage was of 93,42 and it has low e-value.
TR2 comprise four scaffolds of which we selected one, QGOO01037360.1, which in his turn, is divided in 12 fragments of alignment. Its average of identity percentage is 91,86 and e-values are very low.
TR3 haves 4 scaffolds of which we selected just one, QGOO01036677.1, that has 15 fragments of alignment. The average of identity percentage is 92,4 and it presents a low e-value.
The blast showed 2 scaffolds and we selected the QGOO01037162.1 because it presents the best e-value and an average identity percentage of 71.318.
The scaffold chosen was QGOO01037138.1, as it was the only one that the Blast showed up. It has a low e-value and an average identity percentage of 88,21. This scaffold has 5 fragments of alignment.
Only one scaffold have been found in SelU3 protein: QGOO01037438.1. This scaffold presents a low e-value and an average identity of 95,4545.
Members of this family function as repair enzymes that protect proteins from oxidative stress by catalyzing the reduction of methionine-R-sulfoxides to methionines.
MSRB2 was found in two different scaffolds, but scaffold QGOO01000487.1 was chosen because it was the longest and the one with the best e-value. It contained 4 fragments of alignment and its identity percentage average was of 93,60.
Two scaffolds were found in the results of the Blast for this protein. The chosen one was QGOO01037410.1 for being the one with the best e-value. This scaffold had 4 fragments of alignment and its identity percentage average was 96,87.
Seblastian prediction is made once it is found a methionine upstream to a selenocysteine which, in his turn, is upstream to a SECIS structure located at 3’UTR. For this reason, in general terms, Seblastian is unable to find any selenoprotein machinery because the selenoprotein machinery proteins have cysteines instead of selenocysteines except for SPS2 that has a Sec residue.
We found only one scaffold for this protein: QGOO01036852.1. It had 10 fragments of alignment with a low e-value and an average identity of 88,2808.
Blast result showed 9 scaffolds. We selected the scaffold QGOO01037345.1, which presented the best e-value and an average identity of 92,751.
PSTK only presented one scaffold: QGOO01037476.1. This scaffold presented a low e-value and an average identity of 92,6385.
The scaffold chosen was QGOO01036893.1 because it had the lowest e-value. Its 4 fragments of alignment gave an average identity score of 92,01 and thay have the lowest e-value. They were 13 possible scaffolds in the blast.
SBP2 presented two different scaffolds. We have selected the QGOO01037436.1 because the identity percentage average is 94,171 and it has the lowest e-value.
Two different scaffolds were found in SPS1 and the scaffold chosen was QGOO01036418.1, that presents a e-value of 0 and a percentage identity of 71,675.
Among thirteen possible scaffolds the blast showed up, we chose QGOO01036418.1. It just has a single alignment, an average identity of 99.760 and an e-value of 0,0 meaning it is impossible this sequence was found by chance and also was the longest alignment found.
T-coffee output showed a score of 996, meaning that there is an excellent alignment with the predicted protein in Mus spicilegus. The protein predicted starts with a methionine. A single selenocysteine residue was found in the sequence and its position is conserved.
The prediction of the gene obtained with Exonerate showed 2 exons, whose coordinates were 50000-50245 and 50468-50824 respectively.
Regarding the SECIS prediction, two SECIS elements were predicted and one SECIS group was found in the relative position 50866 to 50947 on the positive strand. We found two exons and the last position of the exons found is 50824. So, these results are consistent because SECIS element is found downstream, on the 3’ UTR.
In definitive, this protein has a crucial role protecting the hemoglobin from oxidative damage. In addition, this protein avoids the Unfolded Protein Response induced by stress among its protective effect against redox injuries as lung inflammation or related. All that makes important GPx1 to be a well conserved protein in evolution as we can appreciate.
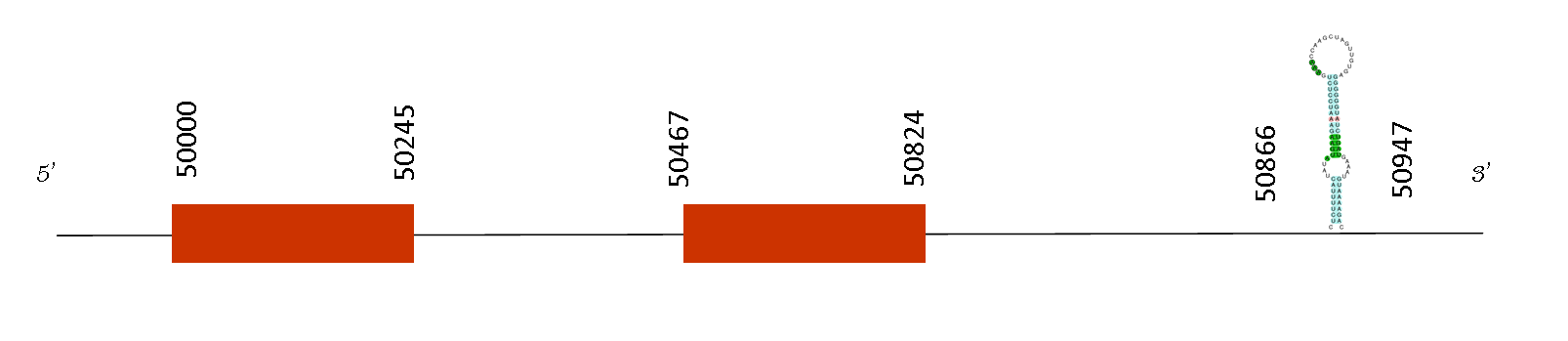
Glutathione peroxidase 2 (GPx2)
T-coffee result showed a score of 995, which is a very high score, so the alignment with the predicted protein is excellent. The protein starts with a methionine in both species of mice. The protein is located in the negative strand and a single selenocysteine residue has been found in the sequence, according to T-coffee result and SECIS prediction.
Two SECIS elements were predicted but just one selenoprotein was predicted. As reported by Seblastian prediction, the SECIS element is situated between the positions 49730 and 49795. Exonerate obtained a prediction of 2 exons in this gene. The position of these exons are 50000-50347 and 52489-52710 respectively, so the SECIS position coincides with the length of the exons, because it is found in a downstream position than the last position of the exon, meaning that it is found in the 3’ UTR.
The selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 2 (GPx2) is expressed in the epithelium of the gastrointestinal tract, where it is thought to be involved in maintaining mucosal homeostasis. Knockout studies in mice lacking this gene suggest a role for this isozyme in intestinal inflammation and colon cancer development. So, it seems that GPx2 might be important for the modulation of cell fate decisions in the murine intestinal epithelium although is not clear how. In addition, as all Gpx family does, GPx2 protects against the toxicity of ingested organic hydroperoxides, which is an important function and for this reason it’s a conserved protein in the evolution.
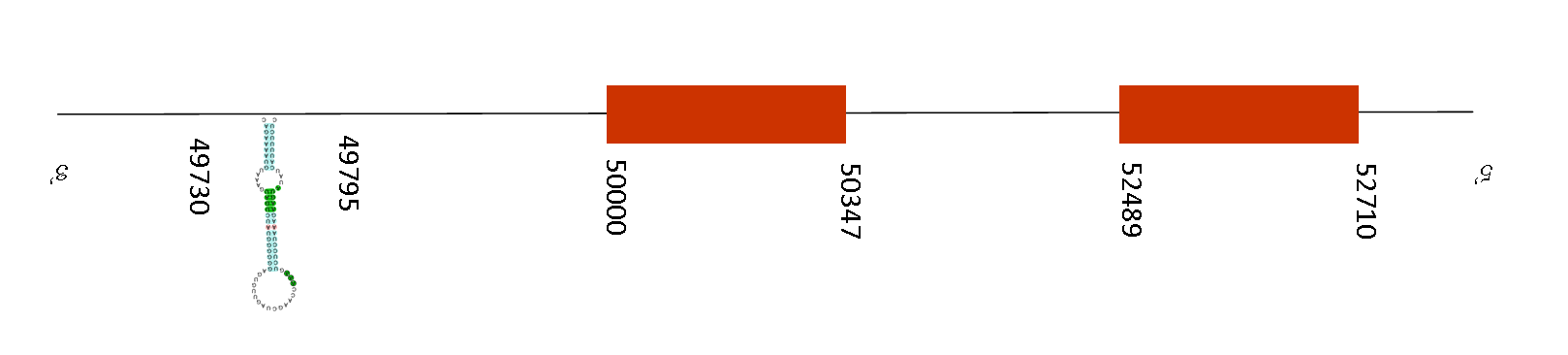
Glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPx3)
T-Coffee alignment with Mus musculus had a score of 998, which is very high, meaning there is an excellent alignment between the two sequences. The protein starts with methionine and a single selenocysteine residue was found in the Mus spicilegus sequence and its position is conserved.
Total number of SECIS elements predicted were two and it showed a SECIS sequence in the relative position 53070-53143 on the positive strand. Moreover, Exonerate’s result displayed 5 exons with the following absolute positions for each one of them: 45802-45888, 50003-50156, 51435-51552, 51938-52037 and 52335-52553. These are consistents results because the SECIS sequence is meant to be found in the region 3’ UTR, which means that it is found downstream from the last exon position (52553).
Gpx3 belongs to the glutathione peroxidase family, members of which catalyze the reduction of organic hydroperoxides and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by glutathione, and thereby protect cells against oxidative damage.This isozyme is secreted and is highly expressed in mouse kidney, which appears to be the major source of the enzyme in plasma. It has a role in mouse organogenesis, and dysregulation of this isozyme has been associated with obesity-related metabolic complications, platelet-dependent thrombosis, colitis-associated carcinoma, and thermosensitive phenotype. Thus, it is a key protein involved in several processes that makes clear why it has been conserved in Mus spicilegus.
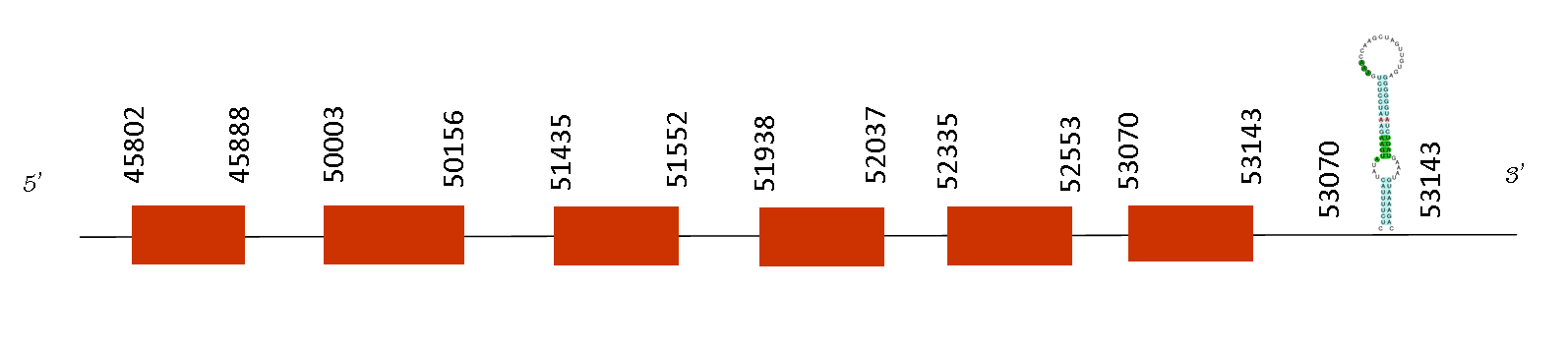
Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4)
T-coffee alignment had a high score of 987, so there is a good alignment between the two species. The protein in Mus spicilegus starts with methionine. A single selenocysteine residue was found and its position is conserved.
Total number of SECIS elements predicted was 2. In this case, a SECIS sequence was found in the positions 49865 to 49941 on the negative strand. The result obtained with Exonerate showed only one exon located between the position 50000 and 50533. So, the SECIS element is found downstream from the last exon position (50533).
This isozyme has a high preference for lipid hydroperoxides and protects cells against membrane lipid peroxidation and cell death. It is also required for normal sperm development; thus, it has been identified as a 'moonlighting' protein because of its ability to serve dual functions as a peroxidase, as well as a structural protein in mature spermatozoa. Disruption of this gene in mouse spermatocytes is associated with male infertility.It is an important antioxidant peroxidase, so it should be conserved in evolution, and in fact it is conserved between the two mice species.

Glutathione peroxidase 5 (GPx5)
The T-coffee sequence had a score of 935, so there is a good alignment between species. The protein predicted does not start with a methionine but instead it starts with Tyrosine. It does not have a selenocysteine in the sequence but it has a cysteine that it is conserved in the two mice species.
We found two SECIS predicted. The SECIS sequences are found in these positions: 90173-90250 in the negative strand and 74132-74210 in the positive strand. On the other hand, the protein presents 9 exons in this absolut positions: 50000-50134,51226-51379, 53280-53397, 53810-53909, 55041-55244 (positive strand), 29361-29520, 26118-26235, 25551-25650, 24129-24329 (negative strand). So, the SECIS are distant from the last positions of the exons and also this protein only presents a cysteine, meaning that it might present a loss of selenoprotein function.
This enzyme has a function in the protection of cells and enzymes from oxidative damage as all its family does. However, its expression is restricted toward genital fat pad adult. There is little information about this protein function because it seems to be a restricted temporally protein and tissue specific and is seleno-independant.
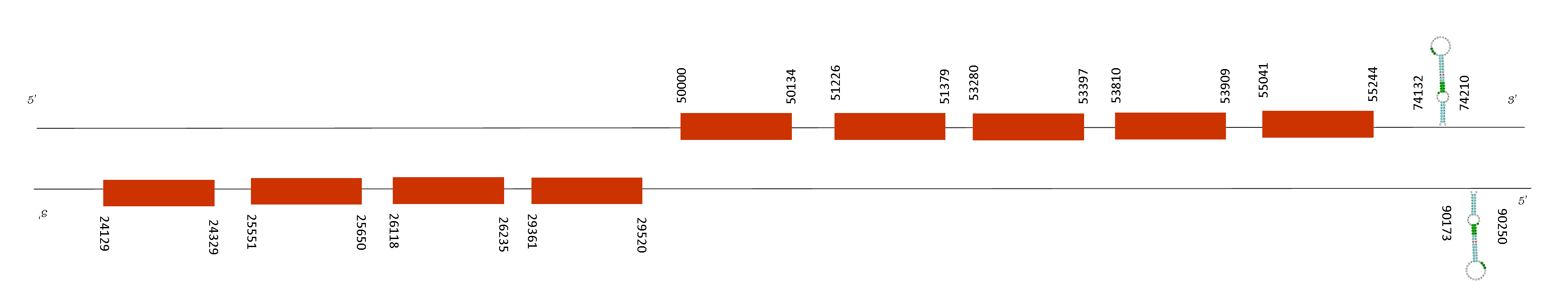
Glutathione peroxidase 6 (GPx6)
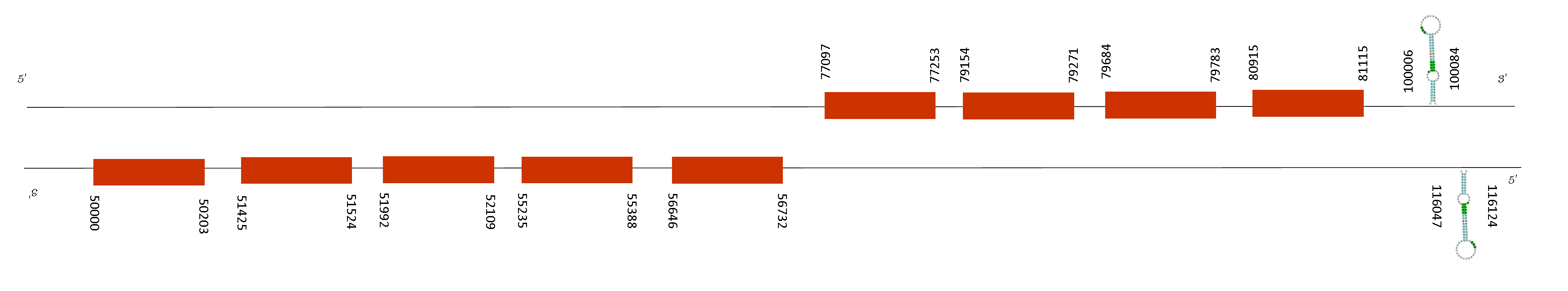
The T-coffee result showed a score of 1000, therefore the alignment between the two species is perfect. In both species of mice, the sequence strats with a Methionine. The sequence doesn’t present any selenocysteine residue, but it has a cysteine in both mice species.
Gpx6 contained 9 exons in the following absolut positions: 77097-77253, 79154-79271, 79684-79783, 80915-81115 (in the positive strand), 56646-56732, 55235-55388, 51992-52109, 51425-51524 and 50000-50203 (in the negative strand). Moreover, two SECIS elements could be predicted in this sequence in these positions: 116047-116124 in the negative strand and 100006-100084 in the positive strand, however we couldn’t predict any selenoprotein with Seblastian and this SECIS elements are in the 5UTR compare with the last position of the exons. A possible explanation for the fact is that it has been a loss in the selenoprotein function.
Expression of Gpx6 gene is restricted to embryos and adult olfactory epithelium. The mouse and rat orthologs contain a cysteine (Cys) residue at the active site, unlike the human counterpart, which is a selenoprotein, containing selenocysteine (Sec) instead. That may be the reason why Seblastian could not find any selenoprotein. However, it may be a selenoprotein with a Cys residue and its function conserved as well as in Mus musculus.
Glutathione peroxidase 7 (GPx7)
The T-coffee performed a 1000 score, meaning an excellent alignment with Mus musculus. The protein predicted starts with a methionine and it has reverted the selenocysteine to cysteine. This amino acid is conserved in position and in identity between the two species.
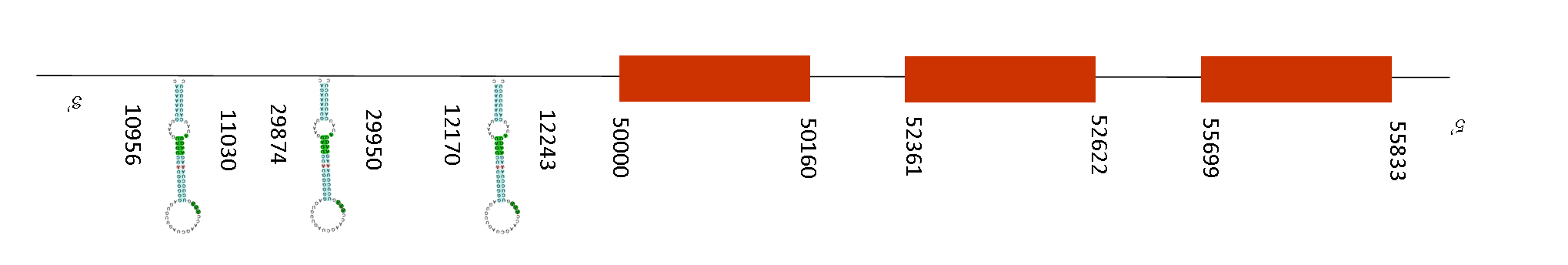
Three SECIS elements could be predicted, but no selenoproteins were predicted using Seblastian. The SECIS elements positions are: 10956-11030, 29874-29950 and 12170-12243 (all in the negative strand).
Exonerate displayed 3 exons in this sequence in the negative strand. The absolute positions for each one were 55699-55833, 52361-52622 and 50000-50160. So, SECIS elements are away from the last position of the exons, meaning that possibly it has been a loss of selenoprotein function in the proteome.
It is expressed in several tissues and, among other functions, it protects from oxidative DNA damage and double-strand breaks. Nevertheless, little information has been found about this protein in Mus musculus.
Glutathione peroxidase 8 (GPx8)
The blast presented 7 scaffolds, from which we selected the scaffold QGOO01037047.1, as it had the best e-value. It showed 3 fragments and an average identity of 81,47.
The T-coffee displayed a score of 1000, meaning that there is a perfect alignment between Homo sapiens and Mus spicilegus. The sequence started with a Methionine residue and it did not present any Selenocystein residue.
Exonerate result showed 3 exons in the reverse strand. The absolute positions of each exon were: 53014-53217, 52274-52535 and 50000-50160. Seblastian did not predict any Selenoproteins in this sequence, but displayed one SECIS element situated between the positions 35077-35157 in the negative strand. This result is coherent with the previous data obtained as the protein did not have any Sec. Thus, it probably is a Cysteine homolog with a similar function.
The protein has glutathione peroxidase, oxidoreductase and peroxidase activity.The protein has glutathione peroxidase, oxidoreductase and peroxidase activity. Unbalanced endoplasmic reticulum (ER) homeostasis (ER stress) leads to increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Disulfide-bond formation in the ER by Ero1 family oxidases produces hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and thereby constitutes one potential source of ER-stress-induced ROS. However, Ero1α is rapidly cleared by glutathione peroxidase GPx8. Loss of GPx8 causes ER stress, leakage of Ero1α-derived H2O2 to the cytosol, and cell death.
Iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO)
Iodothyronine deiodinase 1 (DIO1)
The T-coffee showed a score of 997, therefore demonstrating a very good alignment between Mus musculus and Mus spicilegus. The two species sequences start with a Methionine and one selenocysteine residue has been found.
The protein presents 4 exons, all in the positive strand, in that positions: 50000-50336, 58733-58876, 62326-62525 and 63872-63961. The sequence is found in the positive strand, and Seblastian predicted two selenoproteins and four SECIS elements.
The sequence of both predicted selenoproteins are exactly the same because they have the same exons, that could be due to a possible duplication of this region in the genome of Mus spicilegus due to a paralog phenomena.
DIO1 catalyzes the activation, as well as the inactivation of thyroid hormone by outer and inner ring deiodination, respectively. The activation reaction involves the conversion of the prohormone thyroxine T4, secreted by the thyroid gland, to the bioactive thyroid hormone T3 by 5'-deiodination. DIO1 is expressed predominantly in the liver and kidney and provides most of the circulating T3, which is essential for growth, differentiation and basal metabolism in vertebrates.
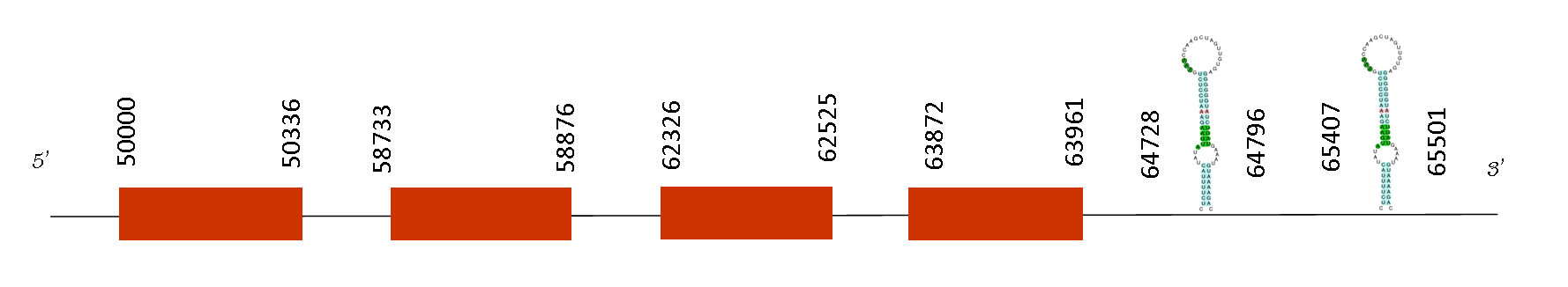
Iodothyronine deiodinase 2 (DIO2)
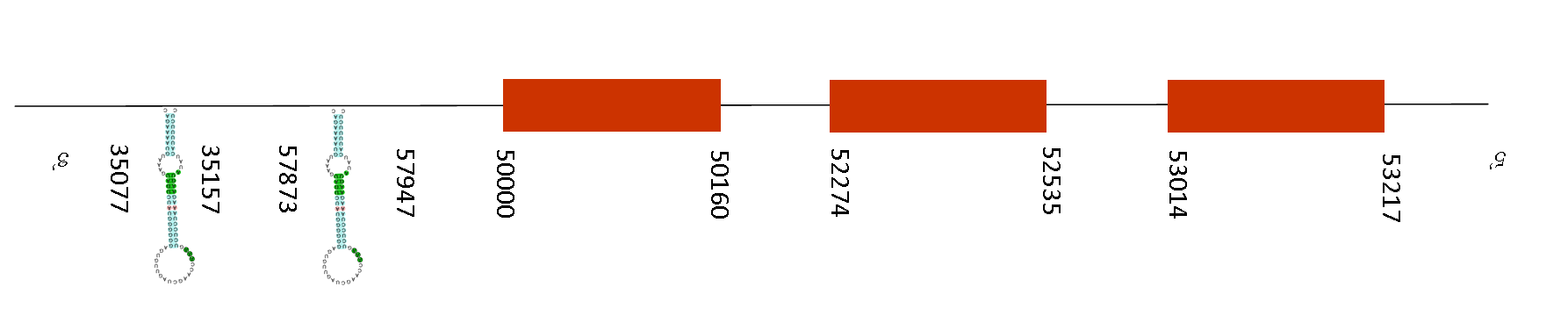
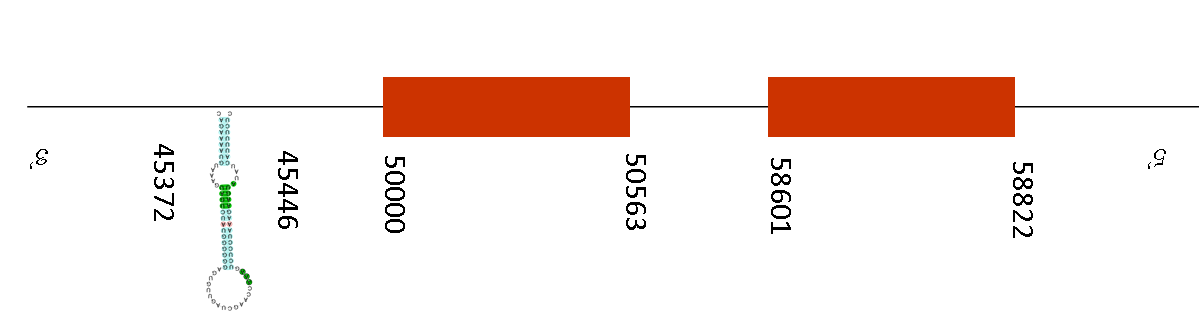
T-coffee results showed a score of 996. A selenocysteine residue was found in the sequence of Mus musculus, but in the Mus spicilegus there is a gap.
Seblastian predicted 3 SECIS elements but no selenoprotein was predicted in this sequence. The SECIS elements are in the negative strand, between these positions: 93583-93657, 103199-103275 and 45372-45446. Exonerate predicted 2 exons located between the positions 58601-58822 and 50000-50563. So, two SECIS elements are located in the region 5’UTR but one of them is located in the region 3’UTR (45372-45446) and thus it is a plausible SECIS.
DIO2 catalyzes the conversion of prohormone thyroxine T4 to the bioactive thyroid hormone T3 by outer ring 5'-deiodination. This gene is highly expressed in brain, placenta and mammary gland. It is thought to be responsible for the 'local' production of T3, and thus important in influencing thyroid hormone action in these tissues. Knockout studies in mice suggest that this gene may play an important role in brown adipose tissue lipogenesis, auditory function, and bone formation.
It could be possible that in this species, we find the DIO2 selenoprotein, though the Seblastian was not able to find it, because it starts with a methionine and a possible SECIS was predicted. This means a mutation from selenocysteine into cysteine occurred but the function is still conserved.
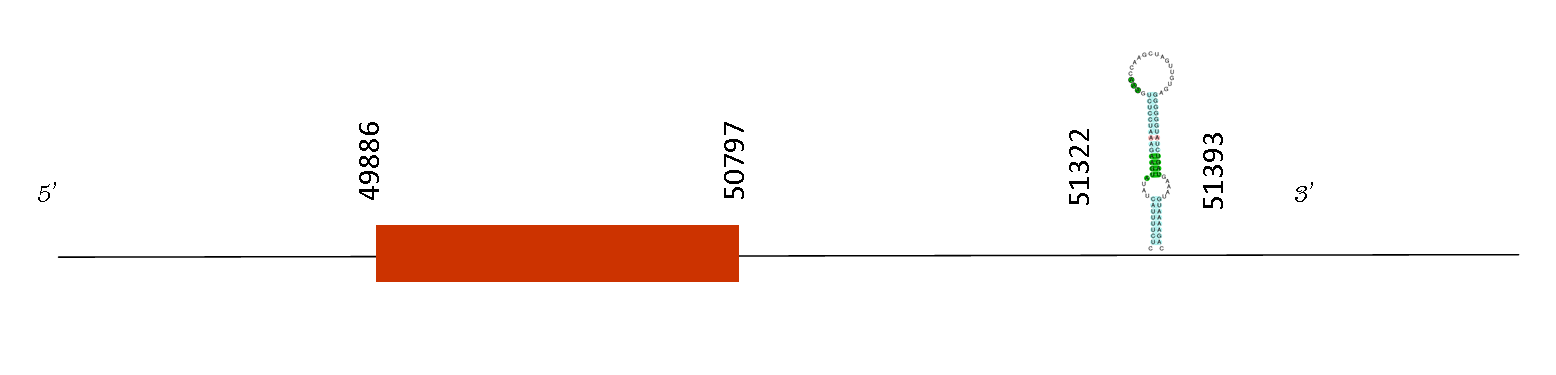
Iodothyronine deiodinase 3 (DIO3)
Regarding the T-coffee analysis, the results showed an excellent alignment between the two species compared, it had a 996 score. The protein predicted starts with a methionine and one selenocysteine was found in the exact same position than in Mus musculus .
We found only 1 exon and its absolute position is: 49964-50788. The Seblastian algorithm has found two SECIS predicted. Only one SECIS element forms part of a selenoprotein. Its sequence is on the position 51322-51393 in the positive strand, it is localised downstream than the last exon (50797) and for this reason it is a consistent SECIS.
This is an intronless, imprinted gene that is preferentially expressed from the paternal allele in the mouse fetus. The encoded protein belongs to the DIO family, and catalyzes the inactivation of thyroid hormone by inner ring deiodination of the prohormone thyroxine (T4) and the bioactive hormone (T3) to inactive metabolites, RT3 and T2, respectively. It is highly expressed in placenta, fetal and neonatal tissues, and thought to prevent premature exposure of developing fetal tissues to adult levels of thyroid hormones. It thus plays a critical role in mammalian development by regulating circulating fetal thyroid hormone concentration. Knockout mice lacking this gene exhibit severe abnormalities related to development and reproduction. Above all, we can appreciate that the functions of this selenoprotein is essential, leading to abnormalities when it is not present. So, it has een conserved in Mus spicilegus proteome as well as in other species.
Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA)
T-coffee analysis had a score of 1000, meaning an excellent alignment between the two sequences. The protein starts with a methionine but it does not have a selenocysteine, it has changed into a cysteine in both species. This cysteine is also conserved in Mus spicilegus.
It presents 6 exons in the negative strand between these absolute positions: 376652-376787, 242961-243029, 210122-210241, 159641-159745, 136588-136694 and 50000-50161. On the other hand, Seblastian has predicted 10 possible SECIS sequences, which are situated in this positions:
All the SECIS elements are not present in this selenoprotein, because some of them are far away from the last position of the exons and some are not in the 3'UTR region.
Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA), is abundantly localized in the mitochondria and reduces methionine-S-sulfoxide, scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). It is a repair enzyme for proteins that have been inactivated by oxidation and catalyzes the reversible oxidation-reduction of methionine sulfoxide in proteins to methionine. Although this function has been lost in our specie because it has loss its properties as a selenoprotein. This also happens in Mus musculus, but as they are very similar species, it is normal that the sequence is conserved. Furthermore, in cases of deficiency it has been observed
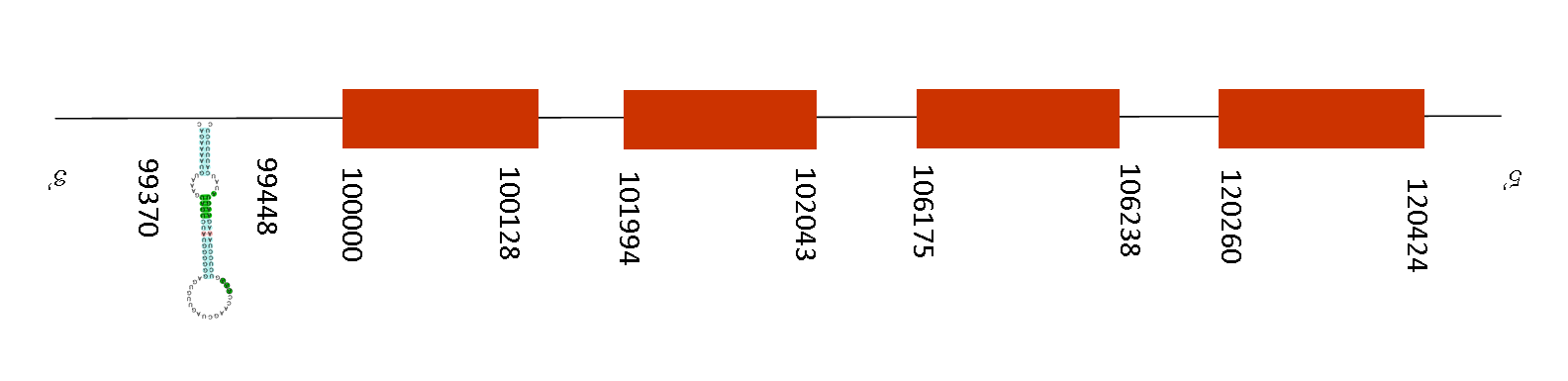
15kDa Selenoprotein (Sel15)
On the T-coffee analysis, results showed a very good alignment between sequences with a score of 996. The protein starts with a methionine in both species and a single selenocysteine residue was found on the same position.
Exonerate shows 4 exons, situated between these positions in the negative strand: 77196-77270, 70260-70427, 56175-56238, 51994-52043 and 50000-50128. Moreover, regarding the SECIS, there are 3 SECIS predicted. Although only one has been found at the relative position of 99370-99448 of the negative strand being part of the selenoprotein. The position of the SECIS is consistent because is located on the 3’UTR as we can appreciate.
Taking into account that Sel15 participates in cell apoptosis and in the mediation of chemopreventive effects of selenium, it is a protein that is useful for this specie and this is the reason of its conservation in the proteome. If it was not present, that could lead to a massive tumor apparition and death.
Selenoprotein H (SelH)
Regarding the T-coffee analysis, results showed a really good alignment of the sequences and obtained a score of 993. The protein starts with a methionine and a single selenocysteine residue was found conserving the same position as Mus Musculus.
Sel H contains 3 exons in the following positions of the positive strand: 50000-50103, 50197-50342 and 50472-50569. Moreover, Seblastian predicted two SECIS. Although only one SECIS was found between the 21200-21273 position of the positive strand, downstream to the last exon, which is 50569. So, it matches with the description of a selenoprotein due to SECIS element is located in the 3UTR region of the last exon.
SelH is a nucleolar protein, which belongs to the SelWTH family. It functions as an oxidoreductase, and has been shown to protect neurons against UVB-induced damage by inhibiting apoptotic cell death pathways, promote mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial function, and suppress cellular senescence through genome maintenance and redox regulation. As we can appreciate, this protein is found in Mus spicilegus proteome also, meaning that it has probably maintained all this functions because are really important.
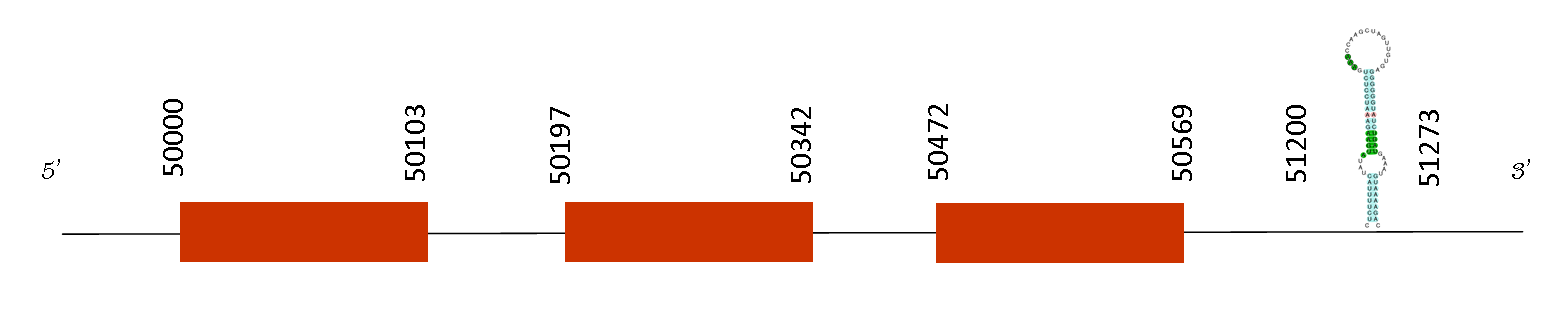
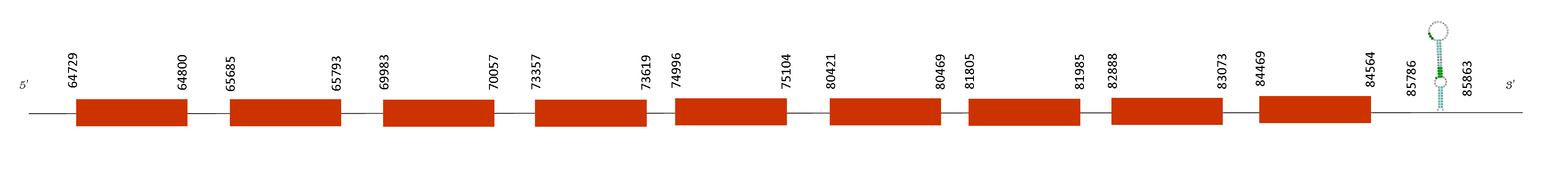
Selenoprotein I (SelI)
The T-coffee alignment with Mus musculus showed an excellent alignment with a score of 998. Furthermore, the protein starts with a methionine and just one selenocysteine was found conserving the same position as the reference genome Mus musculus.
Taking into account the SECIS, we found two SECIS predicted but we obtained just one on the relative positions 85786-85863 on the positive strand. Moreover, SelI has 9 exons in these absolute positions in the positive strand: 50000-50056, 64732-64800, 65673-65793, 69983-70057, 73357-73619, 74996-75104, 80421-80469, 81805-81985, 82888-83073 and 84469-84564. The last position of which is 84564 so, the SECIS element that is located on the position 85786-85863 on the positive strand its in the region 3’UTR, downstream the last exon.
The multi-pass transmembrane protein encoded by SelI gene belongs to the CDP-alcohol phosphatidyltransferase class-I family. It catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine from CDP-ethanolamine to diacylglycerol to produce phosphatidylethanolamine, which is involved in the formation and maintenance of vesicular membranes, regulation of lipid metabolism, and protein folding. For that reason, it is important the maintenance of this selenoprotein because is involved in cell communication and neurotransmitter production, both of which are pretty essential.
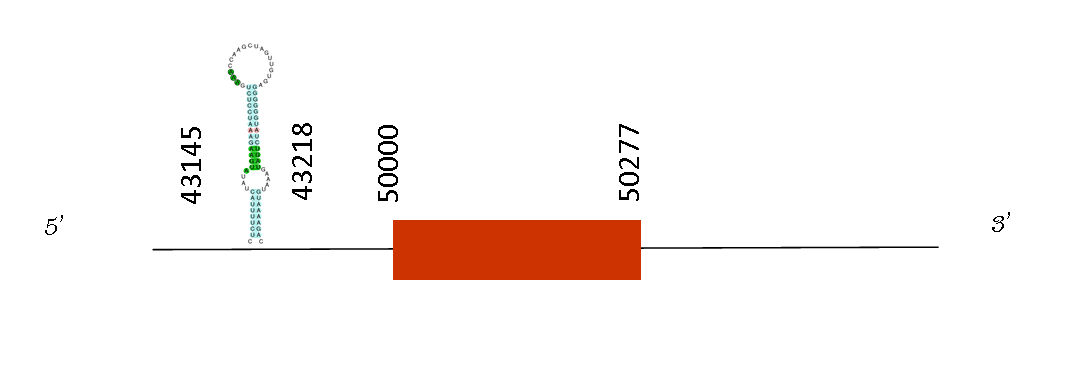
Selenoprotein K (Selk)
The T-coffee alignment with Mus musculus showed a good alignment with a score of 791. In addition, the protein starts with a methionine and it has been a substitution of the selenocysteine by a valine. That change produced the loss of the selenoprotein function and could not be found by Seblastian. However, one SECIS was predicted in the positive strand and in this position: 43145-43218. Moreover, Exonerate showed only one exon between the positions 50000-50056 in the positive strand.
It is a transmembrane protein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and is involved in ER-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded, glycosylated proteins. It also has a role in the protection of cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis. SelK has also been related with T-cell proliferation and T-cell and neutrophil migration. Knockout studies in mice show the importance of this gene in promoting Ca(2+) flux in immune cells and mounting effective immune response. Meaning that the lack of this protein would lead to an immunosuppression. So, that is why it has been conserved on Mus spicilegus genome, because the important roles it plays.
Selenoprotein M (SelM)
Regarding the T-coffee alignment, it presented an alignment score of 993 that was really good. Moreover, this protein starts with a methionine and has 2 selenocysteine residues and both of them were conserved in their position and identity. For that reason, we found two selenoproteins with one SECIS in each.
That findings suggest that a duplication on the genome has been produced and now Mus spicilegus has two SelM genes on its genome. Furthermore, this selenoprotein has 5 exons situated between the following positions: 52079-52207, 50851-50886, 50628-50662, 50224-50302 and 50000-50155. So, the last position of which is 50155, meaning that both SECIS are located on the 3’UTR region.
The exact function of this protein is not known. It is localized in the perinuclear region, is highly expressed in the brain, and may be involved in neurodegenerative disorders. Transgenic mice with targeted deletion of this gene exhibit increased weight gain, suggesting a role for this gene in the regulation of body weight and energy metabolism. SelM may also function as a thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase that participates in disulfide bond formation. We know that disulfide bond formation play a key role in the folding of the proteins so they can perform their correspondent function. As some of these functions may be vital, it is important its presence on the genome.
Selenoprotein N (SelN)
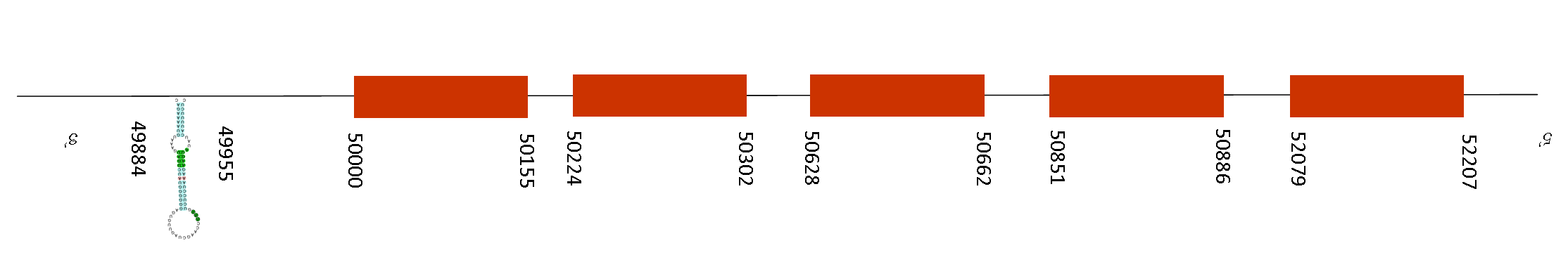
The T-coffee alignment of both sequences was excellent, its score was of 998. In addition, the protein sequence starts with a methionine and has a single residue of a selenocysteine conserved on its position in both species.
Exonarate detected 13 exons, that are located between the following absolute positions in the negative strand: 65642-65690, 62485-62618, 61983-62100, 58526-58659, 55830- 56039, 55505-55629, 54891-55028, 53358-53439, 53021-53209, 52647-52752, 51148-51260, 50959-51060 and 49958-50128. Two SECIS were found but just one was forming part on the selenoprotein on a relative position of 48977-49044 on the negative strand. That make sense because it is located on the region 3’UTR because the last position of the exon is 50128.
This protein is a glycoprotein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It plays an important role in cell protection against oxidative stress, and in the regulation of redox-related calcium homeostasis. Mutations in the orthologous gene in human are associated with early onset muscle disorders, referred to as SEPN1-related myopathy. Knockout mice deleted for this gene exhibit abnormal lung development. Meaning that is a key protein, reason why it is also conserved in Mus spicilegus.
Selenoprotein S (SelS)
T-coffee alignment results showed an excellent alignment with a score of 998. Furthermore, this protein starts with a methionine and has a single selenocysteine residue conserved on its position.
Two SECIS were found and one of them was on a selenoproteins, it was localised in the positions 59538-59625 of the positive strand forming part of the selenoprotein. That protein has 8 exons in these positions in the positive strand: 50000-50075, 50604-50738, 53624-53730, 57156-57245, 57401-57479 and 59139-59221. So, the last position is 59221, so SECIS element its situated downstream from the last exon, on the 3’UTR.
SelS is a transmembrane protein that is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). It is involved in the degradation process of misfolded luminal proteins in the ER and its transfer to the cytosol where they will be destroyed. Also it may have a role in inflammation control. Thus this protein realises an essential role on Mus spicilegus as well as it does in Mus musculus, reason why it is conserved.
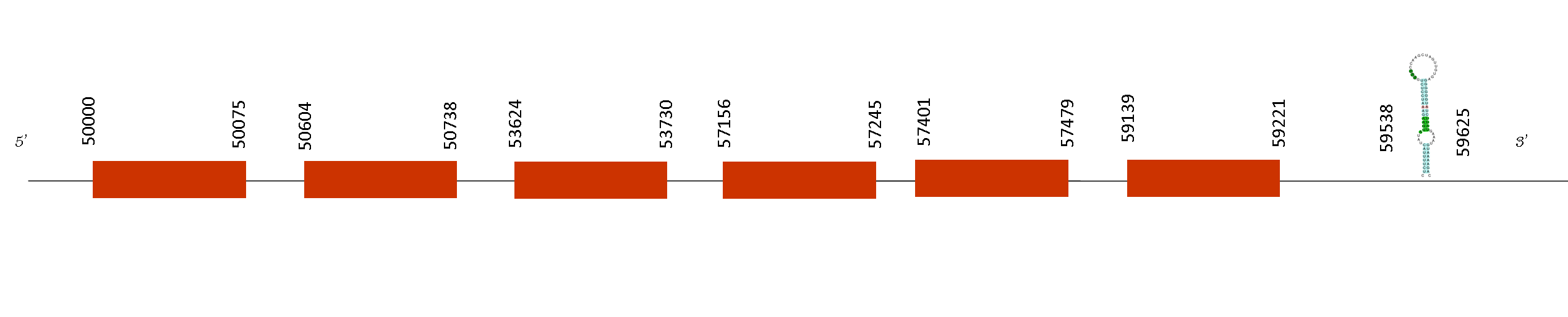
Selenoprotein T (SelT)
T-coffee showed an alignment with a score of 1000, thus proving an excellent alignment. There was not any selenocysteine residue in the sequence. The protein starts with the amino acid Methionine.
Exonerate displayed one exon located between the position 1963 and 2373, in the forward strand. Seblastian could not predict any selenoprotein in this sequence nor any SECIS element. This result is coherent, based on the fact that there were not any Sec in the sequence.
This protein is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum. It belongs to the SelWTH family that possesses a thioredoxin-like fold and a conserved CxxU (C is cysteine, U is Sec) motif found in several redox active proteins.
According to the literature, this protein has thioredoxin reductase-like oxidoreductase activity and protects dopaminergic neurons against oxidative stress and cell death. It is also involved in calcium mobilization, neuroendocrine secretion and plays an important role in fibroblast anchorage and redox regulation.
Selenoprotein W (SelW)
Selenoprotein W1 (SelW1)
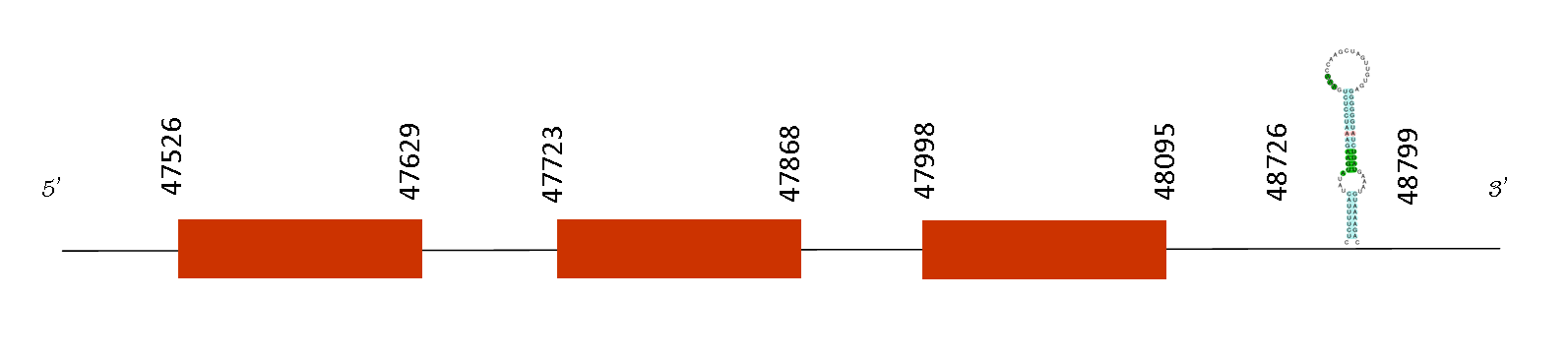
Selenoprotein W2 (SelW2)
T-coffee alignment was a perfect match with a score of 1000. The protein starts with a methionine and has a cysteine residue. However, it has not a selenocysteine residue.
This protein has 4 exons between the following positions: 50793-50881, 50582-50679, 50172-50248 and 50000-50080, all in the negative strand. No selenoproteins or SECIS could be predicted with Selenodb. So Mus spicilegus has not this selenoprotein on its proteome, and there are not a convertion of a selenocysteine into a cysteine.
SelW is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and brain and has been shown to function as a glutathione-dependent antioxidant in vivo. Studies in mouse suggest that this selenoprotein is involved in muscle growth and differentiation, and in the protection of neurons from oxidative stress during neuronal development. Seblastian database seems to take into account only SelW in general. When we tried to detect SelW1, it matched SelH. So, our conclusion is that Mus musculus have only one protein of this family called SelenoW and this selenoprotein has not been conserved in and Mus spicilegus because it has no SECIS elements.
Thioredoxin reductase (TR)
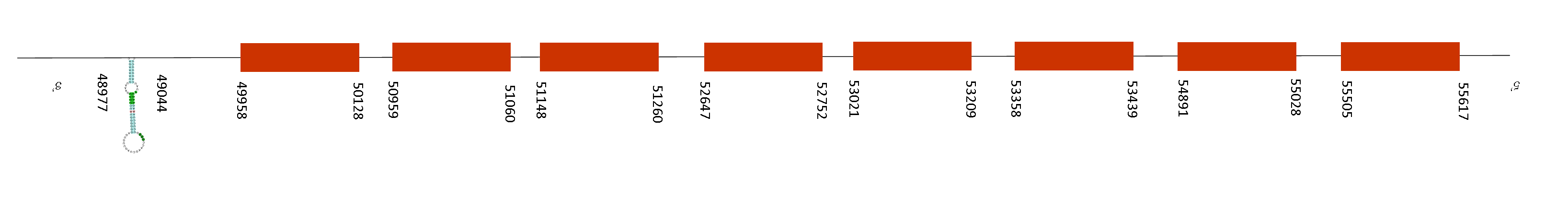
Thioredoxin reductase 1 (TR1)
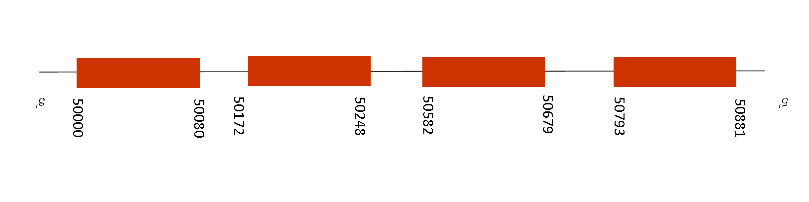
T-coffee alignment against Mus musculus was almost perfect with a score of 999. In addition, it starts with a methionine and has a single selenocysteine residue conserved on its position.
Two SECIS were predicted but only one being part of the selenoprotein found. This protein has 13 exons that are located at these positions in the negative strand: 67220-67525, 65741-65879, 64773-64838, 63067-63186, 61081-61223, 60565-60680, 58506-58731, 56496-56588, 55940-56016, 55383-55539, 55186-55293, 53253-53348, 50024-50158 and 44517-44582. The SECIS was located at 44210-44285 positions of the negative strand and as the last position of the exons is 44582, that means it is located downstream, at 3’UTR.
TR1 presents different isoforms. The isoform 1 have flutaredoxin and thioredoxin reductase activity and induces polymerization and regulation of the intracellular redox environment. Isoform 4 enhances estrogen receptors alpha and beta transcriptional activity, while isoform 5 only enhances the alpha activity and also it mediated cell death. As we found one selenopreotein with the right conditions, that means that TR1 is conserved in Mus spicilegus.
Thioredoxin reductase 2 (TR2)
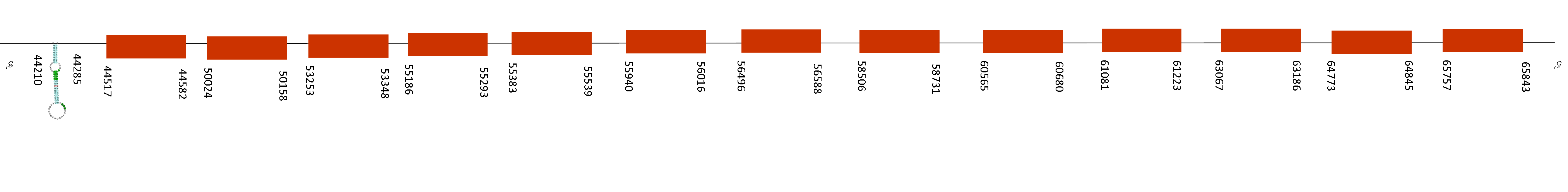
On T-coffee alignment we found a score of 998. Therefore, this protein starts with a methionine residue and has a single selenocysteine conserved on its position.
Just a single SECIS was predicted and it is the one that is present on the selenoprotein found. Moreover, Exonerate found 15 exons in the following positions of the positive strand: 39403 -39517, 42728 -42793, 49188 -49244, 50082-50226, 50874-50948, 53669-53747, 54618-54680, 56088-56158, 67216-67327, 68771-68945, 81768-81904, 85217-85312, 87786-87857, 88701-88798 and 90847-90973. The positions where thr SECIS element was predicted is 92175-92245 of the positive strand and final position of the last exon is 90973, so it matches with our findings because it is situated downstream, in the 3-UTR region.
TR2 function is to reduce proteins and has an impact on mitochondrial redox homeostasis as well as it is activated against oxidative stress. This protein is conserved in Mus spicilegus due to all mentioned.
Thioredoxin reductase 3 (TR3)
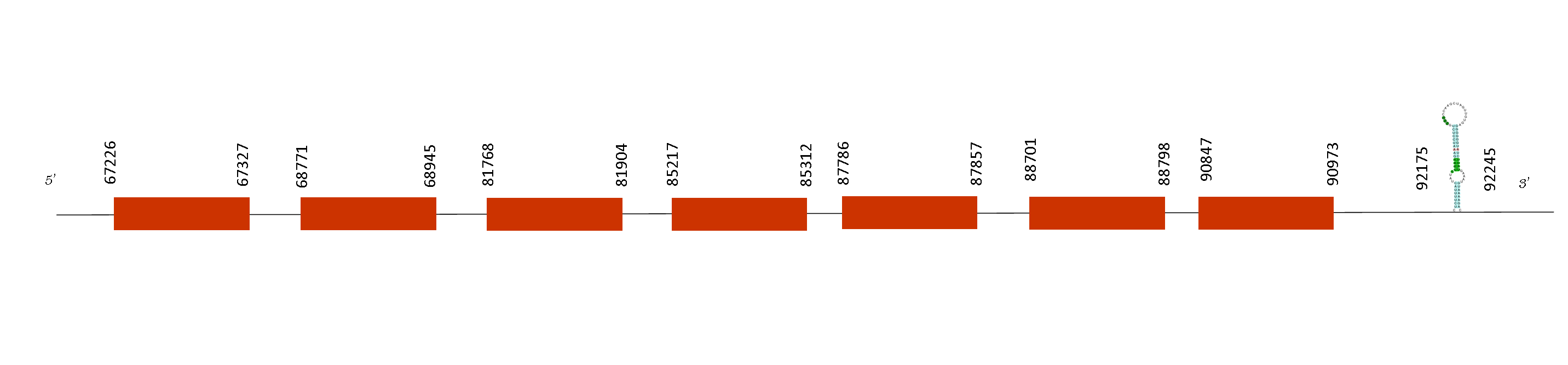
Regarding T-coffee alignment, the score obtained is of 1291,168. Moreover, this protein starts with a methionine and has a single residue of selenocysteine conserved on its position compared to Mus musculus.
Three SECIS were predicted but just one forming part of the selenoprotein found. This SECIS was located at 49223-49295 positions of the negative strand. Furthermore, Exonarate showed 16 exons located in these positions in the negative strand: 80656-80814, 74470-74530, 73445-73554, 69637-69741, 69374-69446, 67681-67800, 62577-62719, 60992-61107, 59583-59808, 58386-58478, 54846-54922, 54253-54409, 51925-52032, 51140-51235, 50003-50137 and 49463-49528. So, last exon ends on 49528 so our prediction makes sense, because SECIS element is located downstream, in 3-UTR region.
This protein which unlike the other two isozymes, contains an additional N-terminal glutaredoxin (Grx) domain, and shows highest expression in testis. The Grx domain allows this isozyme to participate in both Trx and glutathione systems. It functions as a homodimer containing FAD, and selenocysteine (Sec) at the active site. In definitive, it presents thioredoxin, glutaredoxin and glutathione reductase activities. Moreover, it promotes disulfide bond formation between GPX4 and sperm proteins. For this reason, it plays a role in sperm maturation and in the formation of sperm components.
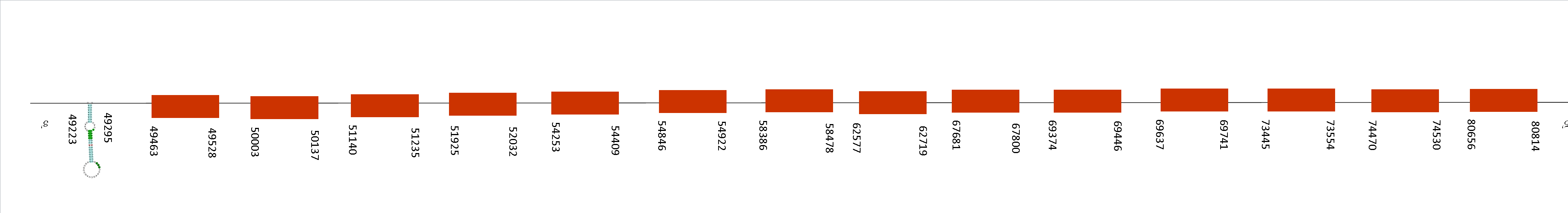
Selenoprotein O (SelenoO)
The blast showed two scaffolds. We selected the one with the best e-value, which was QGOO01037475.1, with an average identity of 89,44 and 7 fragments of alignment.
T-coffee result displayed a score of 999, meaning that the alignment with Mus musculus was almost perfect. Sel O starts with a methionine and has a single residue of selenocysteine on the same position of Mus musculus.
This protein contains 9 exons located in these positions: 50000-50556, 53303-53506, 54721-54907, 56183-56313, 57217-57497, 59306-59450, 59950-60135, 60274-60430 and 60518-60670. All of them are situated in the positive strand. Moreover, on Seblastian we found a selenoprotein with a single SECIS located on 60754-60830 of the positive strand. Taking this into account, the last position of the exons is 60670, meaning that SECIS is located downstream of this position, concretely on the 3’UTR where it belongs.
The function of this selenoprotein is to be a redox-active mitochondrial selenoprotein which interacts with a redox target protein, meaning that although its function may not be essential, it is conserved.
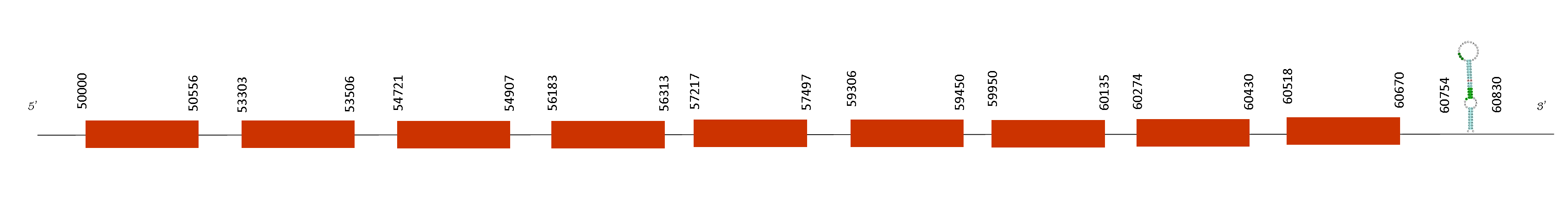
Selenoprotein P (SelenoP)
In this protein prediction, the blast showed only one possible scaffold that was QGOO01036879.1, it has 4 fragments of alignment, an average identity percentage of 98,02 and the e-value was very low. This means it is a good protein to be further analysed.
T-coffee analysis had a good score of 979, meaning there was a very good alignment between the two species. This protein starts with a mehthionine and has 11 selenocysteines in its sequence and they are conserved in both mice species.
Seblastian was able to predict two SECIS elements and both of them are contained in the selenoprotein.
Both of them have the same 4 exons in the negative strand, situated at these positions: 54817-55019, 53926-54138, 52433-52550 and 50000-50605. As the SECIS are found on a downstream position than the last exon position of the protein (54817), they are localised in the 3’UTR region which is consistent with our results.
Regarding our findings, the fact that we found two selenoproteins is due to a duplication event inside the genome and generated two selenoproteins which are paralogues.
This gene encodes a selenoprotein that is predominantly expressed in the liver and secreted into the plasma. This selenoprotein is unique because it contains multiple selenocysteine (Sec) residues per polypeptide (10 in mouse). It plays an imporant role in the transport of selenium to extra-hepatic tissues via apolipoprotein E receptor-2 (apoER2), as well as being an extracellular antioxidant. Mice lacking this gene exhibit neurological dysfunction, suggesting its importance in normal brain function. In addition, lately it has been reported that SelenoP and Gpx3 are potentially involved in the transport of Se from the pregnant female to the developing fetal tissues and organs.
Regarding all the information above, we can affirm that indeed it is an essential selenoprotein with lots of functions in the organism. Thus, it is conserved in Mus spicilegus.
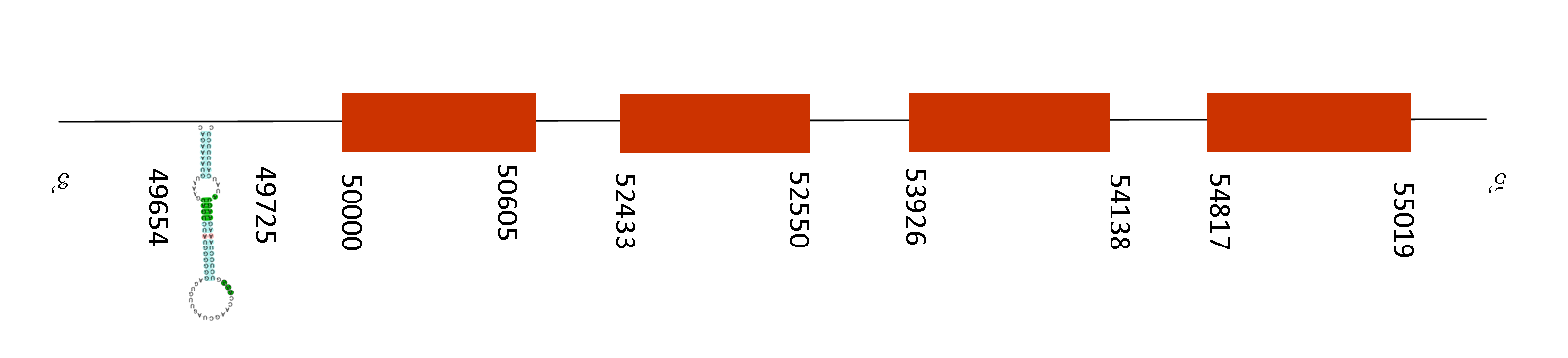
Selenoprotein U (SelU)
Selenoprotein U1 (SelU1)
Observing T-coffee alignment, the score obtained is 1000, meaning that the alignment with Mus musculus is perfect. Furthermore, the protein starts with a Methionine in both species, Mus Musculus and Mus Spicilegus and the sequences does not have any selenocysteine, but it presents two conserved cysteines.
SelU1 contains 5 exons in the positive strand between these positions: 50000-50177, 51688-51779, 55218-55358, 56320-56484 and 59567-59671. Moreover, we predicted 2 SECIS elements in the positive strand, located between the following positions: 57155-57230 and 67424-67522. The second SECIS element is situated downstream from the last exon position, meaning that maybe the selenocysteine has reverted into an homologous cysteine.
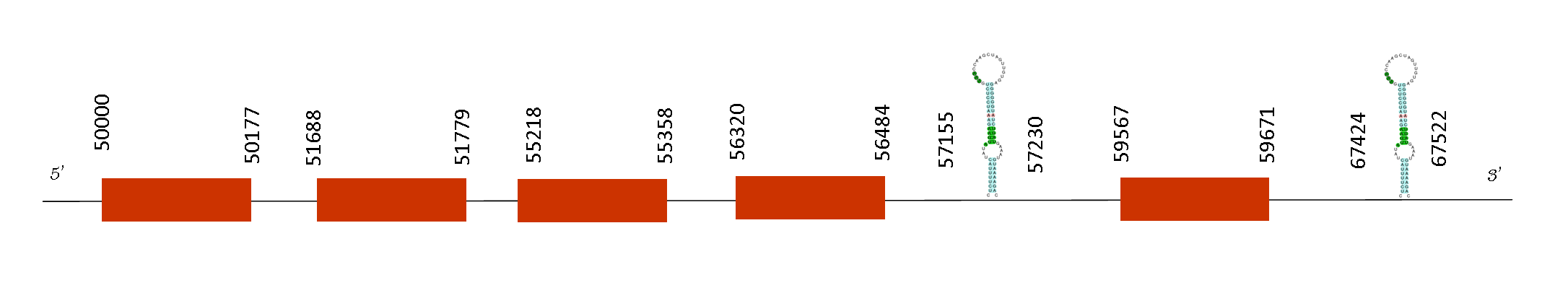
Selenoprotein U2 (SelU2)
The T-coffee analysis has a score of 1000, meaning there is an excellent alignment between the sequence of the two mice species. The protein predicted does not start with a methionine, but instead starts with an alanine. Furthermore, the sequence does not have any selenocysteine.
Exonerate showed that the protein has 6 exons with these absolute positions in the negative strand: 73127-73312, 72901-72969, 69726-69779, 69455-69560, 53989-54120 and 50000-50124. Seblastian was able to predict one SECIS element, but it was not part of a selenoprotein because this SECIS is located in the positions 81870-81950 on the negative strand.
In conclusion, SelU2 is not found in Mus spicilegus because although it has SECIS, it has not any Sec residue.
Little is known about SelU function in Mus musculus. In chickens, SelU may regulate biological processes through its redox functions. Moreover, its knockdown triggers autophagy through PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway inhibition in rooster Sertoli cells.
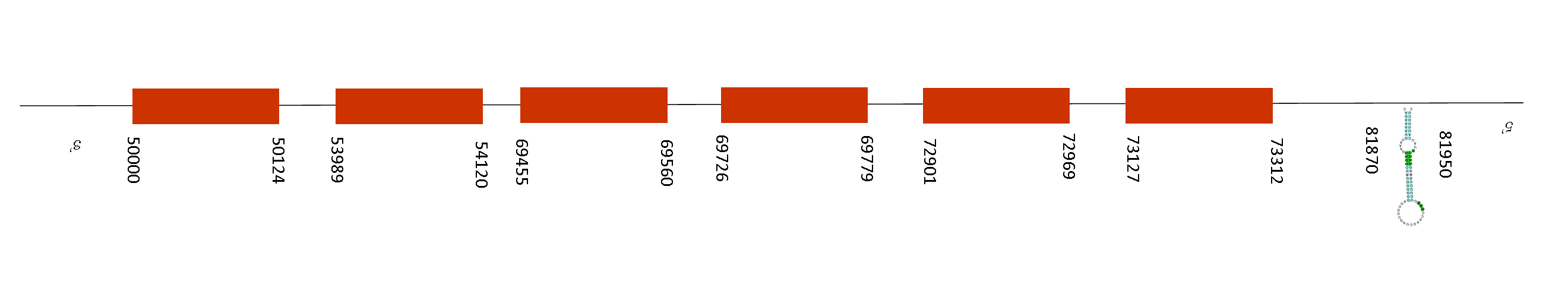
Selenoprotein U3 (SelU3)
T-coffee analysis presents an score of 1000. So, there is a great alignment with Mus Musculus. The protein predicted starts with a Methionine in both species of mice. However, the sequence does not present any selenocysteine but it presents different conservated cysteines.
SelU3 contains 7 exons situated in these absolute positions: 51904-51966, 51437-51641, 51089-51140, 50466-50529, 50309-50384, 50000-50118 and 49534-49557. All of them are located in the negative strand. Moreover, only one SECIS element was found. This SECIS element is located in the negative strand, concretelly in the position: 15079-15155. So, the last position of the exon (49557) is located away from the SECIS element meaning that this protein does not have selenocysteine functions.
As any SelU was found in Mus spicilegus, that suggests that the functions of this family of selenoproteins may be prescindible and have been deleted through evolution events.
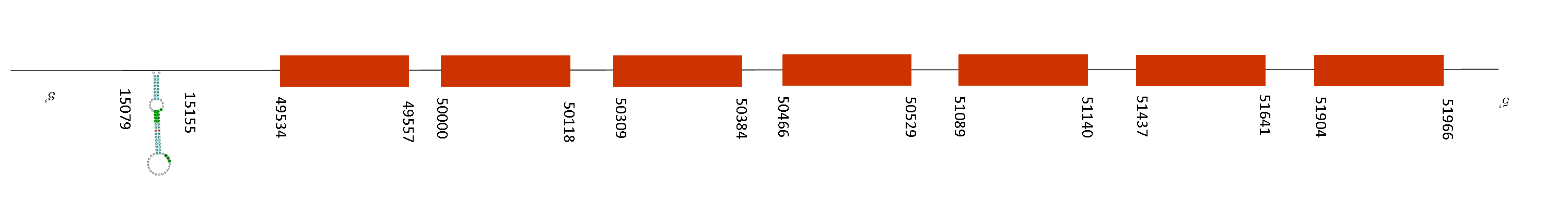
MSRB Family
MSRB1
A single scaffold was found on MSRB1 protein, QGOO01037226.1, which contains 3 fragments of alignment. The average of identity percentage was 86,73.
The alignment made by T-coffee showed an excellent alignment with a score of 993. Moreover, MSRB1 starts with a methionine in both Mus musculus and Mus spicilegus and its selenocysteine residue is conserved on its position.
This protein consists on 4 exons on the positive strand, located at the positions 50000-50054; 52803-52951; 53378-53492 and 54991-55019. In addition, just one SECIS was found in the position 55445-55516 on the positive strand also. This is consistent because as we can appreciate, the SECIS is found on the 3’UTR, being part of the selenoprotein.
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase B (MsrB) family. Members of this family function as repair enzymes that protect proteins from oxidative stress by catalyzing the reduction of methionine-R-sulfoxides to methionines. This protein is highly expressed in liver and kidney, and is localized to the nucleus and cytosol. It is the only member of the MsrB family that is a selenoprotein, containing a selenocysteine (Sec) residue at its active site. It also has the highest methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase activity compared to other members containing cysteine in place of Sec. It also acts as a regulator of actin assembly and plays an important role in innate immunity by reducing oxidized actin, leading to actin repolymerization in macrophages. In definitive, this selenoprotein is conserved in Mus spicilegus.
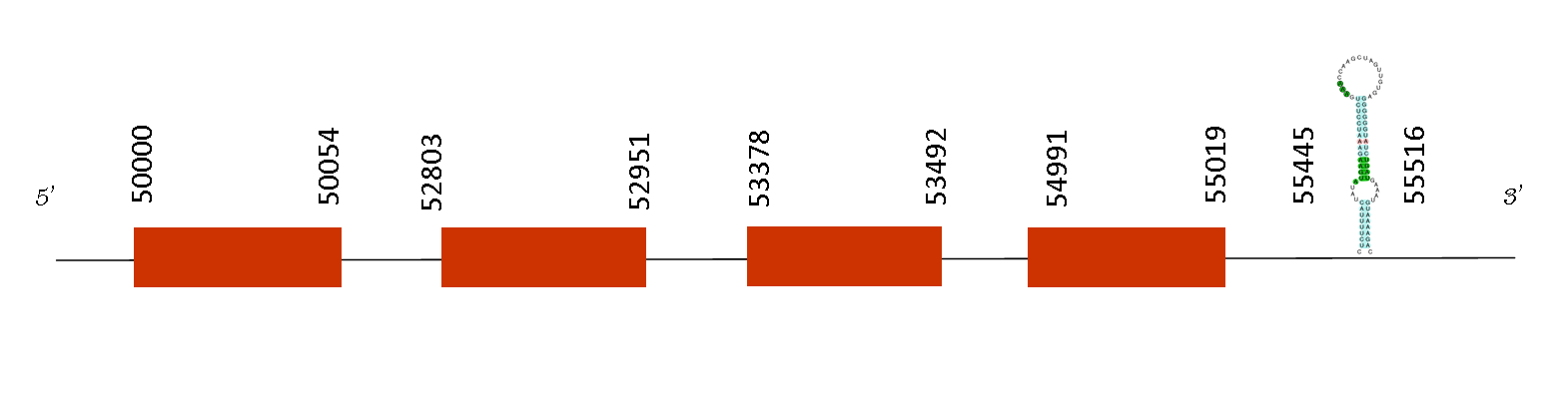
MSRB2
It has 4 different exons. The T-coffee alignment with Mus musculus showed a perfect alignment, with a score of 1000. However, the protein predicted does not start with a methionine but instead it starts with Lysine. It does not have a selenocysteine in the sequence but it has a conserved cysteine in the two mice species.
Exonerate showed 4 different exons located on these positions: 65507-65623, 61001-61077, 50953-51100 and 50000-50092 on the negative strand. Seblastian predicted 2 possible SECIS elements. One of the SECIS predicted is located on the region 3’ UTR on the negative strand, in the positions 20767-20852 and it might be a possible SECIS to be part of a selenoprotein. The other one was located in the positions 51212-51277, meaning it was predicted to be in the middle of the gene.
MSRB2 reduces methionine R-sulfoxide back to methionine and it plays a role in the preservation of mitochondrial integrity. FUNCIO
All in all, MSRB2 has been found in Mus spicilegus but is not considered a selenoprotein as it does not have selenocysteine in its sequence.
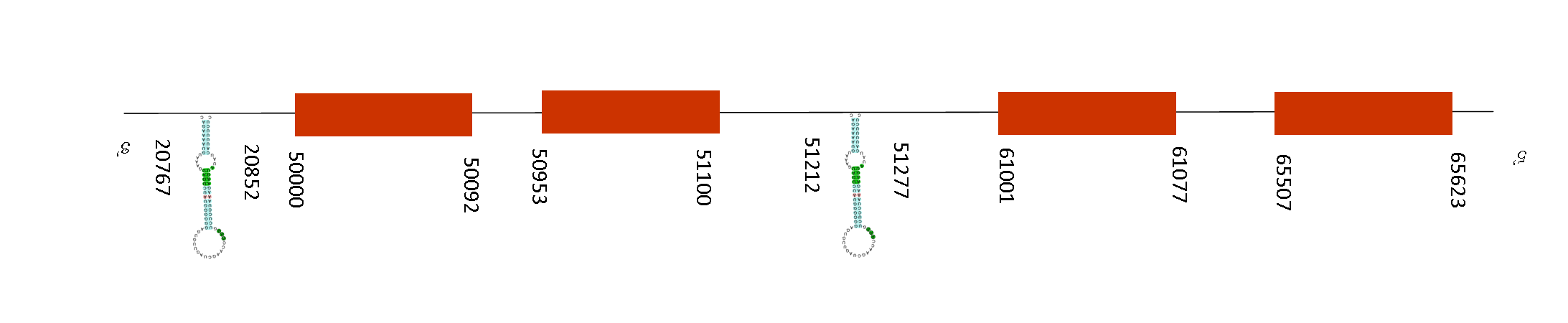
MSRB3
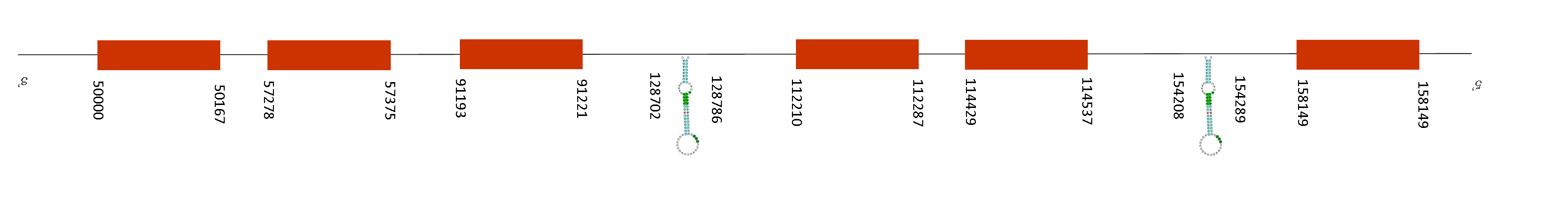
It is important to mention that this sequence does not start with a methionine, it has a serine instead. By running the program we realised that we did not obtained any results from Fastasubseq when we aligned with Mus Musculus. For this reason, we aligned the sequence of Mus Spicilegus with Homo sapiens, that starts with the amino acid methionine. T-coffee presented a score of 1000, meaning that there is a perfect alignment with Mus musculus. The sequence does not present any selenocysteine but it presents conserved cysteines.
The protein presented 6 exons in these positions in the negative strand: 158149-158230, 114429-114537, 112210-112287, 91193-91221, 57278-57375 and 50000-50167. Moreover, Seblastian predicted 2 SECIS elements in the negative strand and between these positions: 128702-128786 and 154208-154289. These SECIS are located upstream from the last position of the exons, so they do not belong to any selenoprotein.
MSRB3 is a protein repair enzyme that reduces methionine-R-sulfoxide to methionine. Some genetic studies showed that MSRB3 gene is associated with autosomal recessive hearing loss in human deafness DFNB74, although the role of this gene in the auditory system is still unknown. A knockout study in mice showed that MSRB3 protein is expressed in the sensory epithelia of the cochlear and vestibular tissues. It is accumulated at the base of stereocilia on the auditory hair cells. Its deficiency causes a degeneration of stereocilia and apoptosis of cochlear hair cells.
Selenoprotein machinery
Selenocysteine synthase (SecS)
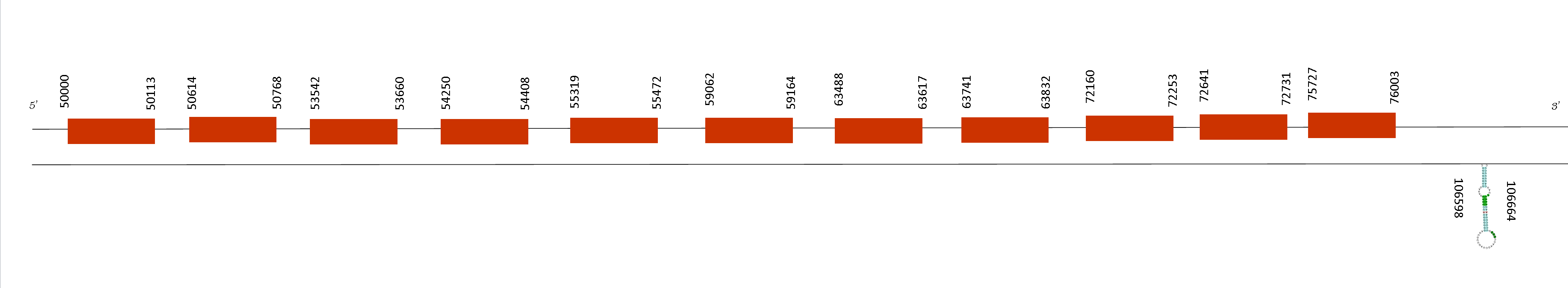
The alignment made with T-coffee showed an score of 1000, meaning that there are a perfect alignment between the two species of mice. Moreover, both sequences started with the amino acid Methionine and do not present any selenocysteine. However, there are different conserved cysteines.
Exonerate showed 11 exons in the positive strand, concretely in these absolute positions: 50000-50113, 50614-50768, 53542-53660, 54250-54408, 55319-55472, 59062-59164, 63488-63617, 63741-63832, 72160-72253, 72641-72731 and 75727-76003. All of them are present in the positive strand. Selenodb predicted only one SECIS between these positions: 106598-106664. However, this SECIS is situated in the negative strand, so it is not part of a selenoprotein because the exons are in the positive strand.
SecS is a protein which converts O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) to selenocystenyl-tRNA(Sec). It incorporates a selenophosphate into the backbone of the amino acid, forming Sec-tRNA. It participates in the last step of selenocysteine biosynthesis. Eukaryotic SecS is also a member of the pyridoxal phosphate‐dependent transferase superfamily and associates with the supramolecular complex mediating Sec incorporation into selenoproteins.
Eukaryotic elongation factor (eEFsec)
The T-coffee presented a perfect alignment with Mus musculus, thus the score was 1000. The protein does not start with a Methionine but instead it starts with an Alanine. There is not any Selenocysteine predicted nor any cysteine predicted.
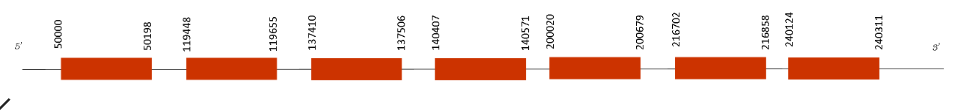
Seblastian predicted one SECIS element, but there is not any selenoprotein in this sequence. We found that eEFsec protein contains 7 exons in the following absolute positions: 50000-50198, 11944-119655, 137410-137506, 140407-140571, 200020-200679, 216702-216858 and 240124-240311. All of them are present in the positive strand.
This protein is a translation factor needed for the incorporation of a selenocysteine into proteins. For this reason, it is indispensable that this protein is present on Mus spicilegus genome. Although is not a selenoprotein predicted by Seblastian, the score of T-coffee was perfect because its importance, so it is perfectly conserved and aligned in Mus spicilegus.
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase (PSTK)
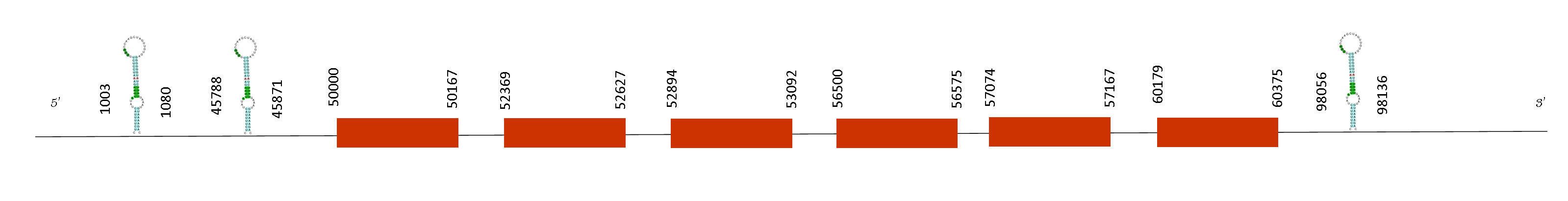
T-coffee analysis with Mus musculus showed a perfect alignment, with a score of 1000. However, this predicted protein starts with a Lysine (K) instead of a Methionine. Moreover, it does not present any selenocysteine but it presents conserved cysteines.
This protein shows 6 exons on the positions 50000-50167, 52369-52627, 52894-53092, 56500-56575, 57074-57167 and 60179-60375 on the positive strand. Seblastian has found three SECIS elements in these positions: 98056-98136, 1003-1080 and 45788-45871 in the positive strand. Two of these SECIS are not located in the right place to form part of the selenoprotein as they are in the region 5’ UTR from the last exon position. On the other hand, SECIS predicted by the Seblastian that is located in the positions 98056-98136 and might be a possible SECIS of the selenoprotein, meaning that selenocysteines of the sequence might have reverted into homologous cysteines.
The function of the protein is to phosphorylate seryl-tRNA(Sec) turning it into O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec). Although it does not start with a methionine and does not present any selenocysteine, it has a T-coffee score of 1000,and it is indicative of a conserved protein as it is perfectly aligned with Mus musculus.
tRNA Sec 1 associated protein 1 (SECp43)
T-coffee analysis showed an excellent score of 1000 meaning there is a great alignment in the sequence of the two species. In this case the protein does not start with a methionine but instead it does start with a Isoleucine in both species. Moreover this protein does not have any selenocysteine nor a cysteine.
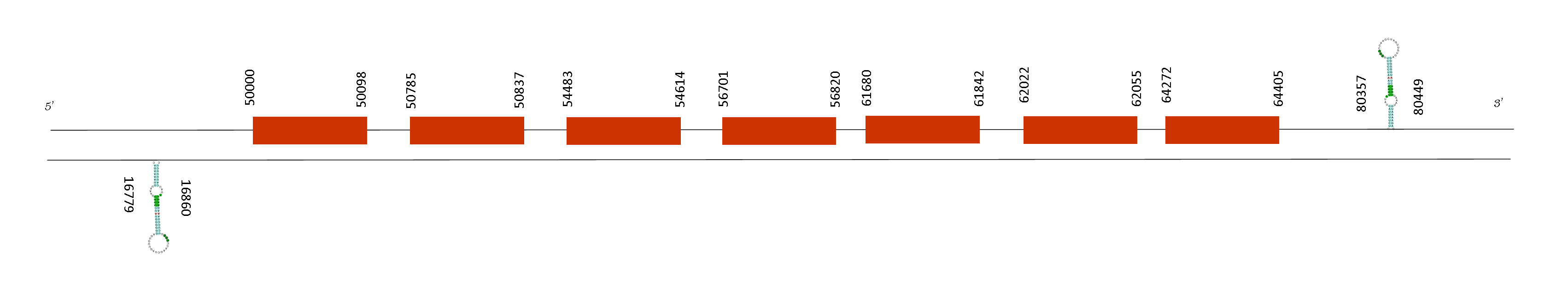
SECp43 is formed by 7 exons whose positions are: 50000-50098, 50785-50837, 54483-54614, 56701-56820, 61680-61842, 62022-62055 and 64272-64405 (in the positive strand). No selenoprotein could be predicted in this sequence although two different SECIS were predicted. The first SECIS was located in the positions 16779-16860 on the negative strand and the second SECIS is located in the positions 80357-80449 on the positive strand.
SECp43 is a selenoprotein machinery that has a role as a co-factor in selenoprotein expression. Although one might think is necessary for the expression of all the selenoproteins, previous studies have found that mice carrying mutations in SECp43 are able to express selenoproteins. However, as we obtained a perfect alignment in T-coffee analysis, we can affirm that Mus spicilegus has this machinery protein although is not considered a selenoprotein by Seblastian because it has not a selenocysteine residue on its sequence.
SECIS binding protein 2 (SBP2)
The t-coffee with Mus musculus showed a score of 1000, meaning there are a perfect alignment between the two mices. Also, SBP2 starts with a Methionine in both species and they do not have any selenocysteine. However, it presents different cysteines.
Concretely, SBP2 presents 17 exons in the following positions: 49171-49206, 50003-50151, 51803-52052, 52515-52656, 54315-54544, 60014-60092, 62400-62602, 67925-68047, 69973-70062, 70807-70948, 73213-73379, 74061-74199, 75753-75909, 76665-76885, 78945-79099, 79389-79578 and 80227-80327. All the exons are situated in the positive strand. Moreover, Selenodb does not present any SECIS element.
The function of this protein is the binding of the SECIS element in the 3-UTR of some mRNAs encoding selenoproteins. It belong to the machinery family, so his function is very important. As we obtained a perfect alignment in T-coffee analysis, we can affirm that Mus spicilegus has SBP2 conserved on its genome although is not considered a selenoprotein by Seblastian because has not a Sec residue on its sequence.
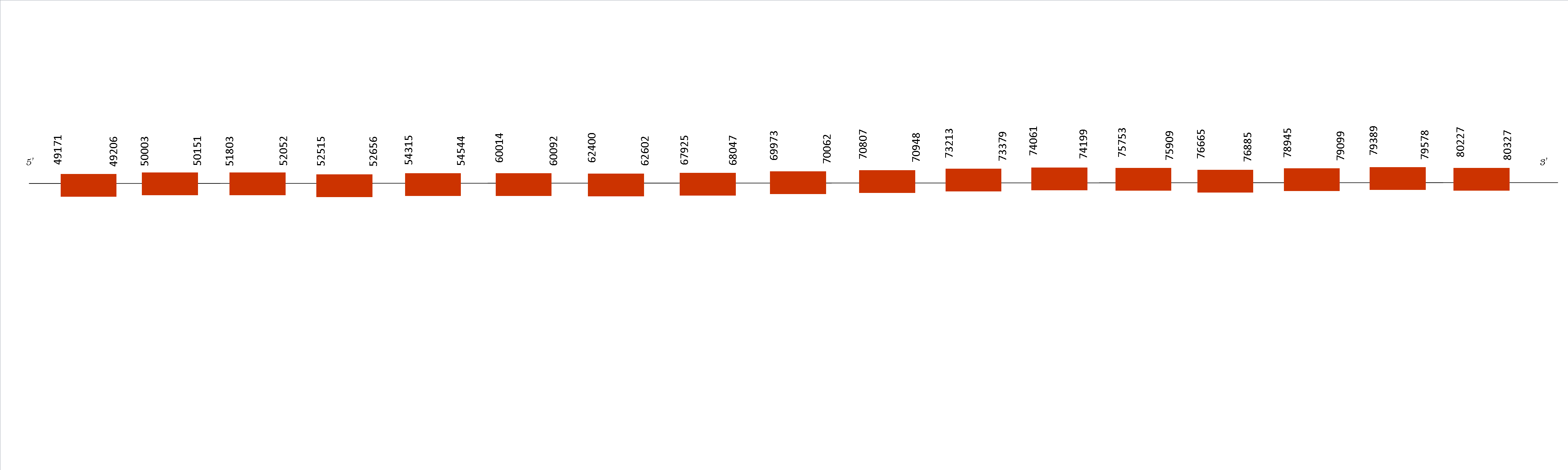
Selenophosphate synthetase 1 (SPS1)
T-coffee alignment against Mus musculus presented a perfect alignment, with a score of 1000, and the protein starts with a Methionine in the two species.
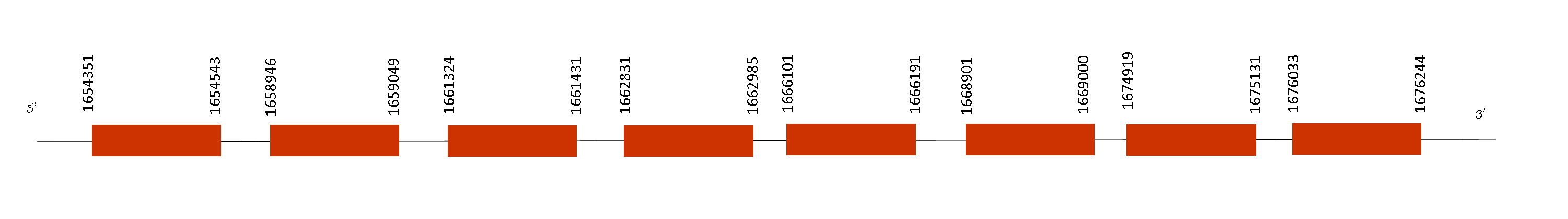
This protein contains 8 exons located in the positions 1654351-1654543, 1658946-1659049, 1661324-1661431, 1662831-1662985, 1666101-1666191, 1668901-1669000, 1674919-1675131, 1676033-1676244 on the positive strand. Seblastian could not predict any selenoprotein in the sequence. However, SPS1 presented 21 predicted SECIS elements located too far away from the protein predicted or on the strand (negative), being impossible that they were forming part of a selenoprotein.
Moreover, it belongs to the machinery proteins family and synthesizes selenophosphate from selenide and ATP. This protein showed also a perfect alignment, which means that it is conserved on Mus spicilegus genome because its importance.
Selenophosphate synthetase 2 (SPS2)
The alignment made by T-coffee had a 996 alignment meaning it is a good alignment between the two mice species. The protein predicted starts with a methionine. It has just one selenocysteine conserved in position with mus musculus.
This protein just has one exon located in the positions 49952 to 5130 on the positive strand. A single SECIS structure was found and it conserved the selenocysteine in the same position as Mus musculus. This SECIS was located at 51812-51888 on the positive strand. Exonerate predicted one exon located between the position 49952 and 51301. This structure is on the 3’UTR because is located downstream from the last position of the exon 51301, forming part of the selenoprotein found.
This protein forms part of the selenoprotein machinery and it synthesizes selenophosphate from selenide and ATP. SEPHS2 or Selenophosphate Synthetase 2 (SPS2) is a protein coding gene. Among its related pathways are metabolism and folate metabolism. As we know folates are imprescindible for the organism and thus we expect this protein to be present in Mus spicilegus as it is also present in Mus musculus.