DISCUSSION
In this project, Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome has been compared with a total of 42 Homo sapiens proteins, from which 27 have been characterized as selenoproteins. From the total of the proteins analysed, 8 proteins were machinery enzymes involved in the selenocysteine synthesis.
Homo sapiens selenoproteome was chosen because of the phylogenetic proximity with Neophocaena asiaeorientalis, due to the fact that both species are mammals. In addition, the selenoproteome of Homo sapiens is well characterized and annotated and therefore it appeared to be a good model to compare with.
Homo sapiens selenoproteome was obtained from SelenoDB 1.0 database, which is a reliable database that presents manually corrected human selenoproteins. Nevertheless, some machinery proteins, specifically Sec2, SEPHS1, PSTK and SECp43, were not characterized in SelenoDB 1.0 so, in this cases we used SelenoDB2 database. SelenoDB2 provides a larger number of annotated selenoproteins but these are not manually corrected, supplying a less reliable information.
We compared the results of the selenoproteins predicted in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis with Seblastian using the fastasubseq sequence obtained from our program. Seblastian’s prediction was not accurate and a considerable number of selenoproteins present in Homo sapiens could not be predicted in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis. For this reason, and with the aim to find selenoproteins which could not be predicted before, we studied Tursiops truncatus selenoproteosome, as this specie is phylogenetically closer to Neophocaena asiaeorientalis.
The results obtained when we studied Tursiops truncatus were discouraging because no more selenoproteins could be predicted. Besides, some SECIS predicted comparing with Homo sapiens were not found, as for example, in the case of SelT where we predicted 2 SECIS comparing with Homo sapiens while we only found 1 SECIS comparing with Tursiops truncatus. Moreover, a larger number of proteins such as SelI were not starting with a Methionine, oppositely to what we reported in Homo sapiens. Therefore, we hypothesise that the selenoproteosome in Tursiops truncatus was not well annotated.
For this reason, below we will discuss the proteins predicted only with the homology analysis considering Homo sapiens. In order to ensure that selenoproteins predicted with our program but not with Seblastian were in fact good predictions, we also performed a SECISsearch3 analysis. With this program we confirmed that SECIS elements were in the same strand where the protein was predicted. That was the case of GPx4 and GPX6, among others.
We also runned Genewise in order to validate the exonerate results. The t-coffee obtained with the genewise showed the same results as the tcoffee obtained from the exonerate output.
Another tool which was used is Phylogeny.fr. The phylogenetic tree confirmed that the proteins predicted are phylogenetically close to the ones in Homo sapiens and therefore our predictions are validated. Only PSTK and SelO presented a distant homology. A possible explanation could be the appearance of mutations. However, we can reject this considering the results of the alignment obtained in each case, which has been of a high quality. Therefore, we could think that experimental errors have occurred in the process of providing the fastatranslate to the Phylogeny.fr.
A brief introduction for each protein function will be provided along with their characteristics in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis.
Our group considered several factors in order to make the predictions of the selenoproteome in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis. The first essential requirement for a selenoprotein is the possession of a Selenocysteine residue (Sec) in its active site. Another important factor is the presence of SECIS elements, which have been previously explained to be a conserved stem-loop structure necessary for the recognition of the UGA codon as a Sec rather than a stop codon. SECIS elements are found in the 3’-UTR region of the same RNA strand.
Moreover, we considered that functional selenoproteins had to present the Methionine amino acid at the first position of the predicted protein in order to begin the translation.
Nevertheless, a wide number of the selenoproteins predicted and machinery proteins were lacking a Methionine in the first position of the prediction. This fact could be pointed as a bad annotation but since the alignment with human proteins using t-coffee presents a high score, we can conclude that our predicted proteins are not completed in the 5’UTR region. Another but less likely hypothesis could be that the protein predicted in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis is not a functional protein and therefore it will not be translated.
Finally, we have also taken into account the fact that predicted proteins were not found colocalizing in the same scaffold position in Neophocaena asiaeorientalis. Even so, in 4 proteins which were SPS2, GPx5, TR2 and TR3, when we chose the best hits we found a colocalization with different scaffolds obtained from other proteins. Then, we chose the second best hit in order to predict a new protein with no colocalization. The results were not better than before. For example, in the case of GPx5, the score of the t-coffee was lower and considering SPS2 protein, the Sec found in the t-coffee, although the score was high, was not aligned with the human protein Sec. Therefore, although the colocalization, we have decided to analyse the first hits obtained in each case.
SELENOPROTEINS AND CYSTEINE-CONTAINING HOMOLOGUES GPxs family
GPxs (Glutathione peroxidase) is a family of enzymes that has an important role in the antioxidant defense due to its relation to glutathione molecule (GSH). Glutathione peroxidase molecules (GPxs) react with GSH and catalyze the reduction of peroxide radicals to alcohols and oxygen.[15] GPxs also present tissue-specific functions and are able to reduce H2O2 and hydroperoxides from free fatty acids. In mammals, there are 8 GPx paralogs from which GPx1-GPx4 and GPx6 contain a Sec residue in the active site while GPx5, GPX7 and GPx8 have this Sec replaced by Cys. [16]
GPx1FunctionGPx1 was the first selenoprotein identified due to the presence of a Sec residue in the active site. It constitutes an homotetramer which reduces hydrogen peroxide but also some other hydroperoxides from free fatty acids when it reacts with GSH. As it has been reported in several articles [17], when GSH is not active GPx1 can react with γ-glutamylcysteine. GPx1 has been labeled as one important enzyme in the oxidative stress body defense and its mutation may result in severe acute oxidative stress.[18][19] It is mainly found in the cytoplasm, mitochondria and in some cells inside peroxisomes. [20]
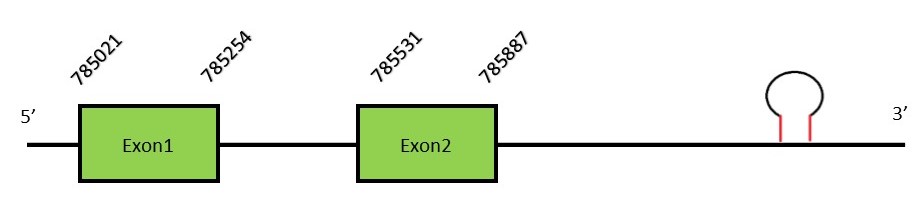
Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 996) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with a Met. We conclude that selenoprotein GPx1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686378.1, between positions 785042 and 785884, in the forward strand (+).
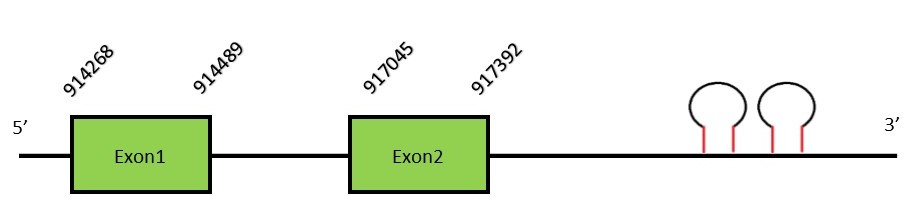
This protein contains 2 exons: GPx2FunctionGPx2 is a selenoprotein with a single Sec residue which is mainly expressed in gastrointestinal epithelial cells. Some authors have reported GPx2 to have an essential protective role in gastrointestinal tumors development, regarding that selenium deficiency and chronic inflammation are risk factors for colon cancer.[21] Moreover, GPx2 have been also related with mucosal homeostasis.[22] Protein predictionThe alignment with human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also 2 SECIS elements are predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein GPx2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687437.1, between positions 914268 and 917392, in the forward strand (+).
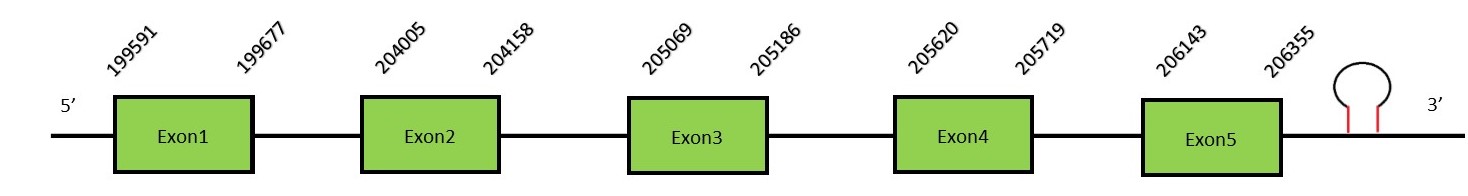
This protein contains 2 exons: GPx3FunctionGPx3 is a selenoprotein and represents the only member of the glutathione peroxidase family expressed in the extracellular compartment, specifically in plasma, where it can bind and reduce complex lipids.[15] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 998) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein GPx3 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686489.1, between positions 205068 and 206355, in the forward strand (+)
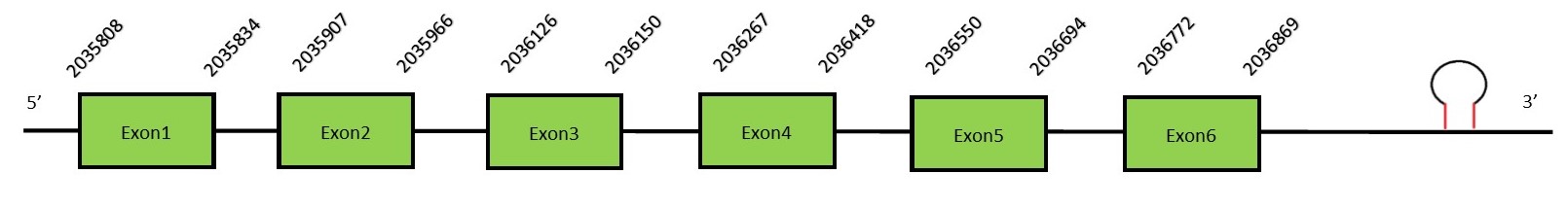
This protein contains 5 exons: GPx4FunctionGPx4, also known as phospholipid hydroperoxide GPx (PHGPx), is a selenoprotein with a particular domain, different from the other glutathione peroxidases, which allows the reaction with hydroperoxides found in complex lipids. While other GPx family members are mainly soluble in water, GPX4 can work in membranes due to its lipophilic nature.[22][23] It is ubiquitously expressed, being the highest expression located in spermatids (but not spermatozoa, which possess an inactive form of GPX4)[24]. Therefore, GPx4 has been pointed as an important enzyme in male fertility and sperm maturation.[15] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 999) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query. Seblastian predicts 2 SECIS elements, but in SECISearch3 we see that both SECIS are in different strands, so we only take into account the SECIS that is in the 3’-UTR region of the reverse strand. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region, but as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein GPx4 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686867.1, between positions 2035805 and 2036866, in the reverse strand (-).
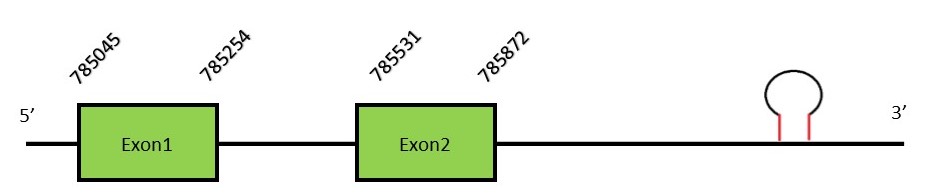
This protein contains 6 exons: GPx5FunctionGPx5 presents a similar expression with GPx4, being mainly expressed in the male reproductive tract. Distinctively, GPX5 can not be considered a selenocysteine due to the replacement of the selenocysteine residue for a cysteine along evolution in humans. It has been hypothesized that the selenocysteine was present in the common ancestors of Neophocaena asiaeorientalis and Homo sapiens. Therefore, GPx5 is a cysteine-containing homologe.[25] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 990). As we said before, the protein in the human genome has a cysteine and we found that in the same position our genome has a selenocysteine. These results prove that the common ancestor had a selenocysteine and then along the human lineage there was replacement into a cysteine. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein GPx5 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686378.1, between positions 785045 and 785872, in the forward strand (+).
This protein contains 2 exons: GPx6FunctionGPx6 is a selenoprotein mainly expressed in the olfactory epithelium and during embryonic development.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 919) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query and we find a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein GPx6 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688217.1, between positions 519458 and 494951, in the forward strand (+).
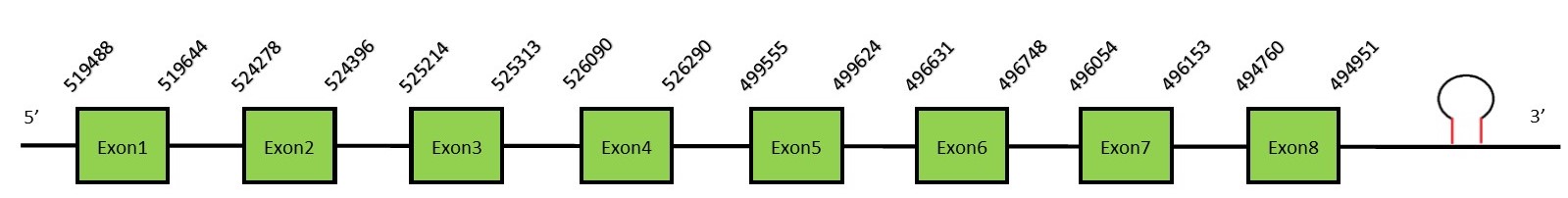
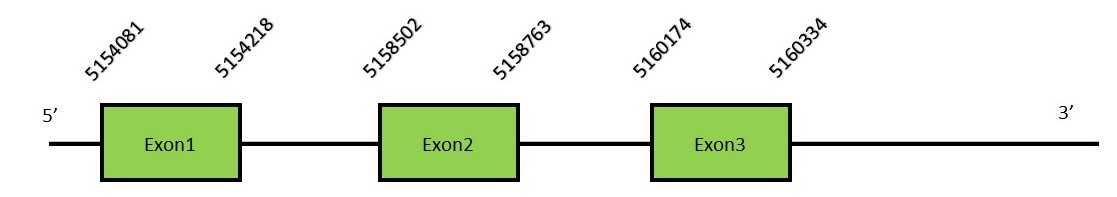
This protein contains 8 exons: GPx7FunctionGPx7 is not a selenoprotein because the selenocysteine residue has been replaced by a cysteine. GPx7 protects esophageal epithelia from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress. It suppresses acidic bile acid-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protects against oxidative DNA damage and double-strand breaks.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 999). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they have a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS element or selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that GPx7 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ686824.1, between positions 5154138 and 5160331, in the forward strand (+).
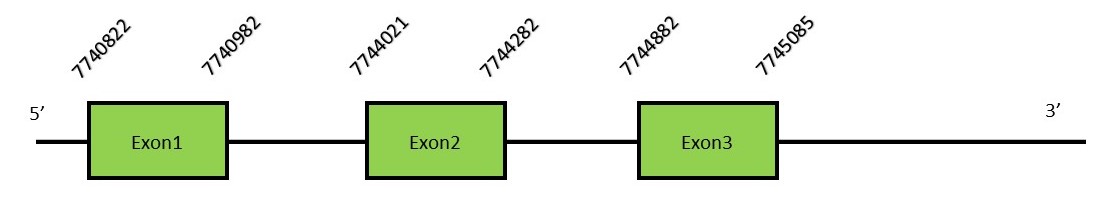
This protein contains 3 exons: GPx8FunctionGPx8 is similar to GPx7 and it is also considered a cysteine-containing homologe since it is lacking the Selenocysteine residue.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they had a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS element or selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that GPx8 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688285.1, between positions 7740822 and 7745085, in the reverse strand (-).
This protein contains 3 exons:
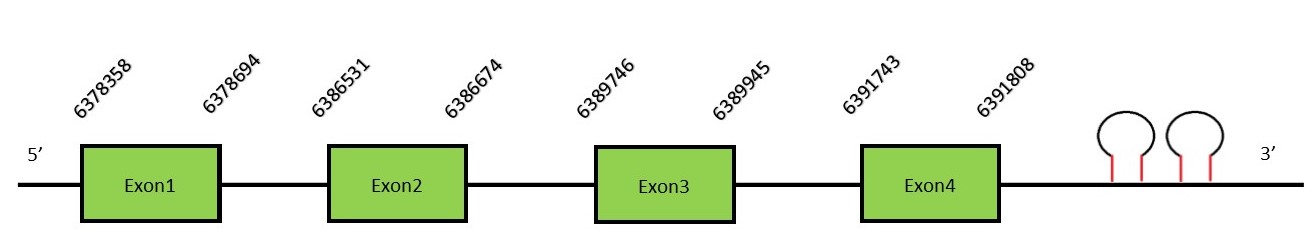
Iodothyronine deiodinase familyThe thyroid hormone deiodinases are a family of selenoproteins constituted by 3 paralogous proteins in mammals: DI1, DI2 and DI3. Homologous of mammalian deiodinases can be also found in some simple eukaryotes and bacteria. All three deiodinases contain a transmembrane domain and form a homodimer structure. Also, in all of them, the active-site contains a Sec residue, which is located in the amino-terminal part of the protein. DI1FunctionDI1 is located on the plasma membrane and converts the inactive form of the thyroid hormone (T4) into the active form (T3) by outer ring deiodination.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also 2 SECIS elements are predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein DI1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686824.1, between positions 6378358 and 6391808, in the forward strand (+)
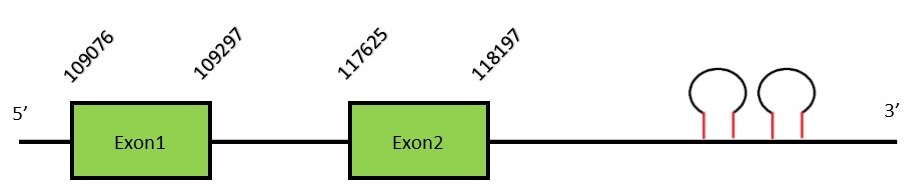
This protein contains 4 exons: DI2FunctionDI2 is found in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Apart from the active-site Sec found in the three deiodinases, DI2 can contain an additional Sec, the function of which is still unknown and is present in the carboxy-terminal domain. The additional UGA codon can function either as a Sec or a stop codon, which can result in two isoforms with one or two Sec residues (this secondary Sec is not essential). DI2 have the same function of DI1.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find 2 SECIS elements in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, therefore we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein DI2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686724.1, between positions 109076 and 118197, in the forward strand (+).
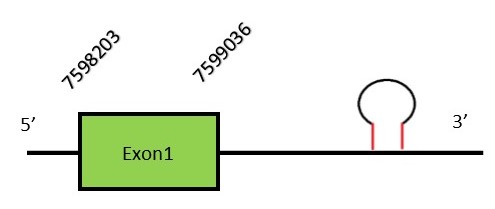
This protein contains 2 exons: DI3FunctionSimilarly to DI1, DI3 is located in the plasma reticulum. Unlike the two previous deiodinases, DI3 is able to remove the inner iodine ring resulting in the inactivation of T3 And T4.[16] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine aligned in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, therefore we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein DI3 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686590.1, between positions 7598239 and 7599036, in the forward strand (+).
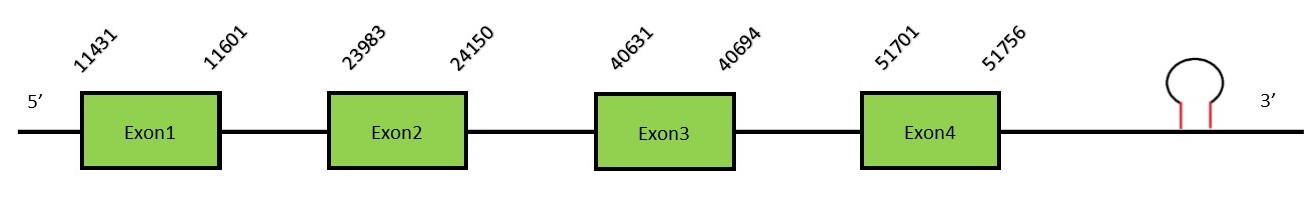
This protein contains 1 exon: Sel15FunctionSelenoprotein 15 is a thioredoxin-like selenoprotein which is located in the endoplasmic reticulum. This protein is involved in the glycoproteins folding through its interaction with UDP-glucose (glycoprotein glucosyltransferase), concretely targeting unfolded glycoproteins. This protein is a selenoprotein only found in eukaryotes and is also related with the redox homeostasis.[26] In mammals, Sep15 expression is related to dietary Selenium intake. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 962) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, for these reasons we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein Sel15 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688413.1, between positions 11431 and 51756, in the forward strand (+).
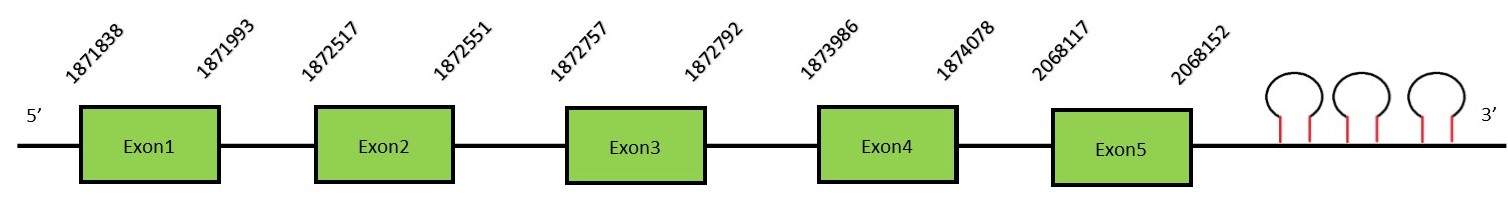
This protein contains 4 exons: SelMFunctionSelM is an ortholog of the Sel15 protein. This selenoprotein is located in the perinuclear region and highly expressed in the brain, suggesting a possible involvement in neurodegenerative disorders.[27] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 971) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also 3 SECIS elements are predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelM is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688414.1, between positions 1871838 and 1874036, in the reverse strand (-).
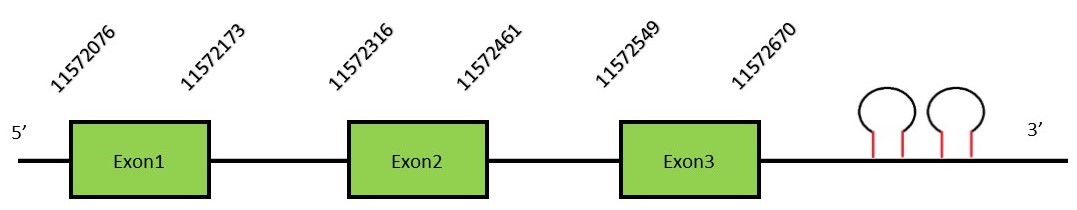
This protein contains 5 exons: SelHFunctionSelH is a selenoprotein oxidoreductase found in the nucleus and its function is not totally understood. Some authors have related SelH deficiency with impairments in the redox balance.[28] In addition, SelH deficiency also promotes inflammatory response and the P53 pathway activation. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find 2 SECIS elements in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, therefore we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelH is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687389.1, between positions 11572076 and 11572598, in the reverse strand (-).
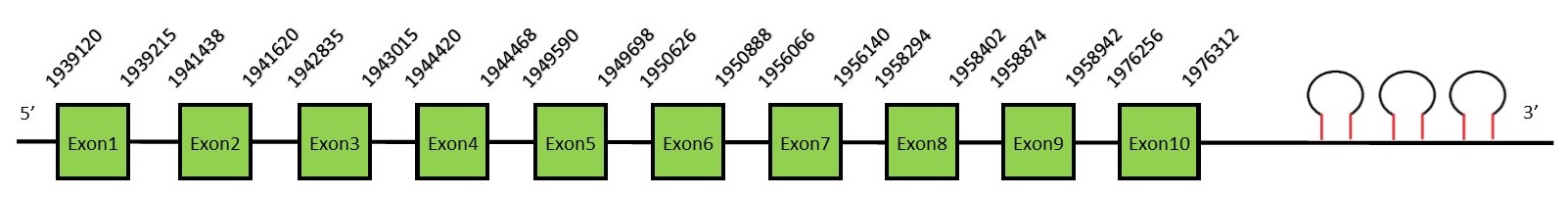
This protein contains 3 exons: SelIFunctionSelenoprotein I belongs to the CDP-alcohol phosphatidyltransferase class I family. This protein is involved in the phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis (which is important in the regulation of lipid metabolism), in the formation and the maintenance of vesicular membranes and in protein folding. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene.[29] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also 3 SECIS elements are predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelI is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688256.1, between positions 1939120 and 1976312, in the reverse strand (-).
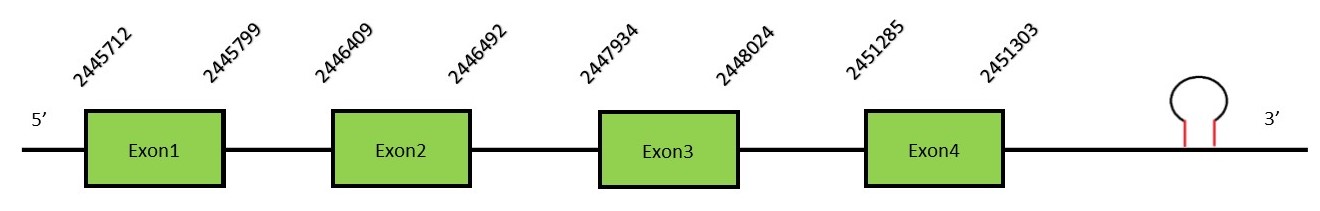
This protein contains 10 exons: SelKFunctionSelK is a selenoprotein localized in the plasma membrane. This protein plays an important role in T-cell proliferation, migration and also in neutrophil migration. It has been also reported its function in soluble glycosylated protein degradation and in the protection of cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis.[30] SelK has a protective effect from oxidative stress.[31] Furthermore, it can act as a cofactor in catalyzing protein palmitoylation reactions. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelK is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687235.1, between positions 2446417 and 2451285, in the reverse strand (-).
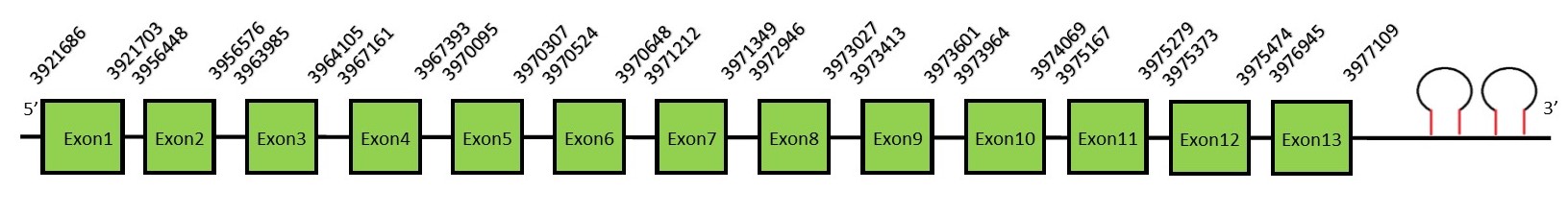
This protein contains 4 exons: SelNFunctionSelN is a selenoprotein located in the ER. Similarly to other selenoproteins, it protects the cell against oxidative stress, but it also has an important role in the regulation of redox reactions involved in calcium homeostasis.[32] In addition, it has been reported that mutations in this gene are related with an early onset of muscle disorders.[32] A second stop-codon redefinition element (SRE), adjacent to the UGA codon, has been identified in this gene. SRE is a phylogenetically conserved stem-loop structure that stimulates readthrough at the UGA codon, and augments the Sec insertion efficiency by SECIS. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 987). The human query has 2 selenocysteines. In the N. asiaeorientalis genome we also find two, but only the second one is aligned in the same position as the second selenocysteine of the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query and we find 2 SECIS elements in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelN is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688383.1, between positions 3921686 and 3977109, in the forward strand (+).
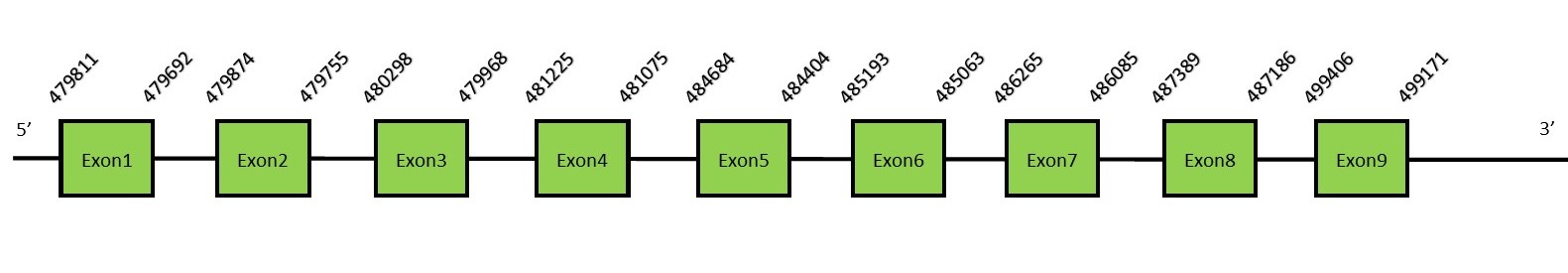
This protein contains 13 exons: SelOFunctionThis selenoprotein is mainly found in the mitochondria. Selenium dietary intake affects SelO expression. This protein is the largest selenoprotein containing a selenocysteine residue. SelO presents orthologs in a wide range of organisms, including bacteria and yeast.[33] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 983) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query and we find a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelO is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686720.1, between positions 479701 and 499361, in the reverse strand (-).
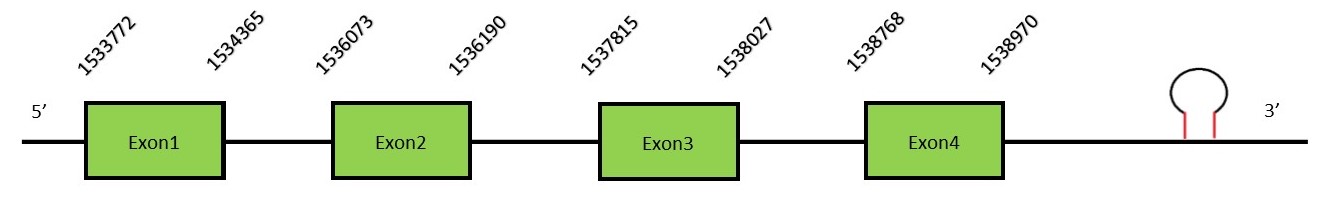
This protein contains 9 exons: SelPFunctionSelenoprotein P is a liver-derived secretory protein. It is associated with insulin resistance in humans. This selenoprotein is unique because it contains different Selenocysteine residues per polypeptide, containing 10 Sec in human. SelP is the major contributor to selenium levels in plasma. This protein has an important role as an extracellular antioxidant but also in the transport of selenium to different tissues from the liver.[34] The mRNA of the human SelP contains two SECIS elements. The use of alternative polyadenylation sites, one located in between the two SECIS, results in two different populations of mRNA containing both SECIS or just the upstream SECIS element. There are different spliced transcript variants.[35] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 971). The human query has 10 selenocysteines and in the N. asiaeorientalis sequence we find 14, most of them aligned in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelP is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686890.1, between positions 1533823 and 1538970, in the reverse strand (-).
This protein contains 4 exons:
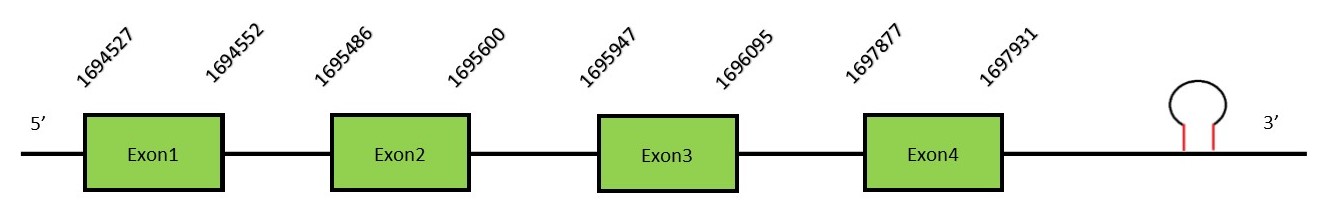
MsrB familyThe proteins found in this family repair enzymes which protect proteins from oxidative stress due to the reduction of methionine-R-sulfoxide to methionines.ROS can oxidize methionine (Met) residues in proteins to form methionine sulphoxide leading to an impairment in protein function. [36] These proteins play an important role in recovering protein functionality and protect against oxidative stress. SelR1 (MsrB1)FunctionSelR1 belongs to the methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase B family. This protein is mainly expressed in the kidney and liver, specifically in the nucleus and the cytosol. MsrB1 is the only protein in the MsrB family which is considered a Selenoprotein, as it contains a Sec residue in the active site compared to the other proteins of the family.[37] Homologous of SelR are found in all organisms except specific parasites or hyperthermophiles.[38] SelR1 exhibited the highest methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase activity due to the presence of the selenocysteine (Sec) in the active site. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelR1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687977.1, between positions 1695603 and 1697931, in the reverse strand (-).
This protein contains 4 exons: SelR2 (MsrB2)FunctionSelR2 is a mitochondrial enzyme which is suspected to have an important role in the preservation of mitochondrial integrity by decreasing ROS and protecting mitochondrial proteins. SelR2 is mainly expressed in heart, kidney and the skeletal muscle.[39] This protein is lacking a Sec residue and therefore is not a selenoprotein.[40] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 997). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they have a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it does predict a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that SelR2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ686645.1, between positions 3712242 and 3724509, in the reverse strand (-).
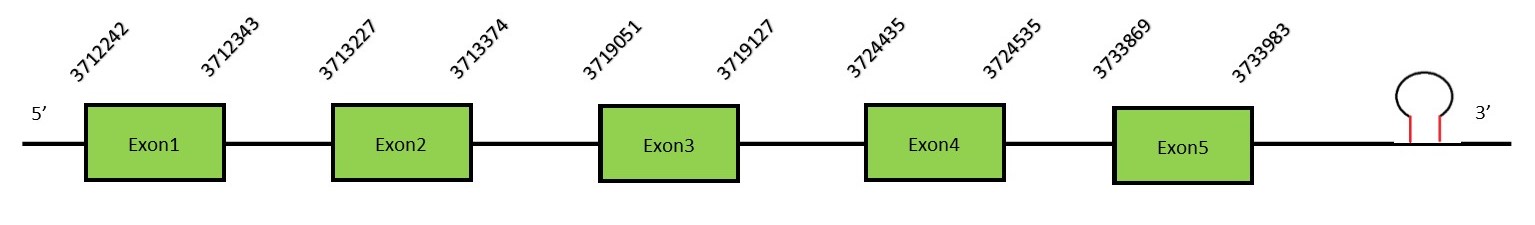
This protein contains 5 exons: SelR3 (MsrB3)FunctionThe human MsrB3 gives rise to 2 protein isoforms, MsrB3A and MsrB3B, located in different places of the cell. The first one is located in the mitochondria while the other is located in the ER. These 2 proteins are generated by alternative splicing.[41] This enzyme acts as a monomer and requires Zn as a cofactor.[42] This protein is lacking a Sec residue and therefore is not a selenoprotein. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 990). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they have a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS element or selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SelR3 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688667.1, between positions 16747508 and 16853237, in the reverse strand (-).
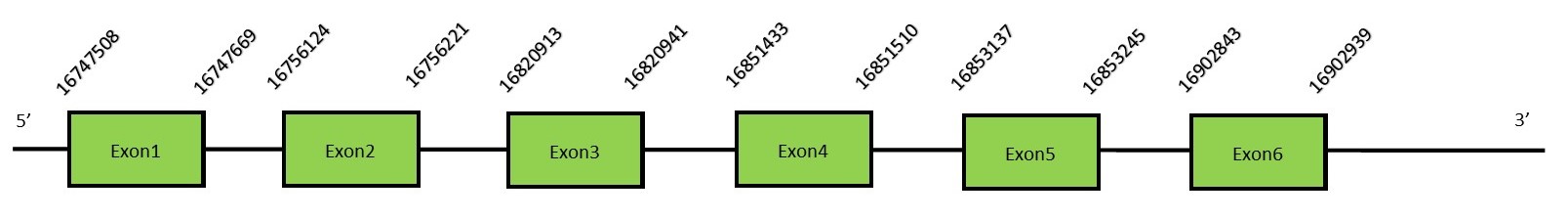
This protein contains 6 exons: MsrAFunctionIn several genomes, SelR and MsrA genes are clustered due to their shared function in the protection against oxidative stress. In mammals, MsrA is coded by one gene regulated by two distinct promoters.[43] Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA) is mainly expressed in kidney and nervous tissue. This protein reduces methionine sulfoxide to methionine and its main function is the repair of oxidatively reduced proteins to restore their biological activity. It does not present the Sec residue and therefore it is not a selenoprotein.[44] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 998). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they have a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it does predict 3 SECIS in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that MsrA is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ687250.1, between positions 784276 and 1157523, in the reverse strand (-).
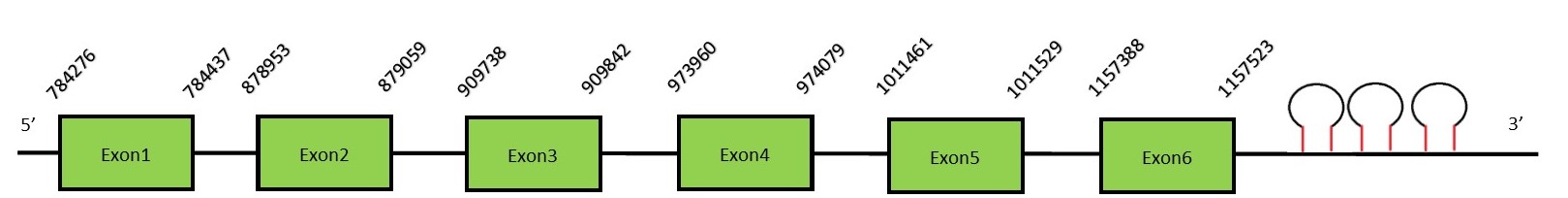
This protein contains 6 exons: SelSFunctionSelenoprotein S, also known as SEPS1, is located in the plasma membrane and ER membrane. It controls ER derived stress and prevents cytotoxicity and apoptosis in macrophages. The expression of this protein is induced by glucose deprivation and ER stress.[45] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 996) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region. 2 SECIS elements are also predicted but only one of them is in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelS is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688257.1, between positions 169717 and 177377, in the forward strand (+).
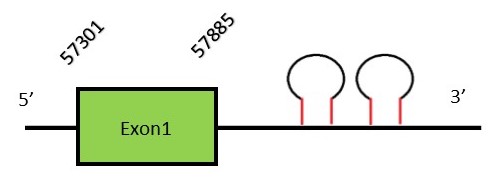
This protein contains 6 exons: SelTFunctionSelenoprotein T is a thioredoxin-like protein with a very high expression during development, which is mostly reduced to endocrine tissues during adulthood. The function of this protein is not well known. Sel T has been identified as a novel subunit in the protein complex oligosaccharyltransferase (OST) which is essential for the ER membrane homeostasis.[46] This protein possess a thioredoxin-like fold and a conserved CxxU motif, being the C a cysteine and the U a selenocysteine. Sel T has been reported in mice as a protection factor in Parkinson disease.[47] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 993) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region. Although, as we see a selenocysteine in the same position as the human query and we find 2 SECIS elements in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, we conclude that N. asiaeorientalis has this selenoprotein. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelT is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687677.1, between positions 57301 and 57885, in the forward strand (+).
This protein contains 1 exon:
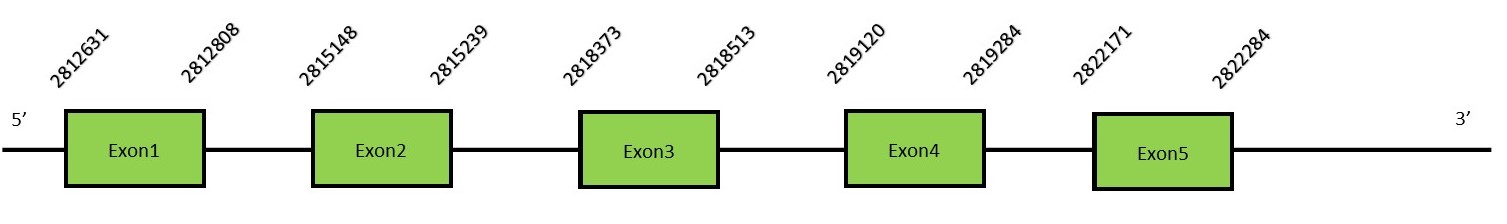
SelU familySelenoprotein U has a restricted phylogenetic distribution, such as chicken and fish. Most of the vertebrate families, such as mammals, have cysteine-containing homologues.[48] It functions as a redox regulatory protein and it has a role in autophagic cell death mechanisms.[49] There are three SelU proteins: SelU1, SelU2 and SelU3 and they are not classified as selenoproteins since they are lacking the Sec residue. SelU1Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 996). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they had a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS element or selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SelU1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ686884.1, between positions 2812631 and 2822284, in the forward strand (+).
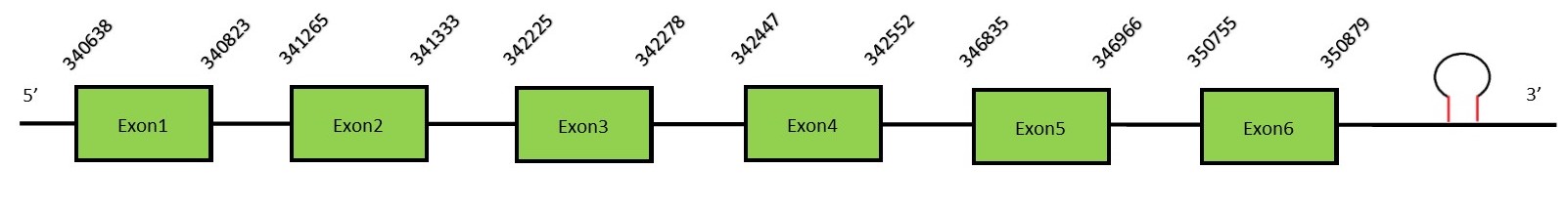
This protein contains 5 exons: SelU2Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 996). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they had a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it predicts a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that SelU2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688101.1, between positions 340620 and 350879, in the forward strand (+).
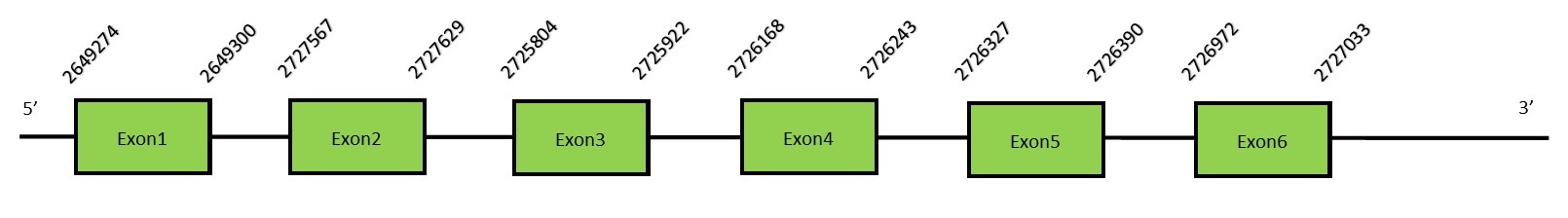
This protein contains 6 exons: SelU3Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 986). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, the human query has a cysteine, but in the same position our genome has a gap so we cannot know if it has the same cysteine. Seblastian does not predict any SECIS element or selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with a Met. We conclude that SelU3 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688031.1, between positions 2725804 and 2727629, in the reverse strand (-).
This protein contains 6 exons: SelVFunctionThis protein is mainly expressed in the testis but it’s function is still unclear. SelV possesses a thiredoxin-like fold and a conserved CxxU motif and has a redox function. It is likely that SelV is a new protein formed by the duplication of SelW. Some authors report that SelV is the least conserved mammalian selenoprotein. In some mammals, such as gorilla, SelV protein has been deleted. [50]) Protein predictionWe couldn't predict this protein (the tblastn couldn't make any alignment). As we have mentioned before, this is the least conserved mammalian selenoprotein and has suffered deletions in some species, so we came with the conclusion that our specie doesn’t have this protein in its genome. It can also be due to experimental errors.
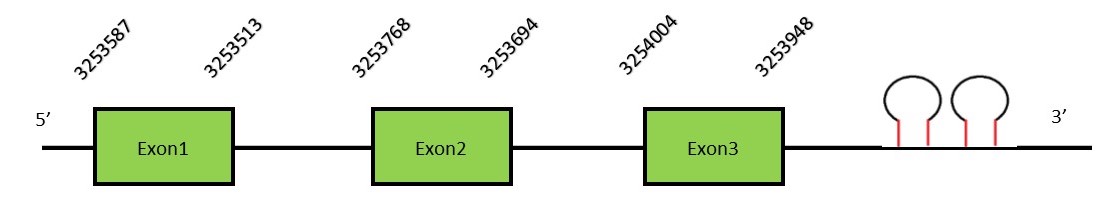
SelW familySelenoprotein W has a thioredoxine-like fold and a conserved CxxU domain. This protein is mainly expressed in skeletal and heart muscle and in the brain, because it participates in muscle growth and differentiation. It is involved in the protection of neurons from oxidative stress during neuronal development.[51] There are two SelW: SelW1 and SelW2. SelW1Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 999). The human query has one selenocysteine but in the same position in the N. asiaeorientalis genome there’s a gap, so we can’t know if our species has a selenocysteine. Although we don’t know if it has a Sec residue, Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also 2 SECIS elements are predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand, so we conclude that our genome contains this protein. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SelW1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688431.1, between positions 3253694 and 3253768, in the reverse strand (-).
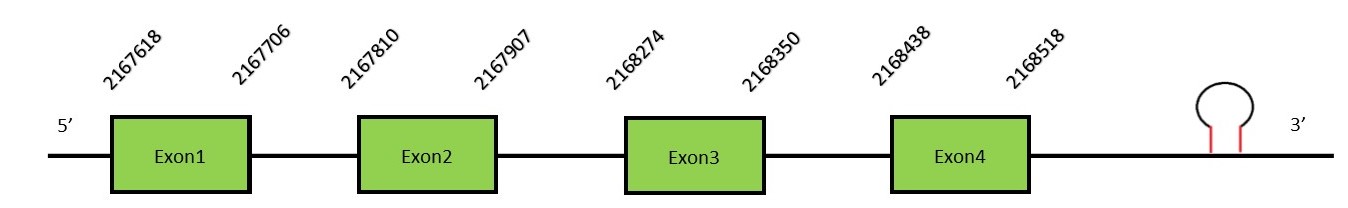
This protein contains 3 exons: SelW2Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Instead, they had a cysteine aligned in the same position. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it predicts a SECIS element in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SelW2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ686466.1, between positions 2167618 and 2168518, in the forward strand (+).
This protein contains 4 exons:
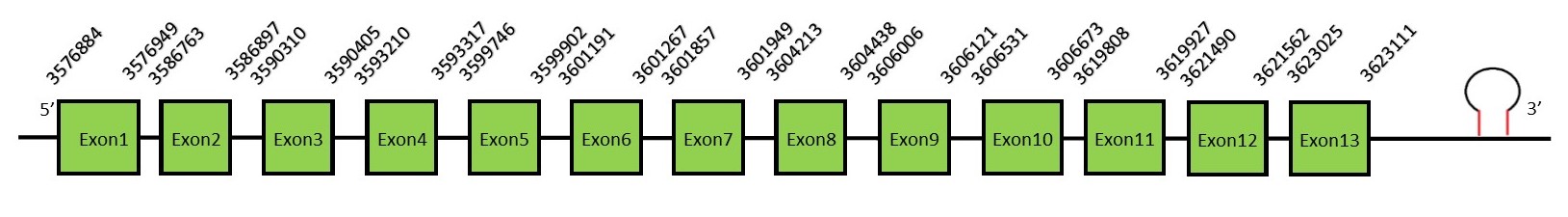
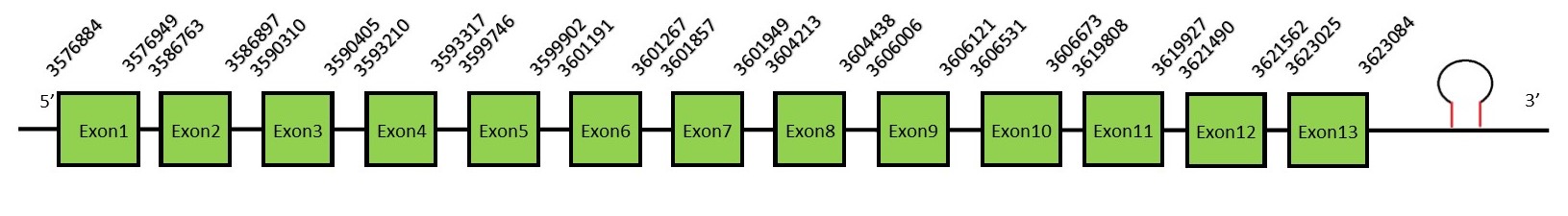
TR familyThe thioredoxin reductase (TR) family in mammals has TR isoforms: TR1, TR2 and TR3 (also called Thioredoxin Glutathione Reductase). TR are flavoenzymes that transfer the reducing equivalents from NADPH to thioredoxin. The broad specificity of TR is due to a C-terminal -Cys-Se-Cys- redoxactive site. This reaction is important for a large number of biochemical reactions, from the reduction of ribonucleotides to the detoxification of oxidants. It has been suggested that these enzymes play a key role in several pathophysiological conditions such as apoptosis, cancer, chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and neurodegenerative disorders.[52] TR1FunctionThioredoxin reductase 1 (or TR1) is a cytoplasmatic protein which function is the reduction and activation of thioredoxin. Thioredoxine reduces cysteine residues on cellular proteins. This is important for effective DNA binding of redox-sensitive transcription factor (such as p53 and NF-κB). Besides, a reduced thioredoxine binds ROS before they can damage the cell, having a major role in the cellular redox homeostasis and protecting the cells against oxidative stress.[53] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein TR1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688579.1, between positions 3576884 and 3623111, in the reverse strand (-).
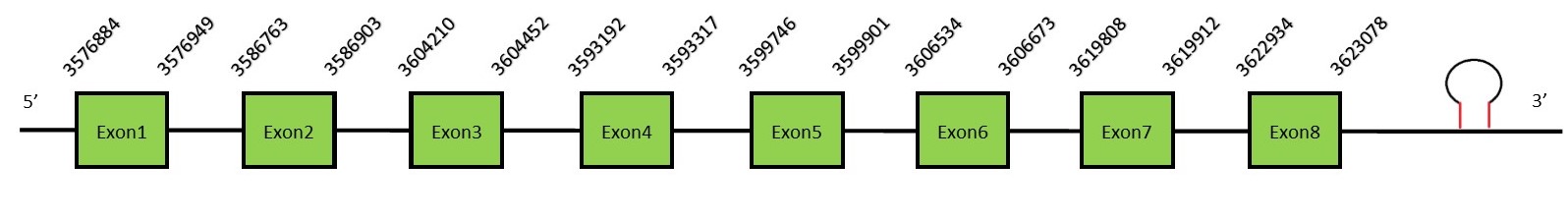
This protein contains 13 exons: TR2FunctionThioredoxin reductase 2 (or TR2) is a mitochondrial protein important for scavenging ROS.[54] It helps to maintain and regulate the mitochondrial redox homeostasis by keeping the thioredoxin in a reduced state. It also may play a main role in redox-regulated cell signaling.[55] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 978) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein TR2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688177.1, between positions 6256779 and 6283812, in the reverse strand (-).
This protein contains 8 exons: TR3FunctionThioredoxin reductase 3 (or TR3) is expressed in specialized tissues, such as testis. This TR protein contains a N-terminal glutaredoxin domain that allows this protein to participate in thioredoxin and glutathione systems.[56] It is thought that TR3 may play a role in sperm maturation by promoting formation of sperm structural components.[57] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 999) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein TR3 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ688166.1, between positions 2969431 and 2997701, in the reverse strand (-).
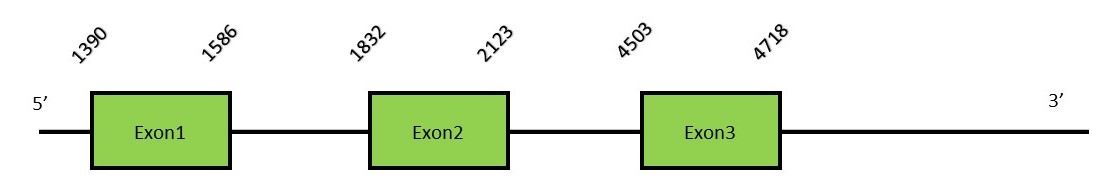
This protein contains 13 exons: MACHINERY PROTEINS PSTKFunctionPSTK performs a crucial step in selenocysteine biosynthesis. It catalyzes the transference of a phosphate group (g-phosphate) from an ATP molecule to the Ser-tRNASec, yielding SeptRNASec and ADP. This will allow afterwards the substitution of the phosphate by the Selenium element.[58] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS nor selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that PSTK is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ687414.1, between positions 1390 and 4718, in the reverse strand (-).
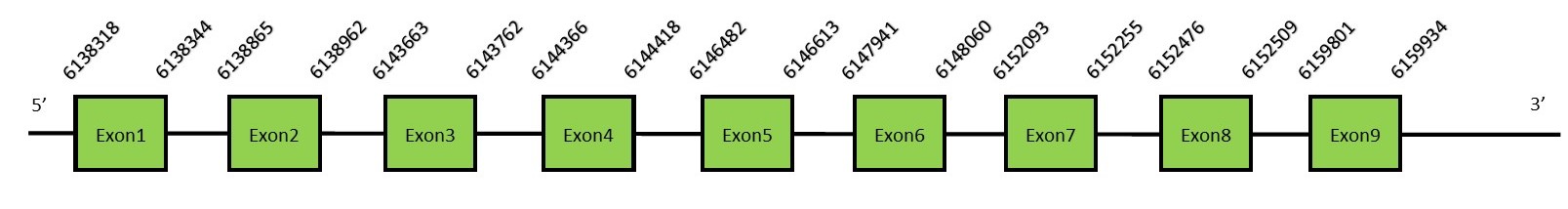
This protein contains 3 exons: SECp43FunctionThis subgroup corresponds to the RRM1 of SECp43, an RNA-binding protein associated specifically with eukaryotic selenocysteine tRNA [tRNA(Sec)]. It plays an adaptor role in coordination with other proteins to approach the ribosome with the Sec-tRNASec, in order to add the selenocysteine to the protein sequence. SECp43 is located mainly in the nucleus and comprises two N-terminal RNA recognition motifs (RRMs), also known as RBDs (RNA binding domains) or RNPs (ribonucleoprotein domains), and a C-terminal polar/acidic region.[59] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS nor selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SECp43 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688383.1, between positions 6138844 and 6159934, in the forward strand (+).
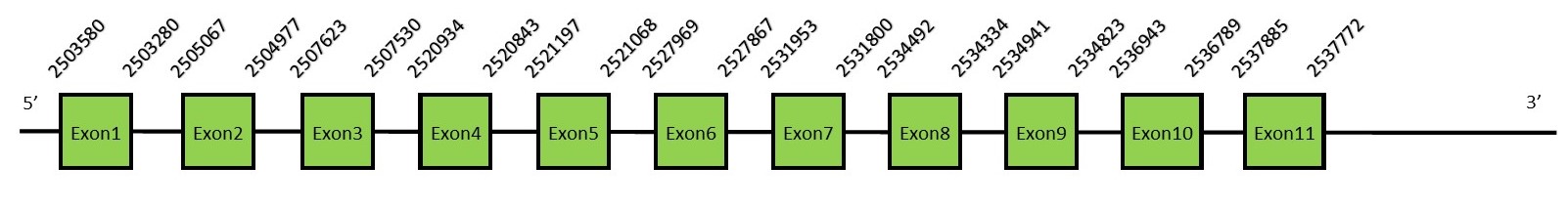
This protein contains 9 exons: SecSFunctionIn Eukaryotes and Archaea, selenocysteine synthase (SecS) converts O-phospho-L-seryl-tRNA [Ser]Sec into selenocysteyl-tRNA [Ser]Sec using selenophosphate as the selenium donor compound. The molecular mechanisms underlying SecS activity are still unknown.[60][61] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 999). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS nor selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SecS is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ687172.1, between positions 2503280 and 2537885, in the reverse strand (-).
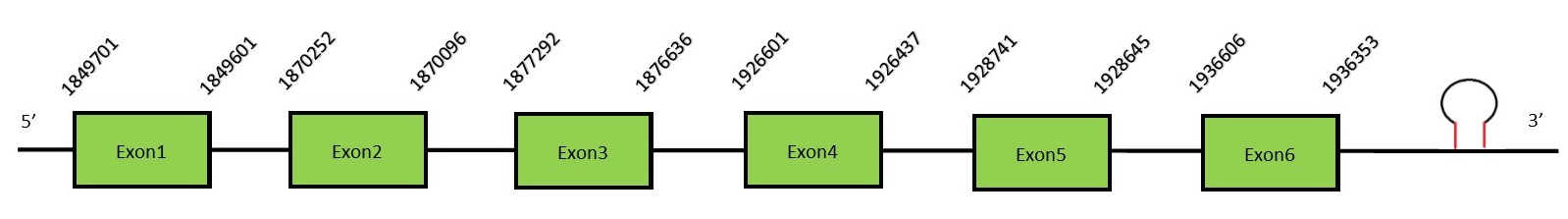
This protein contains 11 exons: eEFSecFunctionSelB in prokaryotes and eEFSec in eukaryotes constitutes an elongation factor, which function consists on the delivery of Sec-tRNASec into the ribosome with the objective of adding the selenocysteine into the protein sequence. It evolved to bind only Sec-tRNASec and no other aa-tRNA.[62] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 996). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it predicts a SECIS in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that eEFSec is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688166.1, between positions 1849532 and 1936606, in the reverse strand (-).
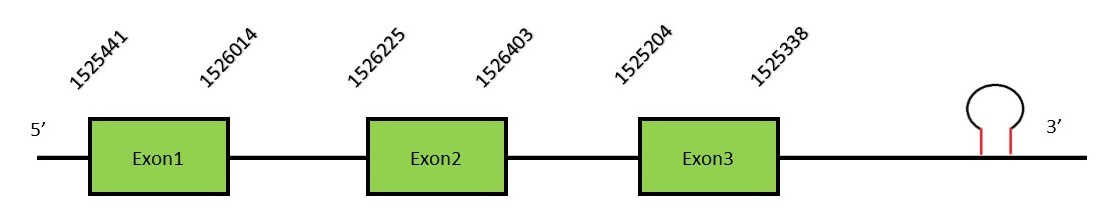
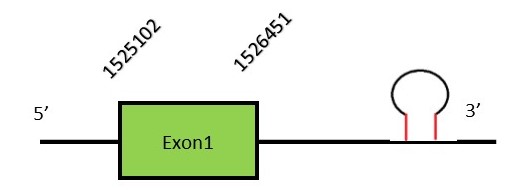
This protein contains 6 exons: SEPHS1FunctionSelenophosphate synthetase 1 or SEPHS1 is an enzyme located in the nucleus and plasma membrane that synthesizes selenophosphate using selenide and ATP. The resultant selenophosphate will act as the selenium donor in selenocysteine.[63][64][65] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 994). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. Surprisingly, we do find a selenocysteine in the N. asiaeorientalis genome. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted does not start with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SEPHS1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ687148.1, between positions 1525204 and 1526403, in the forward strand (+).
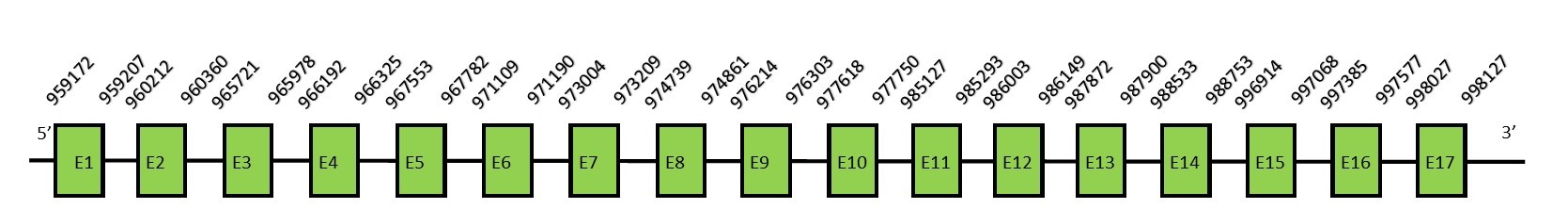
This protein contains 3 exons: SBP2FunctionThere are two key trans-acting factors; the translation elongation factor eEFSec, that binds specifically to Sec-tRNASec, and the SECIS-binding protein 2 (SBP2), that interacts with the SECIS element.[66] SBP2 plays a central role in selenoprotein synthesis because it recruits the eEFSec•Sec-tRNASec•GTP complex. Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 994). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any SECIS nor selenoprotein in this region. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SBP2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ688550.1, between positions 960209 and 997588, in the forward strand (+).
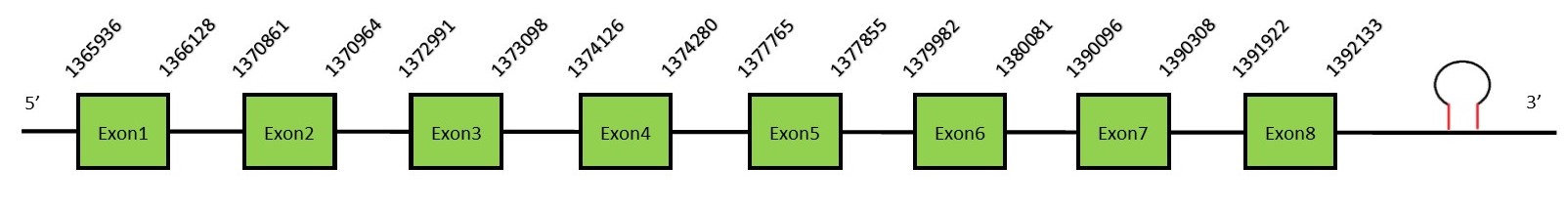
This protein contains 17 exons: SPS1FunctionSPS1 participates, along with other proteins, in the process of generating the intermediate molecules from selenide with the objective of obtaining Selenophosphate. This Selenophosphate will provide the selenium to the Selenocysteine. ATP + selenide + H2O = AMP + selenophosphate + phosphate. It can be found in the nucleus and also in the plasma membrane.[67] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 1000). Neither the human query nor the N. asiaeorientalis sequence have a selenocysteine in their sequence, since this protein is not a selenoprotein. For the same reason, Seblastian does not predict any selenoprotein in this region (but it does predict a SECIS in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand). The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that SPS1 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome, although it is not a selenoprotein. It is located in the scaffold KZ686361.1, between positions 1370782 and 1392133, in the forward strand (+).
This protein contains 8 exons: SPS2FunctionSPS2, similar to SPS1, generates Selenophosphate (H2SePO3−) from selenite and ATP. Selenophosphate will act later as a donor of active Se for SecS in selenocysteine synthesis.[68] Protein predictionThe alignment with the human sequence is accurate (tcoffee score alignment = 998) and we find a selenocysteine in the same position as in the human query. Seblastian predicts a selenoprotein in this region and also a SECIS element is predicted in the 3’-UTR region of the same strand. The sequence predicted starts with Met. We conclude that the selenoprotein SPS2 is present in the Neophocaena asiaeorientalis genome. It is located in the scaffold KZ686361.1, between positions 1365930 and 1392109, in the forward strand (+).
This protein contains 1 exon: |