DISCUSSION
The aim of this project was to determine all selenoproteins and machinery genes present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. In order to determine these proteins, Zebrafish genome was used to identify homologous proteins because it is the most studied and characterized fish genome. All the results obtained for every protein were analysed and discussed individually, paying special attention to the T-coffee outputs and SECIS predictions using firstly SEBLASTIAN and secondly SECISearch3.
As commented through the introduction, bonny fishes present duplicated segments as a result of a whole-genome duplication event termed Ts3R. Moreover, Salmonids such as Oncorhynchus mykiss underwent an additional and recent whole-genome duplication termed Ss4R. For this reason, it is expected to find some duplicated selenoproteins in our results.
The queries from Zebrafish have been obtained from SelenoDB. Even though we expected the Zebrafish selenoproteome to be precisely annotaded, a high amount of the proteic sequences do not start with a methionine. For this cases, we can only conclude that the our predictions are just a part of the protein. Interestingly, for some of the cases, we have been able to retrieve the starting part of the protein in output obtained through SEBLASTIAN.
Finally, in order to confirm that the predicted selenocysteines are indeed selenocysteins and not STOP codons we translated the fastaseq output from the GFF file using the ExPASy website and checking that the position is encoded by a UGA (TGA) codon.
The following section presents the analysis of every protein results along with the predicted protein image and the phylogenetic tree created using phylogeny:fr.
Selenoproteins
Iodothyronine deiodinases (DIO)
There are 3 different DIO subfamilies that contain selenocysteine residues in the N-terminal region: DIO1, DIO2 and DIO3. All of them are involved in deiodination of the thyroid hormone, which regulates its activity.
DIO1
For DIO1 multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SP0000039.1) showed significant hits, being contig CM007939.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes. The gene predicted is located between 51081302-51082379 position in the forward chain and it contains 1077 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image.
A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 51083615-51083683. Hence, DIO3 is reported to be a selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by one gene with 3 exons.
DIO2
Again, for DIO2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000614_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case, two different contigs were selected for further study being: CM007953.1 and CM007959.1 since the T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment. Three different proteins have been predicted predicted, two from contig CM007953.1 and another from CM007959.1. Therefore, DIO2 is found to be triplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as DIO2_1) is located between 22517013-22521454 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 4441 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons as described in the image.
A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure, but since it is located at 5' end of the sequence, it is dismissed.
The second copy (named as DIO2_2) is located between positions 53671818-53672525 in the forward chain and it contains 707 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by only 1 exon as described in the image.
A conserved selenocysteine is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 53672920- 53672993. Moreover, the protein predicted does not start with a methionine while the SEBLASTIAN alignment shows the initial methionine.
The third copy (named as DIO2_3) is located between positions 76409543-76414065 in the forward chain and it contains 4522 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image.
A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 76415982-76416066. The protein predicted starts with a methionine.
The results obtained were unexpected. Due to the whole-genome duplication event Ss4R only two copies of this gene were expected to arise. The gene present in Danio rerio contains 3 different exons, therefore, only the third gene copy reported in Oncorhynchus mykiss encodes for all the exons.
DIO3a
Two different scaffolds with significant hits appeared in this protein blast. The alignment results of the contig CM007938.1 from scaffold SPP00000612_2.0 and contig CM007942.1 from the scaffold SPP00000662_2.0 were the most promising due to their high score, no or less than 3 gaps and a small number of amino acid changes in the t-coffee.
Therefore, DIO3a is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as DIO3a_1) is located between 73208279 -73209058 position in the reverse chain and it contains 707 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 1 exon as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN hasn't been able to predict any SECIS, but SECISsearch3 has predicted two SECIS at the the 3' end, both of them of grade B in positions 73196018-73162045 and 73161129-73161060.
The second copy (named as DIO3a_2) is located between 73208279 -73209058 position in the forward chain and it contains 773 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 1 exon as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 73210187- 73210268. The protein predicted does not start with a methionine while the SEBLASTIAN alignment shows the initial methionine.
Hence, DIO3a is reported to be a duplicated selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by a two different genes with one exon, same number as the Zebrafish DIO3a.
DIO3b
Due to the absence of significant hits comparing the studied genome and Zebrafish respective sequence, DIO3b could not be found in the Oncorhynchus mykiss.
As explained in the introduction, DIO3b is a protein found in all bony fishes as a product of their whole-genome duplication, therefore its absence in Oncorhynchus mykiss is unexpected. This might be the result of the loss of this protein in the studied genome, or an error in the genome annotation.
Finally, in order to check whether the predicted DIO proteins are similar to theirs homologues in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results:
According to the phylogenetic tree, the prediction of DIO1 in the contig CM007939.1 is similar to the Zebrafish DIO1 and the Human DIO1, being more proximal to the zebrafish DIO1. The predictions of the duplicated genes DIO2_1 and DIO2_2 in the contigs CM007953.1 and CM007959.1 are proximal to the Zebrafish DIO2 and the Human DIO2. The predictions of DIO3a_1 and DIO3a_2 in contigs CM007938.1 and CM007942.1 are also close to its query DIO3a in Zebrafish, being more further apart from the Zebrafish DIO3b. Therefore, we can consider that these proteins have been correctly assigned to their contigs.
Regarding DIO1, we have found it in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome with a Sec residue and a SECIS in 3' of grade A. The protein predicted does not start with methionine. On the other hand, SEBLASTIAN predicts 4 exons for this selenoprotein and the alignment includes the starting methionine. So, even though we have predicted a shorter form DIO1, we can conclude that Oncorhynchus mykiss has part of DIO1 in its genome.
Concerning DIO2_1, DIO2_2 and DIO2_3, all have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome with a Sec residue and a SECIS in the 3'. DIO2_1 and DIO2_2 contain 2 and 1 exons, respectively, while DIO2_3 contains 3 exons. As the reference Zebrafish DIO2 protein is encoded in 3 exons we can hypothesize that for DIO2_1 and DIO2_2 we only have predicted a part of the protein. As these two genes are duplicates we believe that the absence of found exons is a sign of gene fractionation (process of gene loss from one homeologous genomic region or its partner region).
About DIO3a_1 and DIO3a_2, they have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome, both of them with a Sec residue and a SECIS structure in 3'. DIO3a_1 and DIO3a_2 contain 1 exon, similarly to the DIO3a protein found in Zebrafish. Therefore, we can conclude that DIO3a is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
Regarding DIO3b, even though it is present in all bony fishes reported, it has not been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
GPx proteins are found in the three domains of life, being the largest family in vertebrates.The members of this family are involved in detoxification of hydroperoxides, in the maintenance of cellular redox homeostasis and in the hydrogen peroxide signaling
GPx1a
For GPx1a multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000621_2.0) showed significant hits, being contigs CM007941.1 and CM007951.1 the one selected since T-coffee output shows a very high score, small number of amino acid changes and no gaps. It is worth pointing out the alignment of GPx1a_2 which shows an excellent alignment just with the query's center. Four proteins are predicted, two of them in CM007941.1 and two in CM007951.1. Therefore, GPx1a is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as GPx1a_1) is located between 52376226-52377295 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 1069 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS structure is predicted, in position 52375951 - 52375878 at the 3' end position of the gene.
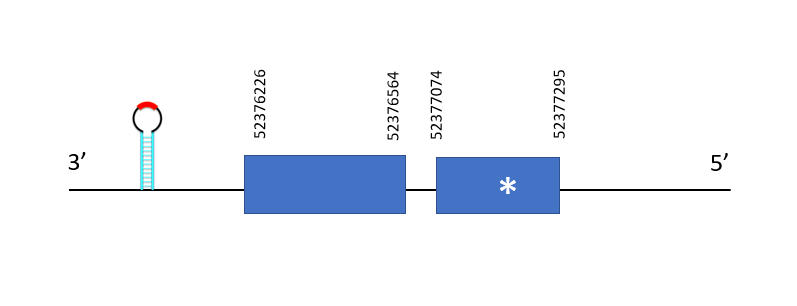
The second copy (GPx1a_2) is located between positions 33364037-33364311 in the forward chain containing 274 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine, in the first exon . Two different SECIS structure are in positions 33412195-33412114 (negative strand) and 33383704-33383770 (positive strand). Both SECIS were discarded due to the big distance between the gene and the SECIS.
The results obtained were the expected ones. Due to the whole-genome duplication event Ss4R two copies of this gene were expected to arise.
GPx1b
Again, for GPx 1b multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000624_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case, CM007951.1 was selected for further study the contig since T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment. Two different proteins are predicted. Therefore, GPx1b is found to be duplicated as GPx1a in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as GPx1b_1) is located between 45465011-45465967 positions in the positive chain and it contains 956 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons as described in the image, with a conserved selenocysteine detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end 51224 - 51297.
The second copy (named as GPx1b_2) is located between positions 64697418-64698282 in the reverse chain and it contains 864 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine in the first exon is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end, in position 64697154- 64697083
The results obtained were the expected ones. Due to the whole-genome duplication event Ss4R two copies of this gene were expected to arise.
GPx2
Different hits appeared in the same scaffold (SPP00000616_2.0). The most significant alignments were found on the contig CM007953.1 and contig CM007959.1. were the most promising due to their high score. Due to the poor aligment obtained at the T-coffee, the one placed at the CM007959.1 was eliminated. Therefore, GPx2 is not duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss. One possibility is the duplication of GPx2, with the copy placed at CM007959.1 that probably has suffered a gene fractionation.
The predicted GPx2 is located between 40384751-40384605 position in the reverse chain and it contains 146 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exon as described in the image with a conserved selenocysteine placed in the first exon and aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS were predicted at the the 3' end, in positions 40384645-40338517.
Hence, GPx2 is reported to be encoded by two different exons, the same number than in Zebrafish.
GPx3a
For GPx3a multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000617_2.0) showed significant hits, being contigs CM007959.1 and CM007948.1 the selected ones due to their E-values and their t-coffee alignments. Therefore, GPx3a is duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (GPx3a_1) is located between 2497231-2490027 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 7204 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image, with a conserved selenocysteine detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end 2489266 - 2489188.
The second copy (named as GPx3a_2) is located between positions 75455324-75459118 in the positive chain and it contains 3794 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine in the second exon is detected aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A total number of 5 SECIS structures were predicted in different genomic positions. 3 of them were placed at the positive strand, at positions 75463417-75463495, 75456285-75456363 and 75408833-75408912 while 2 of them were placed at the negative strand (75490539-75490477 and 75477328-75477253). The one placed at positions 75463417-75463495 is the most suitable SECIS at the 3'UTR region.
GPx3b
For GPx 3b multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000623_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case, one contigs was selected for further study being CM007935.1 since T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
GPx3b is located between 82402030-82408677 positions in the positive chain and it contains 6647 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image, with a conserved selenocysteine detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS is predicted in the 3' UTR at positions 82408937-82409026
Interestingly, we found out that this protein suffered a tandem duplication, copy which lost the last fourth exon, presenting only 3 putative exons.
GPx4a
As in other cases, mulltiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000618_2.0 showed significant hits, being the CM007935.1 selected for further analysis because of the good alignment observed in T-coffee. Oncorhynchus mykiss's GPx4a is located between the positions 17140748-17141135 in the reverse chain, comprising 387 bases. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons, as described in the image, with the selenocysteine placed at the first one. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' UTR in position 17135903 - 17135827
GPx4b
For GPx 4b multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000622_2.0 showed significant hits., selecting for further study CM007939.1 and CM007942.1 since T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Therefore, GPx1b is found to be tetraplicated as GPx1a in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (GPx4b_1) is located between 57547228 - 57552243 in the reverse chain, containing 5015 bases. The exonarate structure is composed by 4 exons with the selenocysteine placed at the second one. Two SECIS were predicted at positions 38843 - 57536071-57535995 and 57514798-57514708, both discarded accord to the distance between them and the gene.
The other copy (GPx4b_2) is located between 71362515-71363325 in the positive chain, comprising 810 bases. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons, while SEBLASTIAN predicted 7 of them (with the selenocysteine placed at the third one). One SECIS was predicted at 7166665-7166742 3' UTR.
GPx7
For GPx 7 multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000620_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case, one contig was selected for further study being CM007939 since T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
GPx7 is located between 78659661-78668304 positions in the positive chain and it contains 8643 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons, lacking any selenocysteine. It presents one SECIS structure at positions 78635176-78635247, discarded for being too far from the gene.
GPx8
Again, for GPx8 multiple contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000620_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case, selecting for further study the contig CM007945.1 and CM007940.1 since T-coffee output showed high score, no gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment. Two different proteins are predicted. Therefore, GPx8 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as GPx8_1) is located between 75815261-75816465 positions in the positive chain and it contains 1204 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end 75816485- 75816558.
The second copy (named as GPx8_2) is located between positions 3794680-3795388 in the reverse chain and it contains 708 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons. A SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end, in position 3794416-3794345.
In zebrafish 9 differents GPx proteins have been described: GPx1a, GPx1b, GPx2, GPx3a, GPx3b, GPx4a, GPx4b, GPx7 and GPx8. Despite this, GPx5 and GPx6 are absent.
As se we said in the Introduction, we expected a large number of GPx proteins due to the whole genome duplication Ssr4. In fact, we predicted 13 proteins in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Then, in order to correctly discuss our results, we decided to perform a phylogenetic tree using phylogeny.fr. For this purpose, human, zebrafish and Oncorhynchus mykiss proteins were selected for the phylogenetic analysis and to observe the distances between them.
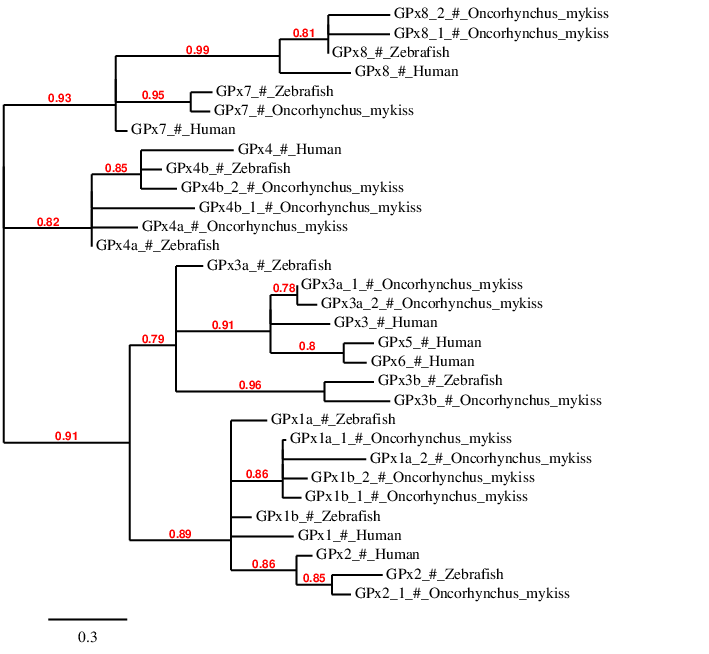
First of all, we can observe how GPx5 and GPx6 are grouped between them, with any similar protein in zebrafish or Oncorhynchus mykiss. Both of them also show a paralogy relationship with human GPx3. These facts coincide with Marotti et al.[10]: GPx6 and GPx5 appeared from a GPx3 duplication in placental mammals. Therefore, they are not present in zebrafish nor Oncorhynchus mykiss.
According with the phylogenetic tree, we can see the paralogy relationship between GPx7 and GPx8 in the three different species. In both proteins, we observe a closer relationship between zebrafish and Oncorhynchus mykiss than with human. We can also observe how GPx8 is duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss while GPx7 lost one of its copies in the salmonid.
Regarding GPx4 family (including GPx4a and GPx4b) we can observe how our predictions grouped together with zebrafish and human sequences. In this case we can see the paralogy between GPx4a and GPx4b (and human GPx4). Moreover, human GPx4 grouped together with zebrafish GPx4b and both GPx4b copies of Oncorhynchus mykiss . Despite this, GPx4b_1 is not grouped so closely to the three porteins said before, probably due to a lose or change of function in Oncorhynchus mykiss. In this case, as happened with GPx7, we can observe the loss of GPx4a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
GPx3 proteins are grouped together between them and the Oncorhynchus mykiss's predictions. Regarding Oncorhynchus mykiss, GPX3a is duplicated while GPx3b lost one of the duplicatied copies. As said by Mariotti et al. GPx3a and GPx3b were generated by a duplication of GPx3 suffered by bony fishes. In this case, GPx3a (GPx3a_1 and GPx3a_2) are closer to human GPx3 than GPx3b, probably due to a function share. In the other hand, Oncorhynchus mykiss GPx3b is closely related to zebrafish's GPx3b.
Finally, we can see a relationship between GPx1 and GPx2 are present and grouped together in the three analysed species. Regarding GPx2, the proteins of the three species are clearly grouped together, apart from GPx1. Moreover, it is observed the deletion of one of the duplicated copies in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
Methionine-R-Sulfoxide Reductase (MSRB family)
The MsrB family is comprised by three different enzymes: MsrB1, MsrB2 and MsrB3.
MSRB1 o Selenoprotein R is a zinc-containing enzyme present in all vertebrates which functions as a Methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase, which allows the repair of oxidized methionine residues in proteins. MSRB2 and MSRB3 are Cys-containing homologs which maintain their catalytic efficiency.
MSRB1a
Three different contigs, all of them from the same scaffold SPP00000645_2.0, have shown significant hits in the protein blast. The hits from the contig MSJN01012408.1 have been rejected due to the absence of Sec residues and small amount of nucleotides comprised (86 nt). The alignment results of the contig MSJN01022804.1 and contig CM007947.1 were the most promising due to their high score, no gaps and almost almost a perfectly conserved alignment.
Accordingly, MSRB1a is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (named as MSRB1a_1)is located between 27257-34948 position in the forward chain and it contains 7691 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted one SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 31265 - 31341.
The second copy (named as MSRB1a_2) is located between 51148340-51160998 position in the forward chain and it contains 12658 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 51152912-51152988. The protein predicted starts with a methionine.
Hence, MSRB1a is reported to be a duplicated selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by a two different genes with 3 exons, same number as the Zebrafish MSRB1a reference protein.
MSRB1b
For MSRB1b multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000644_2.0, showed significant hits, being contig CM007954.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score and no gaps. The gene predicted is located between 20339667- 20340437 position in the reverse chain and it contains 770 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons, same number as the reference gene sequence, as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS at the 3' end, in position 20339389-20339313.
Hence, MSRB1b is reported to be a selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 3 exons, same number as the Zebrafish MSRB1b.
MSRB2
For MSRB2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000646_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007945.1 and CM007949.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, MSRB2 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (MSRB2 _1) is located between 14399111-14400755 position in the reverse chain and it contains 1644 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. No SECIS have been identified neither using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3. Furthermore, the protein predicted does not start with a methionine.
The second copy (MSRB2 _2) is located between 10195145-10197063 position in the forward chain and it contains 1918 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons. A selenocysteine has been detected in the fourth exon, but after checking using the translate tool from ExPASy the position appeared to be coded by a UAG codon, therefore it was rejected a selenocystein. The protein predicted starts with a methionine. Lastly, no SECIS have been identified neither using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3.
Therefore, MSRB2 is reported to be a duplicated protein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by two genes genes with 4 and 5 exons, respectively. Similarly to the MSRB2 gene in Zebrafish, MSRB2 _1 and MSRB2 _1 do not present a selenocysteine in their sequence.
MSRB3
Again, for MSRB3 a group of contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000647_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs MSJN01034164.1 and MSJN01119661.1 the ones selected.
Hence, MSRB3 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (MSRB3 _1) is located between 131841-115871 position in the reverse chain and it contains 15970 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. No SECIS have been identified neither by using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3. Lastly, the protein predicted does not start with a methionine.
The second copy (MSRB3 _2) is located between 1123-23569 position in the reverse chain and it contains 22446 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. No SECIS have been identified neither by using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3. The protein predicted starts with a methionine.
Therefore, similarly to MSRB2, MSRB3 is reported to be a duplicated protein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by two genes genes with 3 and 6 exons, respectively. Similarly to the MSRB3 gene in Zebrafish, none of them present selenocysteines in their sequence. This is consistent with the available information about MSRB3 and MSRB2, which indicates that these proteins are homologs with cysteine, as previously explained in the introduction. Even though, as not all the cisteines appearing in both sequences are aligned, we can not confirm that MSRB3 _1 and MSRB3 _2 are Cys-containing homologs.
Finally, in order to check whether the predicted MSRB proteins are similar to theirs homologues in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results:
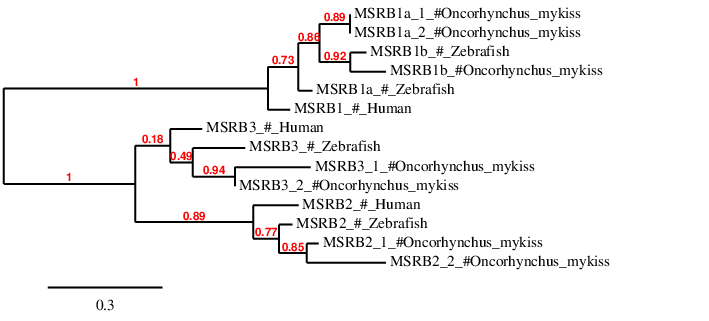
According to the phylogenetic tree, the prediction of MSRB1b is similar to the Zebrafish MSRB1b. The prediction of the duplicated genes MSRB1a_1 and MSRB1a_2 appear to be similar altogether and proximal to both Zebrafish MSRB1b and MSRB1a. Moreover, all this group appears to be close to the Human MSRB1. Surpisingly Zebrafish MSRB1b appears to be closer to MSRB1a_1 and MSRB1a_2 from Oncorhynchus mykiss than Zebrafish MSRB1a. Both MSRB1b and MSRB1a appeared due to the whole genome duplication from MSRB1, therefore this could explain the proximal relation of these two.
The prediction of MSRB2_1 and MSRB2_2 is closer to the Zebrafish MSRB3a, confirming the current hypothesize of them being a duplication of MSRB3a. Same results can be observed for MSRB3a_1 and MSRB3a_2. For all this, we can consider that these proteins have been correctly assigned to their contigs.
Regarding MSRB1a_1 and MSRB1a_2 , we have found both of them in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome with a Sec residue and a SECIS in 3' of grade A. Moreover, both of them contain Methionine as the first aminoacid.
Concerning MSRB1b, it has been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome with a Sec residue and a SECIS in the 3'. Besides, the protein predicted starts with a methionine.
About MSRB2_1 and MSRB2_2, they have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. None of them contain Sec residues or predicted SECIS.
Similarly, MSRB3_1 and MSRB3_2 also have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. Neither of them contain Sec nor SECIS. This is consistent with the fact that MSRB2 and MSRB3 are non-selenocysteine containing homologs from MSRB1.
Sel15
For Sel15 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000632_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007942.1 and CM007962.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, Sel15 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (Sel15_1) is located between 48110374-48087557 position in the reverse chain and it contains 22817 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image. One selenocysteine has been detected in the third exon. Our prediction showed to be shorter than the one from SEBLASTIAN, which had one more exon in the N-terminal domain. Additionally, the SEBLASTIAN prediction contained the initial methionine, which was missing in the zebrafish protein and our prediction. Despite that, we can conclude that Sel15_1 is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. Finaly, SEBLASTAIN has predicted a SECIS has been predicted between the positions 48087164 - 48087090, 3' to the gene.
The second copy (Sel15_2) is located between 31074651-31083743 position in the forward chain and it contains 9092 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image. One selenocysteine has been detected in the third exon. Our prediction showed to be shorter than the one from Seblastian, which had one more exon in the N-terminal domain. Additionally, the SEBLASTIAN prediction contained the initial methionine, which was missing in the zebrafish protein and our prediction Despite that, we can conclude that Sel15_2 is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
Therefore, Sel15 is reported to be a duplicated selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by two different genes with 4 exons, the same number as Danio rerio's Sel15.
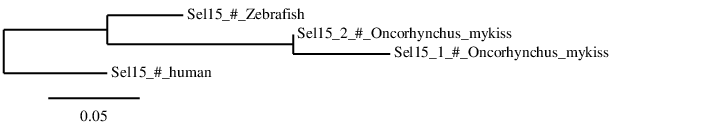
According to the phylogenetic tree we can see that Sel15 from Homo sapiens, Danio rerio and Oncorhynchus mykiss form part of the same family and that the human Sel15 if the farthest of them all. Moreover, Danio rerio and Oncorhynchus mykiss's Sel15 come from the same ancestor and that afterwards the second whole-genome duplication that Oncorhynchus mykiss suffered, the duplicated Sel15 has not been yet eliminated.
MrsA
MsrA can catalyze the reduction of free methionine residues or methionines present in the protein sequence. In some organisms such as unicellular eukaryotes and anaerobic bacterium, MsrA has a Sec residue while in vertebrates the residue is a Cys.
MrsA_1
For this protein multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000625_2.0 showed significant hits, but after analyzing the t-coffee alignment only one contig, CM007942.1 was selected.
Therefore, MrsA_1 is found to be in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
MrsA_1 is located between 45713062-45751630 position in the reverse chain and it contains 38568 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. SEBLASTIAN has not been able to predict any SECIS. Even though, 3 SECIS have been detected using SECISearch. Only one of them is present in the reverse chain, but as it is positioned at 5' we can reject it.
Hence, MrsA_1 is reported to be a non-duplicated non-selenocysteine containing homologue present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 6 exons, same number as in the reference gene from zebrafish.
MrsA_2
Again, for MrsA_2 a group of contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000626_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007942.1 and CM007938.1 the ones selected.
Hence, MrsA_2 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (MsrA_2.1) is located between 20995730-21099307 position in the forward chain and it contains 103577 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. No SECIS have been identified neither by using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3.
The second copy (MsrA_2.2) is located between 62724219-62807722 position in the forward chain and it contains 83503 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons. No selenocysteines have been detected. SEBLASTIAN has not been able to predict any SECIS. Even though, 5 SECIS have been identified using SECISearch3. Four of them are present in the forward chain and only three of them are in the 3' position in positions 62777627-62777705, 62846122 -62846198 and 62778092 - 62778170.
Hence, MrsA_2 is reported to be a duplicated non-selenoprotein homologue present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 5 exons. Interestingly, the zebrafish reference gene contains 4 coding exons.
Finally, in order to check whether the predicted MrsA proteins are similar to theirs homologs in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results:
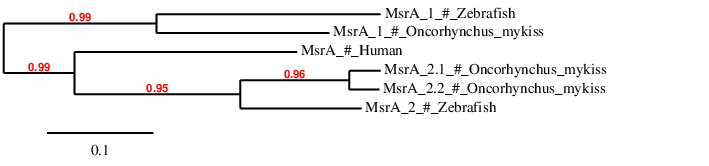
As expected, the prediction of Oncorhynchus mykiss's MsrA_1 is similar to the Zebrafish MsrA_1. The prediction of the duplicated genes MsrA_2.1 and MsrA_2.2 appear to be similar altogether and proximal to both Zebrafish MsrA_2. Therefore, we can consider that these proteins have been correctly assigned to their contigs.
Regarding MsrA_1, it has been identified in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome without a Sec residue. Even though SECISsearch has predicted 3 possible SECIS, we have rejected all of them. The predicted protein does not start with a methionine.
Concerning MsrA_2.1 and MsrA_2.2, both of them have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome without a Sec residue. For MsrA_2.1 no SECIS have been predicted, while for MsrA_2.1 SECISsearch3 predicted 5 possible SECIS being only 3 of them suitable. Moreover, both predicted proteins start with a methionine.
SELENOE
This protein is related to the other members of the selenoprotein family of 15 kDa (e.g. Sep15). It is an selenoprotein of unknown function found only in the ER of fish.
For SELENOE multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000615_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007945.1 and CM007940.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOE is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOE_1) is located between 70457115-70462733 position in the forward chain and it contains 5618 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 2 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected in the first exon. No SECIS was found in region nearby this region neither with SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch. T-Coffee alienation with Zebrafish showed that the C-terminal and N-terminal regions were not found, so it is possible that this gene is being lost due to gene fractionation.
The second copy (SELENOE_2) is located between 40412946-40414495 position in the forward chain and it contains 1549 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image. One selenocysteine has been detected in the second exon and a SECIS has been predicted between the positions 40414528 - 40414618. We can therefore conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
Hence, SELENOE appeared to be duplicated but data analysis showed that one copy, SELENOE_1, is about to be eliminated from the genome as it lacks the C-terminal and N-terminal regions compared to its counterpart SELENOE_2.
SELENOH
Selenoprotein H is localized in nucleus and has glutathione peroxidase activity.
For SELENOH multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000634_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007959.1 and CM007948.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOH is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOH_1) is located between 28194282-28194611 position in the reverse chain and it contains 329 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected in the second exon and a SECIS has been found between the positions 28195894 - 28195819 with SEBLASTIAN. Both protein prediction and T-Coffee alienation do not present the initial methionine. Despite that we can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The second copy (SELENOH_2) is located between 55339436-55339513 position in the reverse chain and it contains 77 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 1 exon. No selenocysteine has been detected because the exon where it was has not been alineated with the zebrafish query. However, SEBLASTIAN prediction showed 3 exons with the selenocysteine in the second exon and a SECIS located between positions 55339185-55339109. Therefore we have predicted a shorter form of the protein. Moreover, either predictions do not begin with methionine.
Hence, even though SELENOH seemed to be duplicated we can only assure the complete form of one of the copies has been identified, SELENOH_1, as for the other one, SELENOH_2, a shorter form has been predicted by the exonerate and a seemingly complete form has been predicted by SEBLASTIAN.
SELENOI
Selenoprotein I is only found in vertebrates. It contains seven transmembrane domains and has three conserved aspartic residues within a particular motif that are required for its activity. Despite that, the physiological function of this protein remains unknown .
For SELENOI multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000635_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007942.1 and CM007941.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOH is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOI_1) is located between 465206-501459 position in the forward chain and it contains 36253 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected in the ninth exon and a SECIS has been found between the positions 502768-502849 with SEBLASTIAN as shown in the image. Our predicton showed 9 exons despite the SEBLASTIAN prediction showed only 7. However, none of them presented the initial methionine. Both protein prediction and T-Coffee alienation do not present the initial methionine. Despite that we can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The second copy (SELENOI_2) is located between 62045309-62051509 position in the reverse chain and it contains 6200 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by only 2 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected, but it does not align with the one from zebrafish and the one zebrafish presents does not alineate with anything because the T-Coffee alienation lacks both C and N terminal parts. This rasults may mean that the gene is being lost due to gene fractionation. SECISearch found 1 possible SECIS for this protein at the 3' end of gene at position 47096-47167. Finaly, our prediction does not contain an initial methionine as it lacks part of the initial sequence.
Hence, even though the gene appeared to be duplicated, data analysis showed that one of the two copies, SLENOI_2, is being lost due to gene fractionation while the other copy, SELENOI_1, will be maintained.
SELENOJ1
Selenoprotein J is only present in actynopterygian fishes and sea urchins, presenting some Cys homologs in cnidarians. The main feature of this protein is, in contrast with the rest of selenoproteins, to serve as a structural protein.
For SELENOJ1 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000636_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007942.1 and CM007945.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOJ1 is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOJ1_1) is located between 79784582-79791603 position in the forward chain and it contains 7021 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons and no selenocysteine has been detected. Nonetheless, there is one selenocysteine in zebrafish that alienates with a cysteine in the seventh exon as shown in the image. This tells that Oncorhynchus mykiss has lost the selenocysteine in this protein and has been transformed to an homolog with cysteine. Moreover, 2 SECIS have been found at the 3' end with SECISearch. We can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The second copy (SELENOJ1_2) is located between 18681130-18688443 position in the reverse chain and it contains 7313 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected in the seventh exon and the corresponding SECIS has been predicted with SEBLASTIAN located at positions 18680786-18680858 as we can see in the image. We can therefore conclude that this protein also is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
Hence, SELENOJ1 showed an interesting behaviour. As proposed it has been duplicated and both copies have been maintained. However, one copy, SELENOJ1_2, has kept the original selenocysteine while the other one, SELENOJ1_1, has changed it for a cysteine changing from being a selenoprotein to a cysteine homolog.
SELENOK
Selenoprotein K is located in the ER and are implicated in ER-associated degradation (ERAD) of misfolded proteins.
For SELENOK only one contig has been selected, CM007943.1, from the scaffold SPP00000633_2.0, due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment. This hit is located between the positions 33285890-33286031 in the reverse strand and contains about 131 nucleotides. 4 exons have been predicted by exonerate and one selenocysteine has been detected in the fourth exon as shown in the image. The SECIS structure was found in the positions 33279816-33279896 at the 3' end of the coding region. As there is only one copy of this gene it means that the other copy generated by the whole-genome duplication has been lost and only one copy of the gene has been maintained in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
SELENOL
Selenoprotein L contains two seclenocysteine residues and is present only among aquatic eukaryotes such as fish, invertebrates and marine bacteria.
For SelenoL only one contig has been selected, CM0079438.1, from the scaffold SPP00000637_2.0, due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment. This hit is located between the positions 60608316 - 60611049 in the reverse strand and contains about 2733 nucleotides. 4 exons have been predicted by exonerate and two selenocysteine were detected. T-Coffee alineation showed that the protein predicted is shorter than the query, missing the initial part. However, SEBLASTIAN alineation showed the whole protein, containing 9 exons with the two selenocysteines located in the sixth exon. Therefore we have predicted a truncated form of the protein. The SECIS structure has been identified in positions 60608148-60608229 at the 3' end of the coding region. As there is only one copy of this gene it means that the other copy generated by the whole-genome duplication has been lost and only one copy of the gene has been maintained in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
SELENOM
Selenoprotein M (SelM) is a thioredoxin-like protein found in the ER that regulates the redox homeostasis.
For SELENOM multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000638_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007945.1 and CM007940.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOM is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOM_1) is located between 56002467-56002741 position in the forward chain and it contains 274 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons and one selenocysteine has been detected in the second exon. T-Coffee alienation showed to be good as the SEBLASTIAN's. SECIS structure has been predicted by SEBLASTIAN between the positions 56002008-56002080. We can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The second copy (SELENOM_2) is located between 26868516-26868765 position in the reverse chain and it contains 249 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons. One selenocysteine has been detected in both sequences. Even though, they do not align with each other or with cysteines. 2 SECIS have been predicted with SECISearch but they are located at 5' end of the coding region. So, even though the protein has been predicted, as the selenocystein does not align and the SECIS is 5' to the coding region we can not confirm that SELENOM_2 is selenoprotein.
Hence, for SELENOM we can only assure the presence of SELENOM_1 in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome, as for the other one, SELENOM_2, the results are doubtful.
SELENON
Selenoprotein N is an ER-resident transmembrane glycoprotein which is highly expressed in the embryonic development, being necessary for muscle development, differentiation and maintenance of satellite muscle cells. It is also expressed in a variety of adult tissues with an unclear function, probably related to regeneration after stress or injury.
For SelenoN only one contig has been selected, CM0079453.1, from the scaffold SPP00000639_2.0, due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
SelenoN is located between the positions 51256096 - 51261373 in the reverse strand and contains about 5277 nucleotides. 11 exons have been predicted by exonerate and one selenocysteine has been detected in the eighth exon. T-Coffee alineation showed that the protein predicted is shorter than the zebrafish query, missing the initial part and not beginning with methionine. However, SEBLASTIAN alineation showed one more exon in the initial part even though it also does not begin with methionine. Therefore, it is probable that we have predicted a truncated form of the protein. The SECIS structure has been identified in positions 51255387-51255460 at the 3' end of the coding region. As there is only one copy of this gene it means that the other copy generated by the whole-genome duplication has been lost and only one copy of the gene has been maintained in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
SELENOO1-2
Selenoprotein O contains a Sec residue located in C-terminal end. Homologs of the human Selenoprotein O have been detected in a wide variety of species, even though, the majority of homologs contain a Cys residue in place of a Sec. The function of selenoprotein O and of its homologues is yet unknown. Despite that there were 2 SELENOO proteins in zebrafish, the resulting blast from them was identical, the results were taken from the SELENOO1 blast and, therefore, analysed. In order to simplify it we'll refer to them as SELENOO1-2.
For SELENOO1-2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000640_2.0 and SPP00000641_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007936.1, CM007955.1 and CM007935.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SELENOM is found to be seemengly triplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SELENOO1-2_1) is located between 67691605-67698540 position in the forward chain and it contains 6935 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons and a selenocysteine has been detected in the last exon as shown in the image. T-Coffee alienation showed to be good as the one shown in SEBLASTIAN's and the SECIS structure predicted was located between the positions 67698883-67698958 at the 3' end of the gene. Therefore, we can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The second copy (SELENOO1-2_2) is located between 11042866 - 11048719 position in the reverse chain and it contains 5853 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons and a selenocysteine has been detected in the last exon as shown in the image. T-Coffee alienation showed to be good as SEBLASTIAN's and the SECIS structure predicted was located between the positions 11042615 - 11042683 at the 3' end of the gene. Again, we can conclude that this protein is part of Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome.
The third copy (SELENOO1-2_3) is located between 11042866-11048719 position in the reverse chain and it contains 5853 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons and 5 selenocysteine have been detected through the whole protein. This is suspicious as they do not align with any other selenocysteine, indicating that maybe some of these predicted selenocysteines are STOP codons instead and the resulting protein is a truncated form. In order to contrast this hypothesis, fastaseq from GFF output file was translated using ExPASy. Suprisingly, the first selenocystein position was in fact a STOP codon encoded by a UAA, therefore the protein gets truncated at this point. Taking this information into account, it is probable that SELENOO1-2_3 is a truncated form of its homolog in Zebrafish being lost by gene fractionation.
Hence, SELENOO1-2 is reported to be a duplicated selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by a two different genes with 9 exons, same number as the Zebrafish SELENOO1-2. Finally, in order to check whether the predicted SELENOO proteins are similar to theirs homologs in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results

According to the phylogenetic tree we can see that human SELENOO is really distant to the ones from Zebrafish or the Rainbow trout. Apart from that, we can see that Oncorhynchus mykiss's SELENOO1-2_1 and SELENOO1-2_2 are the homologs of SELENOO1 and SELENOO2 from zebrafish, respectively. Furthermore it can also be seen that afterwards the second whole-genome duplication that Oncorhynchus mykiss had, the additional copies of SELENOO1 and SELENOO2 have been lost as they only maintain one copy from each.
SELENOP
SELENOP_1
For Zebrafish SELENOP_1 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SELENOP_1.1 and SELENOP_1.2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000642_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007942.1 and CM007962.1 were the ones selected respectively based on the score obtained in the T-coffee.
The predicted SELENOP_1.1 gene is located between the positions 59856457-59858124 in the forward chain and it contains 1667 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image, despite the the reference gene sequence in Zebrafish showed 5. Probably the lacking 2 exons correspond to the last ones, as our predicted protein has 140 less amino acids than the query. However, the selenocysteine is located in the first exon and is conserved in both Oncorhynchus mykiss and Zebrafish. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS at the 3' end, in position 59858896-59858976.
The predicted SELENOP_1.2 gene is located between 20547094-20548042 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 948 nucleotides. Similarly to SELENOP_1.1, the exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image, despite the the reference gene sequence showed 5 and again our protein predicted is shorter (149 amino acids in this case). A conserved selenocysteine is also detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. However, there is a second selenocysteine near this one which does not align with a query's selenocysteine and aligns with an arginine instead. SEBLASTIAN hasn't been able to predict any SECIS, but SECISsearch3 predicted one SECIS at the 3' end, in position 20546400-20546476.
Hence, SELENOP_1.1 and SELENOP_1.2 are reported to be selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by genes with probably 3 exons, a shorter form than the its homologue in Zebrafish. This findings may be a signal of gene fractionation after the whole-genome duplication of Oncorhynchus mykiss.
SELENOP_2
For Zebrafish SELENOP_2 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SELENOP_2.1 and SELENOP_2.2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000643_2.0), and among the different contigs found CM007940.1 and CM007945.1 were the ones selected respectively since they were the best alignments we got:
The predicted SELENOP_2.1 gene is located between 37993124-37994538 positions in the forward chain and it contains 1414 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 3 exons as described in the image, despite the the reference gene sequence showed 4. This missing exon is consistent with the fact that we have predicted a shorter protein (189 less amino acids). A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. However, Zebrafish SELENOP_2.1 has 16 additional selenocysteines which we have not been found in our prediction since they are located at the end of the sequence, which is missing for Oncorhynchus mykiss. Finally, SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS at the 3' end, in position 37995010-37995079.
The predicted SELENOP_2.2 gene is located between 68192785-68197404 positions in the forward chain and it contains 948 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons as described in the image, despite the the reference gene sequence showed 4. 12 selenocysteines were predicted in this protein and exonerate predicted 6 frameshift mutations. Hence, this results may indicate that some of this predicted selenocysteines are STOP codons instead and the resulting protein is a truncated form. In order to contrast this hypothesis, fastaseq from GFF output file was translated using ExPASy and, surprisingly, all selenocysteines predicted were UGA codons. Finally, SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS at the 3' end.
Hence, SELENOP_1.1 and SELENOP_1.2 are reported to be a selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by a gene with probably 3 and 5 exons respectively. It is worth pointing out that the predicted sequence of SELENOP_1.1 is considerably shorter than the query and just 1 selenocysteine is conserved (out of a total of 17). Moreover, SELENOP_1.2 has a similar length compared to the query, but only 2 selenocysteines are conserved. Finally, in order to check whether the predicted SELENOP proteins are similar to theirs homologs in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results
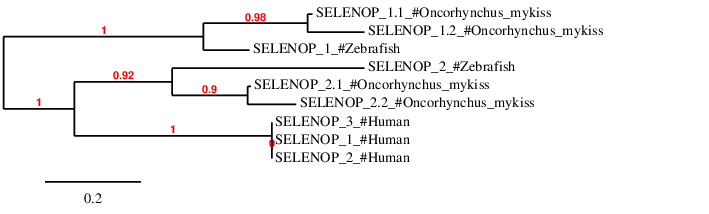
According to the phylogenetic tree, the predicted duplicated proteins SELENOP_1.1 and SELENOP_1.2 are closer to SELENOP_1 than to SELENOP_2. Similarly, SELENOP_2.1 and SELENOP_2.2 are closer to SELENOP_2 than to SELENOP_1. Finally, the three proteins found in human SELENOP family share a common ancestor with all SELENOP_2 proteins predicted both for Zebrafish and Oncorhynchus mykiss, hence they are closer to SELENOP_2 than to SELENOP_1.
Our predictions regarding SELENOP_1.1 and SELENOP_1.2 are similar: both predicted sequences are shorter than the query's (the 2 last exons are missing) but, selenocysteine is conserved in the first exon and a SECIS element has been predicted at 3' end as well. However, SELENOP_1.2 sequence prediction showed a second selenocysteine.
Related to SELENOP_2, the query sequence has a total of 17 selenocysteines. For both SELENOP_2.1 and SELENOP_2.2 a conserved selenocysteine in the first exon has been predicted, but the rest of the sequence was poorly aligned. SELENOP_2.1 predicted sequence was considerably shorter, so no selenocysteines were found besides the first one. SELENOP_2.2 predicted sequence had a similar lenght to the query, but only 12 selenocysteines has been found, and only 2 of them aligned correctly with those in the query. In spite of all these differences, as expected, looking at the tree we can see these three proteins are homologs.
SELENOS
For SELENOS multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000648_2.0) showed significant hits, being contig CM007960.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a high score in spite of having several gaps. The gene predicted is located between 35267112-35270995 positions, in the reverse chain and it contains 3883 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons, one less than the reference gene sequence. Our T-coffee results indicate that the selenocysteine located in the last exon of Zebrafish seems to have been lost in Oncorhynchus mykiss. SEBLASTIAN hasn't been able to predict any SECIS, but SECISsearch3 predicted two SECIS elements. Even though, both have been rejected since they were at the 5' end of the sequence.
Hence, SELENOS is reported to be a non-selenoprotein-containing homolog present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by one gene with 5 exons. Interestingly, our results indicate that selenocysteine have been lost in Oncorhynchus mykiss and this is consistent with the fact that no 3'-SECIS element has been predicted.
SELENOT
SELENOT1
For Zebrafish SELENOT1 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SELENOT_1 and SELENOT_2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000649_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007962.1 and CM007942.1 were the ones selected respectively based on the high score obtained in the alignment.
The predicted SELENOT1_1 gene is located between 28906835-28909883 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 3048 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 5 exons as described in the image, same number as the Zebrafish homologue. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine; but an additional selenocystein is observed in the alignment for the Oncorhynchus mykiss. Three SECIS elements were predicted, but two of them were rejected as they were on the forward strand and in the 5' end respectively. SEBLASTIAN hasn't been able to predict any SECIS, but SECISsearch3 predicted a SECIS element at the 3' end in position 28906427-28906501.
The predicted SELENOT1_2 gene is located between 50428102-50430307 positions in the forward chain and it contains 2205 nucleotides. Similarly to SELENOT_1, the exonerate structure predicts 5 exons as described in the image, the same number as the query's gene. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 50430973-50431047.
Hence, SELENOT1_1 and SELENOT1_2 are reported to be duplicated selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by genes with, similarly to SELENOT1 in Zebrafish, 5 exons. Interestingly, our results suggest that SELENOT1_1 presents a second selenocysteine, which is not present in its homolog in Zebrafish.
SELENOT1b
Due to the absence of significant hits comparing the studied genome and Zebrafish respective sequence, SELENOT1b could not be found in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
As explained in the introduction, SELENOT1b is a protein found in all bony fishes as a product of their whole-genome duplication, therefore its absence in Oncorhynchus mykiss is unexpected. This might be the result of the loss of this protein in the studied genome, or an error in the genome annotation.
SELENOT2
For SELENOT2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000650_2.0) showed significant hits, being contig CM007959.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes. The gene predicted is located between 15703119-15704308 position in the reverse chain and it contains 1189 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. SEBLASTIAN has predicted a SECIS structure at the 3' end, in position 15702845-15702928.
Hence, SELENOT2 is reported to be a selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by one gene with 6 exons.
Moreover, in order to check whether the predicted SELENOT proteins are similar to theirs homologs in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results
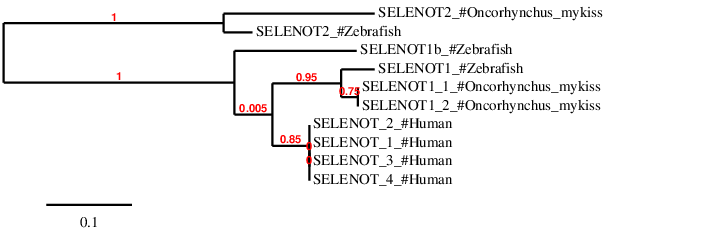
According to the phylogenetic tree, as expected, predictions for SELENOT1_1 and SELENOT1_2 and SELENOT2 are closer to SELENOT1 and SELENOT2 proteins in Zebrafish respectively. Interestingly, as shown in the tree, SELENOT1b protein was not found in Oncorhynchus mykiss. Finally, human protein members of SELENOT family are closer to SELENOT1 than to SELENOT2.
Our predictions for SELENOT1_1 and SELENOT1_2 are similar to Zebrafish SELENOT1 and similar between them: both predicted sequences are composed by 5 exons (the same number of the query) and both are supposed to have a conserved selenocysteine in the second exon aligning with the query's selenocysteine. However, a second selenocysteine has been predicted for SELENOT1_1.
Regarding SELENOT2, the predicted sequence in Oncorhynchus mykiss is very similar to its homolog in Zebrafish: 6 exons and a conserved selenocystein in the second one.
SELENOU
SELENOU1a
For Zebrafish SELENOU1a protein we report a triplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SELENOU1a_1, SELENOU1a_2 and SELENOU1a_3. All of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000652_2.0), and among the different contigs found CM007950.1, CM007935.1 and CM007957.1 respectively were the ones selected since they were the best hits taking into account the score and the alignment:
The predicted SELENOU1a_1 gene is located between 16311869-16316108 positions in the forward chain and it contains 4239 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons as described in the image, slightly different from the 6 exons that has its homologue in Zebrafish. It is worth pointing out that this protein seems to be much larger Oncorhynchus mykiss than in Zebrafish, since there is a long gap between the first 5 amino acids of the query protein and the rest of them in the alignment. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine; but an additional selenocystein is observed in the Oncorhynchus mykiss sequence. The alignment shows the first part of the sequence, which does not align with the query, is a tandem duplication.
The predicted SELENOU1a_2 gene is located between 79681676-79686732 positions in the forward chain and it contains 5056 nucleotides. This alignment is much better than the previous one, since the length of both query and target are almost the same. The exonerate structure predicts only 5 exons as described in the image, closer to the 6 exons of the query's gene. A conserved selenocysteine is detected, aligning with the query's selenocysteine and a SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end by SEBLASTIAN, in position 79687390-79687461.
The predicted SELENOU1a_3 gene is located between 25202962-25209394 positions in the forward chain and it contains 6432 nucleotides. The exonerate structure predicts 8 exons as described in the image, two more than the query's gene. Similarly to SELENOU1a_1, this protein is much larger in Oncorhynchus mykiss than in Zebrafish, since there are about 100 extra amino acids before the first amino acid of the query sequence. However, a conserved selenocysteine is detected, aligning with the query's selenocysteine and a SECIS structure is predicted at the 3' end by SEBLASTIAN, in position 25227469-25227539.
Hence, SELENOU1a_1, SELENOU1a_2 and SELENOU1a_3 are reported to be triplicated selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. SELENOU1a_2 predicted sequence is the most similar to its homologue in Zebrafish, while the other two copies are larger proteins. However, for all of them a conserved selenocysteine in the second exon of the protein have been predicted and a 3' SECIS element too.
SELENOU2
For SELENOU2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000655_2.0) showed significant hits, being contig CM007945.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, few gaps and a small number of amino acid changes. The gene predicted is located between 68069553-68071421 position in the forward chain and it contains 1868 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons, the same number found in the query's sequence. As expected, no selenocysteines nor SECIS were found in this protein, since its homologue in Zebrafish does not have any neither.
Hence, SELENOU2 is reported to be a non-selenoprotein homologue present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 6 exons.
SELENOU3
For SELENOU3 multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000656_2.0) showed significant hits, being contig CM007941.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes. The gene predicted is located between 35629555-35631435 position in the reverse chain and it contains 1880 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons, the same number found in the query's sequence. As expected, since its homolog in Zebrafish does not have neither, no selenocysteines were found. SEBLASTIAN wasn't able to predict any SECIS, but SECISearch predicted 4 SECIS elements. However, all of them were discarded due to they were in the 5' end or too far away from the last exon.
Hence, SELENOU3 is reported to be a non-selenoprotein homologue present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 6 exons.
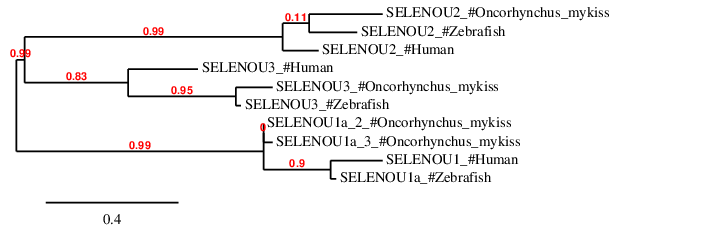
According to the phylogenetic tree, as expected, all the predicted proteins in Oncorhynchus mykiss are closer to its homologs in Zebrafish than to any other subfamily. SELENOU1a_1, SELENOU1a_2 and SELENOU1a_3 are closer to SELENOU1a subfamily than to SELENOU2 and SELENOU3. SELENOU2 is closer to its homolog in Zebrafish than to SELENOU1a or SELENOU3. Similarly, SELENOU3 is also closer to its homolog in Zebrafish than to SELENOU2 and SELENOU3 subfamilies. Finally, SELENOU2 subfamily is closer to SELENOU3 than to SELENOU1.
Among the triplicated proteins predicted for the SELENOU1a subfamily, SELENOU1a_2 is the most similar to its homolog in Zebrafish in therms of sequence lenght and conserved selenocysteines. Both SELENOU1a_1 and SELENOU1a_2 are larger predicted proteins and seem to be duplicated in tandem.
Finally both SELENOU2 and SELENOU3 predicted protein in Oncorhynchus mykiss share with their homologs in Zebrafish the same number of exons (6 for both) and the absence of seleocysteines and SECIS elements.
SELENOW_1
For Zebrafish SELENOW_1 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SELENOW_1.1 and SELENOW_1.2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000657_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007947.1 and CM007946.1 are where the sequences studied are believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes.
The predicted SELENOW_1.1 gene is located between 46534811-46541162 positions in the forward chain and it contains 6351 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 4 exons as described in the image, same number as its Zebrafish homologue. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine and a SECIS element is predicted at the 3' end, in position 46536562-46536628.
The predicted SELENOW_1.2 gene is located between 80085425-80090315 positions in the forward chain and it contains 4890 nucleotides. Similarly to SELENOW_1.1 and its Zebrafish homologue, the exonerate structure predicts 4 exons as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is also detected in the second exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine and a SECIS element is predicted at the 3' end, in position 80087196-80087263.
Hence, SELENOW_1.1 and SELENOW_1.2 are reported to be duplicated selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by genes with, similarly to SELENOW_1 in Zebrafish, 4 exons.
SELENOW2
Due to the absence of significant hits comparing the studied genome and Zebrafish respective sequence, SELENOW2 could not be found in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
As explained in the introduction, SELENOW2 is a protein found in all vertebrates, therefore its absence in Oncorhynchus mykiss is unexpected. This might be the result of the loss of this protein in the studied genome, or an error in the genome annotation.
SELENOW_3
For SELENOW_3 multiple contigs from the same scaffold (SPP00000659_2.0) showed significant hits, being contig CM0079631.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a high score and a small number of amino acid changes, although there are several gaps in the alignment. The gene predicted is located between 30483359-30483787 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 428 nucleotides.
The exonerate structure predicts only 2 exons, whereas its homologue in Zebrafish has 5 exons. This shorter form predicted is missing the first and last exons of the query sequence, where the Zebrafish's selenocysteine is located, so in Oncorhynchus mykiss SELENOW3 no selenocysteine has been found. However, three SECIS elements were predicted by Seblastian, two of which were rejected for being located at the 5' end or too far away from the last exon. The one not discarded was at 3' end and at positions 30483010-30483090.
Hence, SELENOW_3 is reported to be a selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome as a shorter form of its homolog in Zebrafish.
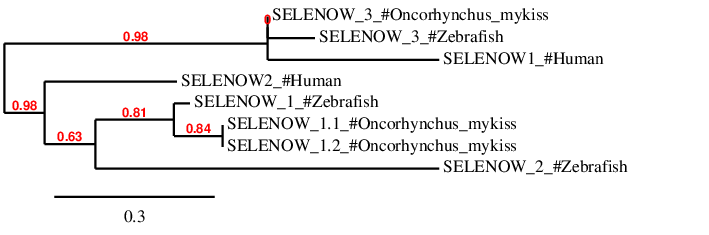
According to the phylogenetic tree, the predicted proteins for each subfamily (SELENOW1, SELENOW2 and SELENOW3) appear altogether with its homologs in Zebrafish.
As expected, SELENOW_1.1 and SELENOW_1.2 predicted proteins in Oncorhynchus mykiss are closer to its homolog in Zebrafish (SELENOW_1) than to SELENOW_2 and SELENOW_3. Similarly, SELENOW_3 is closer to its homolog in Zebrafish than to SELENOW_1 and SELENOW_2. Finally, as it can be seen in the tree, no SELENOW_2 homolog was found in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The duplicated homologs of SELENOW_1 found in Oncorhynchus mykiss (SELENOW_1.1 and SELENOW_1.2) are very similar between them and also very similar to the query: the three proteins have 4 exons, a conserved selenocysteine in the second one and a SECIS element.
However, SELENOW_3 homolog in Oncorhynchus mykiss was predicted as a non-selenocysteine containing homolog. This may be explained because its predicted sequence was much shorter than the query's, and the exon where the selenocysteine was located in the protein of Zebrafish was missing in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
Thioredoxin reductases (TXNRD)
TXNRD2
For Zebrafish TXNRD2 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as TXNRD2_1 and TXNRD2_2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000660_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007940.1 and CM007945.1 are where the sequences studied are believed to be located respectively, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes.
The predicted TXNRD2_1 gene is located between 32406252-32427023 positions in the forward chain and it contains 20771 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 15 exons as described in the image, same number as its Zebrafish homologue. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the last exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. However, a second selenocystein is found only in Oncorhynchus mykiss in the ninth exon. Finally, a SECIS element is predicted at the 3' end, in position 32430367-32430438.
The predicted TXNRD2_2 gene is located between 61835027-61864335 positions in the forward chain and it contains 29308 nucleotides. The exonerate structure predicts 13 exons and 3 frameshift mutations, which may explain the difference observed in terms of number of exons and base pairs. Moreover, 8 selenocysteines have been predicted, which may indicate that at least some of these predicted selenocysteines are STOP codons instead and the resulting protein is a truncated form. In order to contrast this hypothesis, fastaseq from GFF output file was translated using ExPASy and, as expected, the fourth predicted selenocysteine was a non-UGA STOP codon (UAG in this case). Taking this information into account, TXNRD2_2 is probably a truncated form of its homolog in Zebrafish and that is why it has been discarded for further analysis.
Hence, TXNRD2_1 and TXNRD2_2 are reported to be duplicated selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss. However, the second copy of this protein, TXNRD2_2, may be a truncated form due to the prediction of 3 frameshift mutations.
TXNRD3
For Zebrafish TXNRD3 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as TXNRD3_1 and TXNRD3_2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000660_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007941.1 and CM007951.1 are where the sequences studied are believed to be located respectively, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes.
The predicted TXNRD3_1 gene is located between 67297738-67320876 positions in the forward chain and it contains 23138 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 16 exons as described in the image, same number as its Zebrafish homologue. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the last exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. Finally, two SECIS elements have been predicted, one at the 5' and so rejected, and another at the 3' end, in position 67321268-67321350.
The predicted TXNRD3_2 gene is located between 29392144-29422500 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 30356 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 16 exons, the same number as its Zebrafish homologue. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the last exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine, but no SECIS element was predicted.
Hence, TXNRD2_1 and TXNRD2_2 are reported to be duplicated selenoproteins present in Oncorhynchus mykiss.Finally, in order to check whether the predicted TXNRD proteins are similar to theirs homologs in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results
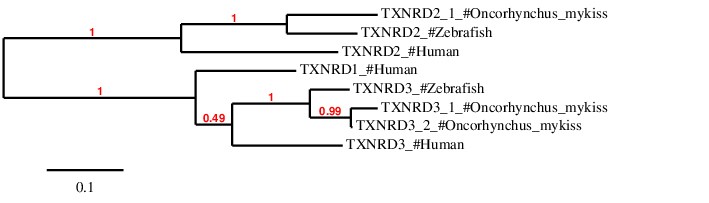
According to the phylogenetic tree, the predicted proteins for each subfamily (TXNRD1, TXNRD2 and TXNRD3) appear altogether with its homologs in Zebrafish and Human, except TXNRD1, which is not present neither in Oncorhynchus mykiss nor in Zebrafish.
As expected, TNXRD2_1 predicted protein in Oncorhynchus mykiss is closer to Zebrafish than to Human, and it is closer to TXNRD2 subfamily than to TXNRD1 and TXNRD3. Similarly, the predicted duplicated TNXRD3_1 and TNXRD3_2 proteins are closer to Zebrafish than to Human and closer to TXNRD3 subfamily than to TXNRD1 and TXNRD2. Finally, TXNRD1, which has no homolgs neither in Oncorhynchus mykiss nor in Zebrafish, is closer to TXNRD3 subfamily than to TXNRD2.
TXNRD2_1 predicted sequence for Oncorhynchus mykiss is much more similar to its homolog in Zebrafish (TXNRD2) than TXNRD2_2 (not shown in the tree) in therms of lenght (both have 15 exons) and conserved selenocysteines and SECIS elements. TXNRD2_2 has been predicted as a truncated form due to several nonsense mutations and hence discarded for further analysis.
Regarding TXNRD3 subfamiy members, the duplicated proteins predicted in Oncorhynchus mykiss are very similar to its homolog in Zebrafish and also between them: 16 exons and a conserved selenocysteine in the last exon. However, only a SECIS element was predicted for TXNRD3_1.
Selenoprotein machinery
SelS
For SecS multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000631_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs CM007943.1 and CM007955.1 the ones selected due to the absence of gaps and high score reported in the blast alignment.
Hence, SecS is found to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The first copy (SecS_1) is located between 25770921-25770921 positions in the reverse chain and it contains 5072 nucleotides. The exonerate structure predicts 8 exons and 2 selenocysteines have been predicted. This is doubtful because the Danio rerio query does not have any selenocysteine, therefore some of these predicted selenocysteines may be STOP codons instead and the resulting protein is a truncated form. In order to contrast this hypothesis, fastaseq from GFF output file was translated using ExPASy. The first selenocysteine checked was in fact encoded by a UAG stop codon.
The second copy (SecS _2) is located between 28278487-28278487 position in the forward chain and it contains 35498 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 11 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected despite that SECISearch found two possible SECIS located 30kb upstream the coding region, too far away to be functional. Furthermore, as it is a machinery protein and zebrafish does not contain any selenocysteine it is logical that no SECIS have been predicted arround the coding sequence. Despite that, we can conclude that SecS_2 is part of our genome.
Therefore, SecS is reported to be a duplicated selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by two different genes with 4 exons, the same as Danio rerio.
SBP2
For SBP2 different contigs from the same scaffold SPP00000627_2.0 showed significant hits. In this case only the contig CM007940.1 was selected for further study since T-coffee output showed high score, only 3 gaps and almost a perfectly conserved alignment.
The gene is located between positions 17517527-17519600 in the reverse chain and it contains 2073 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 7 exons. 4 different SECIS structure were predicted, all of them discarded due to the big distance between them and the gene. Some of these SECIS were also discarded due to their position at the positive chain.
PSTK
For this protein only one contig, CM007935.1, from the scaffold, SPP00000663_2.0 showed significant hits.
PSTK is located between 84101333-84157183 position in the reverse chain and it contains 55850 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons. Two selenocysteines have been detected while no SECIS have been predicted neither by using SEBLASTIAN nor SERCISearch.
However, the reliability of the PSTK prediction is uncertain because of the presence of more than one Sec residue and the bad alignment obtained using t-coffee. Therefore, we cannot conclude that PSTK is present in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. We recommend that for further studies, another PSTK gene from other species should be analysed.
eEFsec
Again, for eEFsec multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000662_2.0 showed significant hits, but according to the t-coffee alignment only one contig, CM007941.1 was selected.
Hence, eEFsec is found to be in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
eEFsec is located between 51272165-51282180 position in the forward chain and it contains 10015 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 8 exons. The predicted protein does not start with methionine. No selenocysteine has been detected. Surprisingly, 3 SECIS have been detected using SECISearch. Only two of them are present in the forward chain. If we look up the closely, one of them is present in 5' so it can be rejected, while the other one is predicted in 3' but really far apart.
Hence, eEFsec is reported to be a non-duplicated non-selenoprotein homologue present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 8 exons. To notice at, the zebrafish eEFsec protein is encoded in 7 exons.
SEPHS
SEPHS1
For Zebrafish SEPHS1 protein we report a duplication in Oncorhynchus mykiss, being these proteins named as SEPHS1_1 and SEPHS1_2. Both of them were found in the same scaffold (SPP00000629_2.0), and among the different contigs found, CM007935.1 and CM007936.1 are where the sequences studied are believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score, no gaps and a small number of amino acid changes.
The predicted SEPHS1_1 gene is located between 31482276-31492129 positions in the forward chain and it contains 9853 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons, same number as its Zebrafish homologue. As expected taking into account the query's sequence, no selenocysteine was detected for this protein. Surprisingly, 3 SECIS have been detected using SECISearch. Only two of them are present in the forward chain. If we look up the closely, one of them is present in 5' so it can be rejected, and the other one is predicted in 3' but really far apart.
The predicted SEPHS1_2 gene is located between 60868651-60872807 positions in the forward chain and it contains 4156 nucleotides. Similarly to SEPHS1_1 and its Zebrafish homologue, the exonerate structure predicts 9 exons. Again, no selenocysteine was found in the predicted sequence and the SECIS element predicted can be rejected since it is located in the reverse chain.
Hence, SELENOW_1.1 and SELENOW_1.2 are reported to be duplicated homologs present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by genes with, similarly to SELENOW_1 in Zebrafish, 4 exons.
SEPHS2
For SEPHS2 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000630_2.0, showed significant hits, being contig CM007943.1 the one selected. In this contig is where the sequence studied is believed to be located, since T-coffee output shows a very high score and few gaps. The gene predicted is located between 67210585-67230174 position in the forward chain and it contains 19589 nucleotides. Surprisingly, despite the alignment had a very high score, the gene sequence for Oncorhynchus mykiss is much larger.
The exonerate structure is composed by 9 exons, same number as the reference gene sequence, as described in the image. A conserved selenocysteine is detected in the first exon, aligning with the query's selenocysteine. A SECIS element is predicted at the 3' end by SEBLASTIAN, in position 67230605-67300703.
Hence, SEPHS2 is reported to be a selenoprotein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 8 exons, same number as its homologue in Zebrafish.
According to the phylogenetic tree, the predicted proteins for each subfamily (SEPHS1 and SEPHS2) appear altogether with its homologs in Zebrafish and Human.
As expected, SEPHS1_1 and SEPHS1_2 predicted proteins in Oncorhynchus mykiss are closer to its homolog in Zebrafish (SEPHS1) than to Human, and are also closer to SEPHS1 subfamily than to SEPHS2. Similarly, the predicted SEPHS2 protein is closer to its homolog in Zebrafish than to Human and closer to SEPHS2 subfamily than to SEPHS1.
As expected, the duplicated proteins SEPHS1_1 and SEPHS1_2 predicted in Oncorhynchus mykiss are very similar between them and also are very similar to its homolog in Zebrafish: the three proteins have 9 exons and neither selenocysteines nor SECIS elements were predicted.
Regarding SEPHS2 subfamily, again both homologs in Oncorhynchus mykiss and Zebrafish are very similar: 9 exons, a conserved selenocysteine in the first exon and a predicted SECIS element.
tRNA Sec 1 associated protein 1 (SECp43)
SECp43_1
For SECp43_1 multiple contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000664_2.0, showed significant hits, being contig CM007948.1 the one selected due to results obtained in the t-coffee. The gene predicted is located between 5411856-5411856 position in the forward chain and it contains 3093 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 6 exons. No selenocysteine or SECIS have been detected using neither SEBLASTIAN or SECISearch.
For all this, SECp43_1 is reported to be a machinery protein present in Oncorhynchus mykiss genome encoded by one gene with 6 exons, same number as in the reference gene from zebrafish.
SECp43_2
For SECp43_2 a diverse group of contigs from the same scaffold, SPP00000665_2.0, showed significant hits, being contigs, CM007962.1 and CM007942.1 the ones selected.
Hence, SECp43_2 is predicted to be duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss.
The second copy (SECp43_2.1) is located between 18052468-18055398 position in the forward chain and it contains 2930 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 8 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. Lastly, no SECIS have been identified neither using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3.
The third copy (SECp43_2.2) is located between 62197635-62191322 position in the reverse chain and it contains 6313 nucleotides. The exonerate structure is composed by 8 exons. No selenocysteine has been detected. Lastly, no SECIS have been identified neither using SEBLASTIAN nor SECISearch3. Both proteins predicted start with a methionine.
For all this, SECp43_2 is reported to be a machinery protein duplicated in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome encoded by two genes with 8 exons, same number as in the reference gene from Zebrafish.
Finally, in order to check whether the predicted SECp43 proteins are similar to theirs homologues in Zebrafish and Human we have done a phylogenetic tree and we have obtained the following results:
The prediction of Oncorhynchus mykiss's SECp43_1 is similar to the Zebrafish SECp43_1. The prediction of the duplicated genes SECp43_2.1 and SECp43_2.2 appear to be similar altogether and proximal to both Zebrafish SECp43_2. Therefore, we can consider that these proteins have been correctly assigned to their contigs.
Regarding SECp43_1, it has been identified in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. The prediction does not contain a Sec residue nor a SECIS structure.
Concerning SECp43_2.1 and SECp43_2.2, both of them have been found in Oncorhynchus mykiss's genome. None of them contain any SECIS or Sec residue. Moreover, both predicted proteins start with a methionine.
All the results are consistent with the fact that SECp43_1 and SECp43_2 are machinery proteins involved in the selenoprotein synthesis and they do not contain neither SECIS nor Sec residues in Zebrafish.

