Selenoproteins
15-kDa selenoprotein
Sel15
Function
Sel15 is an enzyme with thiol-disulfide isomerase activity, and is possibly involved in the formation of disulfide bonds in the endoplasmic reticulum, where it is localized. In humans, loss of heterozygosity at its locus is associated with cancer [7].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 31579 and 23776 of the scaffold BDOT02000186.1, which was accepted since it matched our criteria. Although 2 hits were obtained, the best alignment we found was in the scaffold BDOT02000186.1. Moreover, it has 3 predicted exons (shown in the image below).
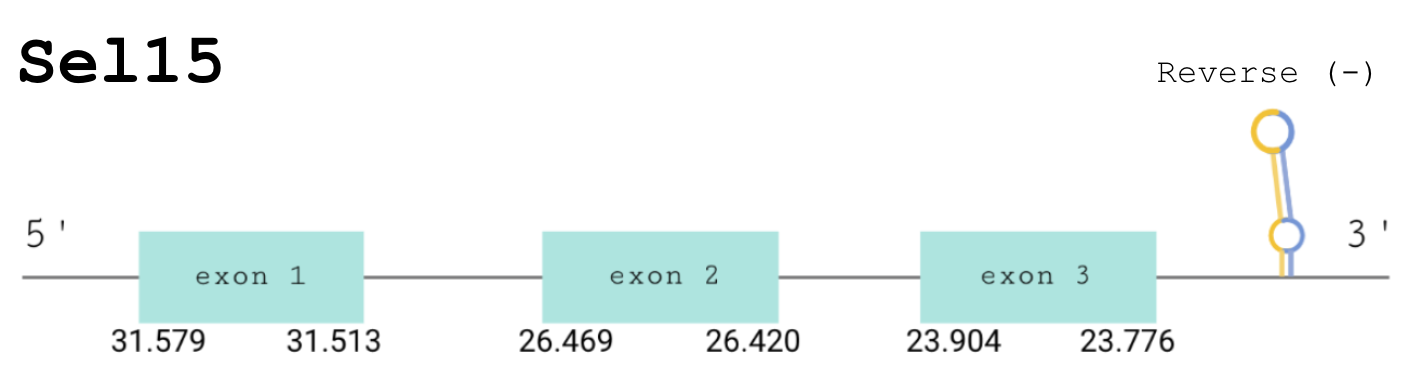
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was 999. Therefore, the selenocysteine of the human protein and the predicted one, aligned in the same position, is conserved. In order to assure it was a “real” selenoprotein we ran Seblastian, and we obtained a positive prediction. There exists a selenoprotein in Gekko japonicus, which is a close species to Pareodura picta. SECIS Search3 was able to find three SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. All three of them were found in the reverse strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the rest. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 23172 and 23098 of the scaffold.
Therefore, we can conclude the existence of selenoprotein Sel15 in Paroedura picta.
Glutathione peroxidase
Function
Glutathione peroxidases (GPx) are a family of closely-related antioxidant proteins which catalyze the reduction of H2O2 and other soluble peroxides inside or outside the cell. In humans, only GPx1, GPx2, GPx3, GPx4 and GPx6 contain Sec, while homologues GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8 contain Cys residues [7].
GPx1
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 60204402 and 60207790 of the scaffold BDOT02000003.1, which was accepted since it matched our criteria. Although 4 hits were obtained, the remaining three were discarded: the e-value was not good enough, Seblastian showed matches with other proteins of the same family and T-Coffee showed a low score. The protein was predicted to have 2 exons (shown in the image below).
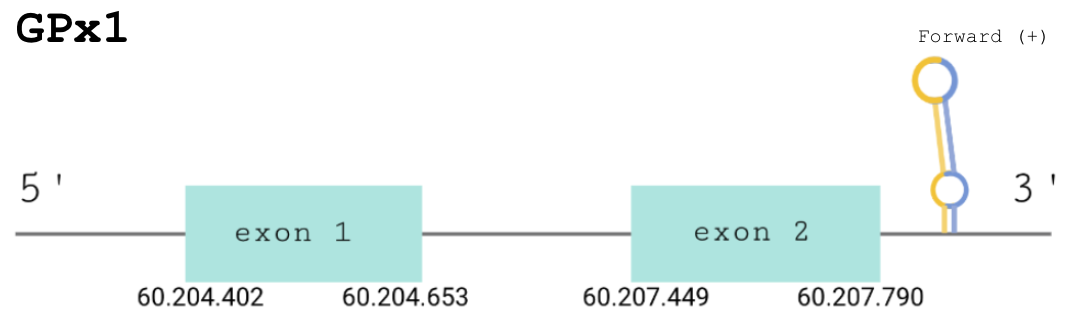
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 943. One of the five selenocysteines present in our predicted protein aligned with a cysteine in the human protein. After running Sebastian we obtained a positive prediction: the same protein was also in Gekko japonicus.
The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment between positions 60205224 and 60205292 of the scaffold. Moreover, they had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score. However, as we can see, the predicted SECIS is contained between both GPx1 predicted exons. Thus, we may hypothesize that either the GPx1 gene in Paroedura picta is just expressed as the predicted exon 1 or that the SECIS which was predicted using the Seblastian software is not the SECIS which allows for the production of the whole selenoprotein.
Nevertheless, according to the given results it could be affirmed that selenoprotein GPx1 is found in Paroedura picta.
GPx2
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 64425158 and 64421492 of the scaffold BDOT02000002.1. Although 4 hits were obtained, as in the previous case, the remaining ones were discarded since, despite the e-value being good, Seblastian found a match with other proteins of the same family and T-Coffee showed a low score. The protein was predicted to have 2 exons (shown in the image below).
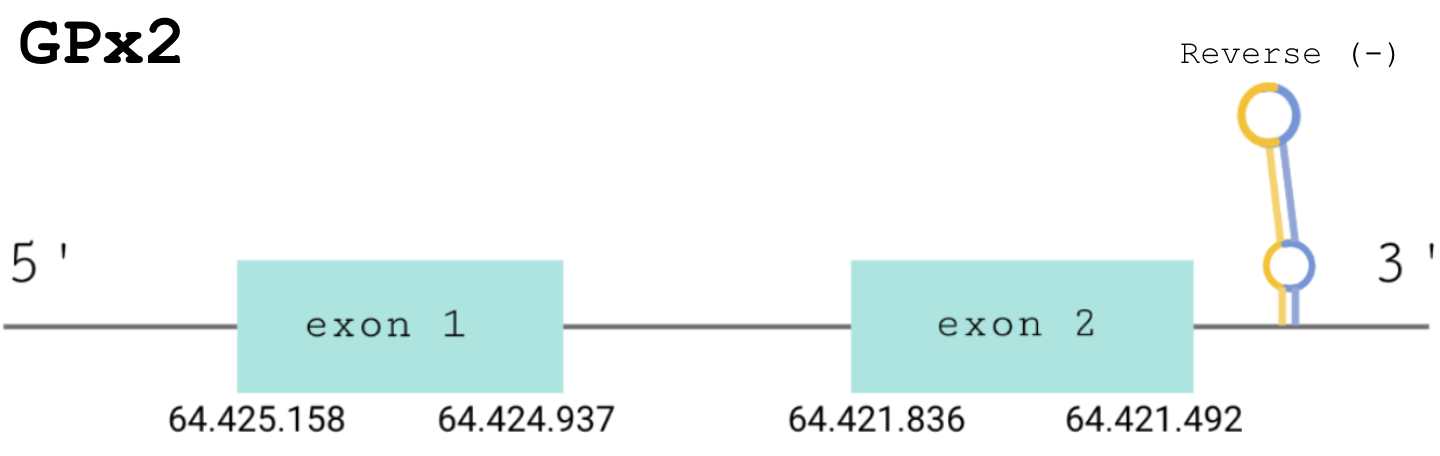
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was perfectly aligned, with a score of 1000. Both proteins start with a methionine, and the selenocysteine is conserved in the same position. Seblastian also found a positive prediction: an alignment with a GPx2 protein in Gekko japonicus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find three SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. All three of them were found in the reverse strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the rest. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 64421287 and 64421223
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein GPx2.
GPx3, GPx4, GPx6, GPx5 GPx7, GPx8
Protein prediction
GPx3, GPx4, GPx6 are the ones that codify for selenoproteins in Homo sapiens, and GPx5 GPx7, GPx8 are homologous proteins which contain a Cys residue in humans and are not selenoproteins. We found that all of them aligned with these two scaffolds in the reverse strand: BDOT02000004.1 and BDOT02000007.1, between the positions 61413391 and 61413236, and 82925535 and 82925371, respectively.
T-Coffee values were high and showed an alignment between a Cys in the predicted protein and a Sec in the Homo sapiens selenoprotein. Seblastian found a positive prediction with no Sec residue but one SECIS element. The SECIS element found in the protein predicted with the scaffold BDOT02000007.1 is between the position 82920532 and 8920611 and had an overall C grade, and the one found in BDOT02000004.1 scaffold is between 61434716 and 61434783 and had an overall C grade.
We cannot consider these predicted SECIS elements as correct, since in the scaffold BDOT2000004.1 it is located 5’ to the predicted gene and both have a very low grade.
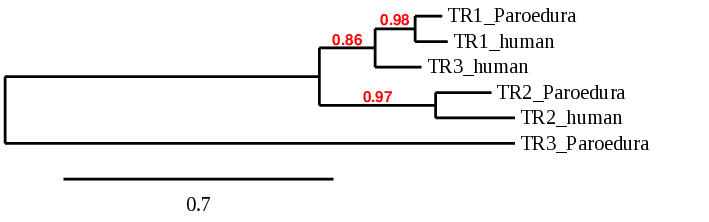
With all this information we can conclude that Pareodura picta has only 2 of the 6 human genes. 3 of them the genes contained Sec residues that aligned with a Cys in Pareodura picta, and the other 3 were homologous genes for a Cys. This superior number of these family genes can be explained because of the progresive specialization and duplication in the Homo sapiens species which may have not occurred in Paroedura picta.
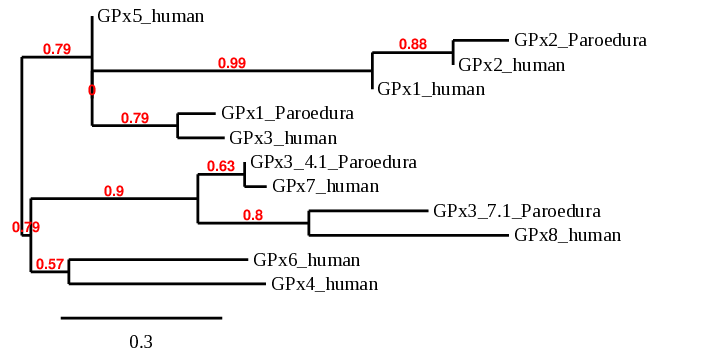
This phylogenetic tree shows the relationship between predicted proteins in Paroedura pictaand in Homo sapiens. As we can see, human GPx6, GPx4, GPx7 and GPx8 aligned with the sequences in BDOT2000004.1 and BDOT2000007.1. This does not happen with GPx5 or, most notably, with GPx3, which seems to be closely related to the predicted GPx1 in Paroedura picta. Nevertheless, we consider our predictions as correct, since the modeling in the phylogenetic tree has not got very high probability and thus their relationships may not be all correct. Not surprisingly, the predicted GPx2 in Paroedura picta is closely related to the GPx2 protein in Homo sapiens.
Iodothyronine deiodinase
Function
Iodothyronine deiodinases (DI) are a family of proteins involved in the thyroid hormone bio- synthetic pathway. DI1 and DI2 convert thyroid prohormone T4 to active hormone T3 by catalyzing the removal of iodine from T4, while DI3 converts thyroid hormone T3 to inactive rT3 by catalyzing the removal of iodine from T3 [7].
DI1
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 62776129 and 62779823 of the scaffold BDOT02000004.1. Although 2 hits were obtained in different scaffolds, we considered these as correct since the Seblastian prediction matched this sequence and not the other. The protein was predicted to have 2 exons (shown in the image below).
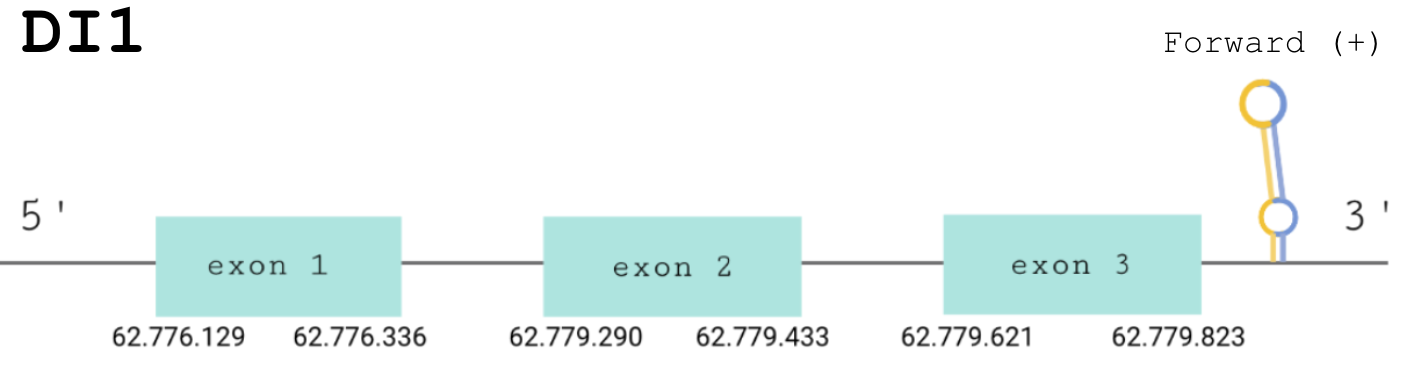
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was perfectly aligned, with a 1000 score. Both proteins start with a methionine and the selenocysteine is conserved in the same position.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. One was discarded because it was found in the reverse strand. The SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 62785662 and 62785732 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction and state that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein DI1.
DI2, DI3
Protein prediction
Both proteins DI2 and DI3 align with the BDOT02000002.1 scaffold between the positions 152754575 and 152755141 and between positions 139297552 and 139298118. In the first ones, Seblastian did not show any matching selenoprotein and predicted 5 SECIS elements, one of which had a grade A score.
In the second alignment, the DI3 of Gekko japonicus was predicted. Thus, and also considering the following phylogenetic tree (in which P. picta DI and human DI appear to be closely related), we can conclude that DI3 is a selenoprotein that exists in Paroedura picta and is aligned with the second scaffold, while DI2 is not a selenoprotein in our species.
Rdx protein family
Function
The members of the Rdx family (SelH, SelT, SelV and SelW1) possess a thioredoxin-like fold and are characterized by the presence of a conserved Cys-X-X-Sec motif and are thiol-based oxidoreductases, although their exact function is not well described [8].
SelV
Function
SelV (selenoprotein V) is only expressed in testes, which makes it presumably involved in male reproduction. According to literature, it most likely evolved recently by duplication from SelW, and is found only in placental mammals.
Protein prediction
SelV was not found during our analysis, since our BLAST output did not give rise to any result. This is probably because, as stated, SelV seems to have appeared in placental mammals and is not present in reptiles such as Paroedura picta.
SelH
Function
SelH localizes specifically in the nucleoli and possesses glutathione peroxidase activity. It has been implicated in the regulation of the transcription of different genes which are involved in the de novo synthesis of glutathione and phase II detoxification enzymes [8].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 66858577 and 66861550 of the scaffold BDOT02000002.1, which was accepted since it matched our criteria. Although 3 hits were obtained, 2 of them were discarded because the e-value was not good enough. The protein was predicted to have 3 exons (shown in the image below).
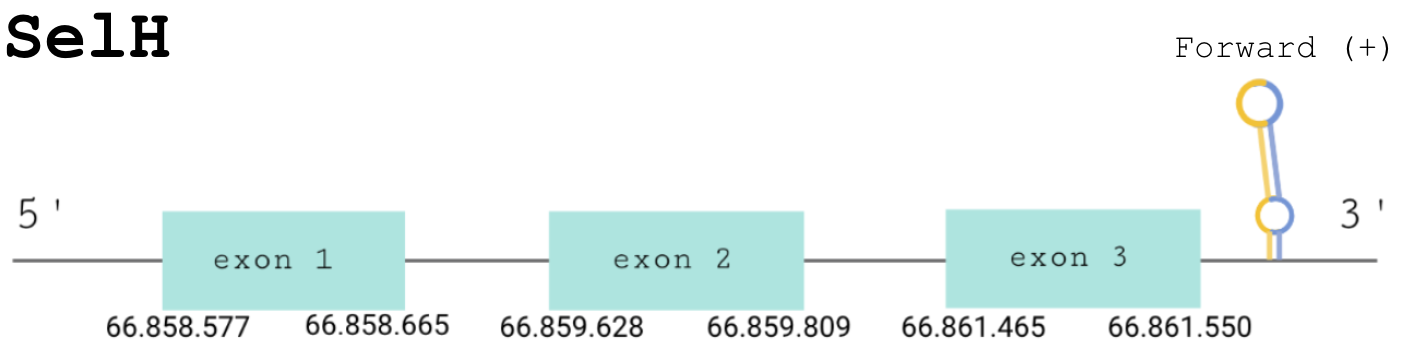
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was high aligned: 995. Both proteins start with a methionine, but the selenocysteine is displaced one position. The Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein of Gekko japonicus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. Both of them were found in the forward strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the other. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 66862842 and 66862923.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein SelH.
SelT
Function
SelT is ubiquitously expressed both during embryonic development and in adult tissues. SelT deficiency alters cell adhesion and enhances the expression of several oxidoreductase genes while decreasing the expression of genes involved in cell structure organization, suggesting the involvement of SelT in redox regulation and cell anchorage. Furthermore, the loss of SelT elevates the expression of another selenoprotein, SelW1. Since both belong to the same protein family, it is suggested that SelW1 may functionally compensate for SelT [7].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 71613502 and 71621794 of the scaffold BDOT02000008.1. The protein was predicted to have 5 exons (shown in the image below).
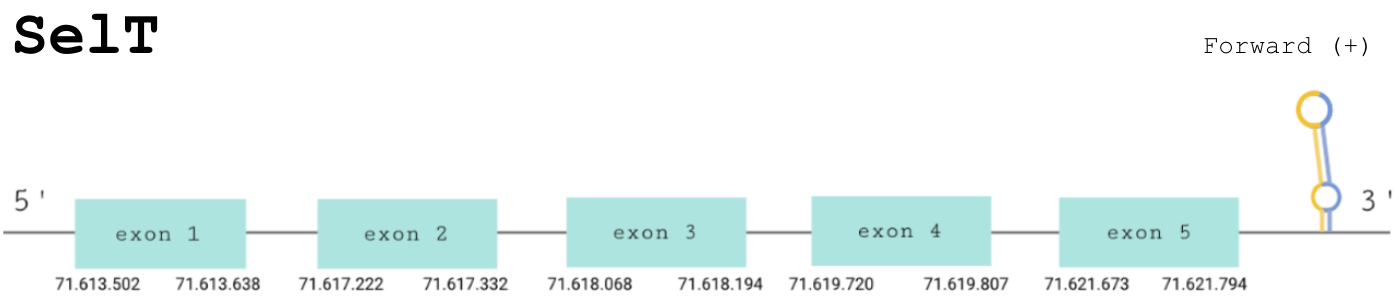
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was high: 975. Both proteins start with a methionine and the selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the human sequence. Moreover, Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein of Python bivittatus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. One was discarded because it was found in the reverse strand. The SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 71622213 and 71622292 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein SelT.
SelW1
Function
SelW1 belongs to the stress-related group of selenoproteins, since its expression is highly regulated by the availability of Se in the diet [8].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 103372041 and 103369852 of the scaffold BDOT02000006.1. The protein was predicted to have 3 exons (shown in the image below).
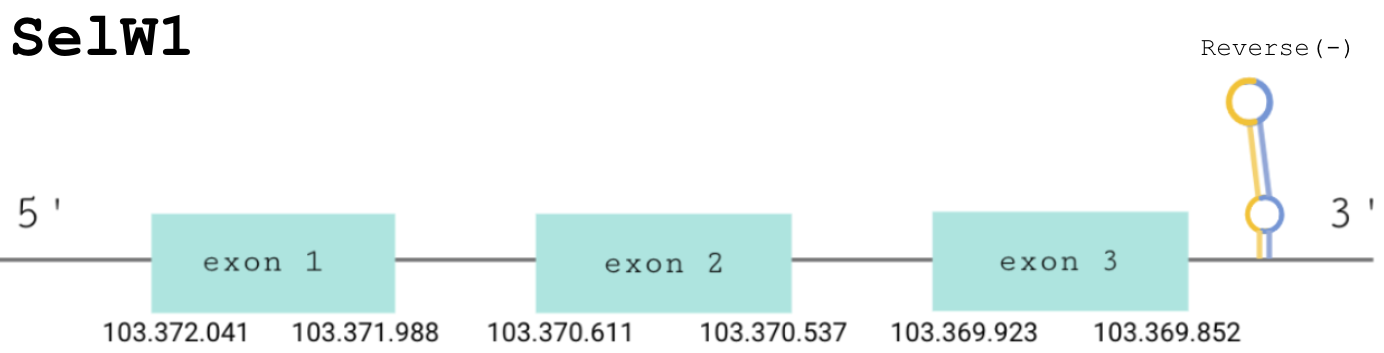
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was the highest: 1000. However, there was no selenocysteine found in our predicted protein. The selenocysteine in the human protein is aligned with a gap in ours. However, Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous selenoprotein T in Python bivittatus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. The best SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 103369100 and 103369016 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
We can conclude that SelW1 in Paroedura picta is not a selenoprotein, but an homologous protein. There is an SECIS element but we can not consider it as a selenoprotein due to the loss of the Sec.
SelM
Function
Selenoprotein M (SELM) is an ER-resident thiol-disulfide oxidoreductase, and is highly expressed in the brain and bestows neuroprotective properties. Its active site consists of a selenocysteine-containing thioredoxin-like domain that mediates thiol-disulfide exchange. Studies performed in cell culture indicate that SELM promotes intracellular calcium homeostasis and protects against oxidative stress [9].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 31514638 and 31518378 of the scaffold BDOT02000013.1. The protein was predicted to have 4 exons (shown in the image below).
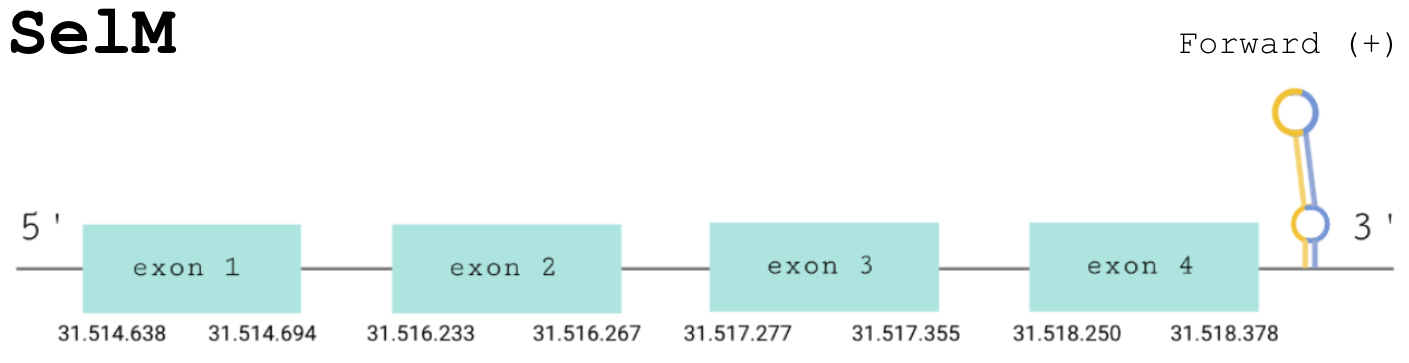
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was high aligned: 994. The selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence. The Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein of a Gekko japonicus.
The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 31519202 and 31519269 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein SelM.
SelO
Function
Selenoprotein O (SelO) is the largest mammalian selenoprotein, localized in the mitochondria. The exact function of this selenoprotein is not known, but it is thought to have redox activity [10].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 1791 and 14826 of the scaffold BDOT02000220.1. Although 3 hits were obtained, all the others were discarded because, although the e-value was good enough, Seblastian did not find any match with other proteins and T-Coffee showed an insufficient score. The protein was predicted to have 9 exons (shown in the image below).
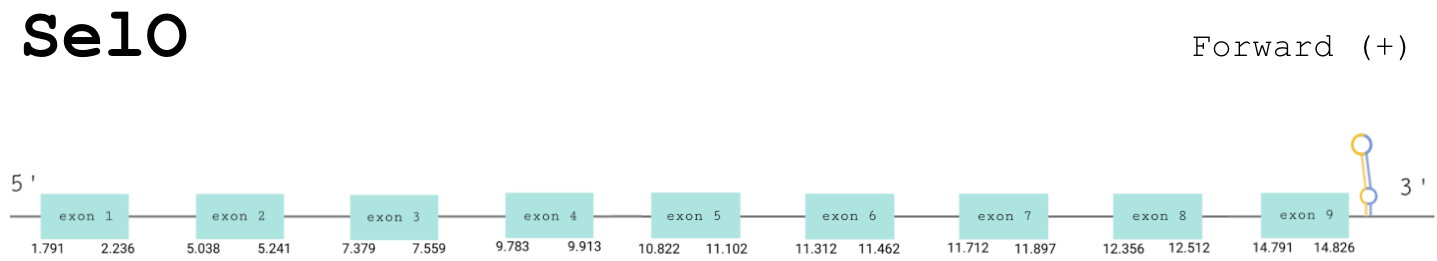
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was highly aligned: 994. There is no selenocysteine in our predicted protein, and the one present in the human one is aligned with a gap. Although in the T-Coffee we could not find a selenocysteine, after running Seblastian was found a positive prediction; an alignment with an homologous protein of a Gekko japonicus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. One was discarded because it was found in the reverse strand. The SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 15233 and 15305 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
Thus, since Gekko japonicus is a closer species to P. picta than humans, we assume that the Sec-gap alignment is due to a high evolutionary distance and can accept the Seblastian prediction: Paroedura picta has selenoprotein SelO.
Thioredoxin reductase
Function
Thioredoxin reductase (TR) is a redox active protein involved in many cellular processes as part of the thioredoxin system. In mammals, TR1 was the first thioredoxin reductase to be characterised and it is known as the cytosolic form. TR3 is the mitochondrial form, and TR2 functions as a Trx and GSSG reductase [11].
TR1
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 22477230 and 22446150 of the scaffold BDOT02000006.1. The protein was predicted to have 14 exons (shown in the image below).
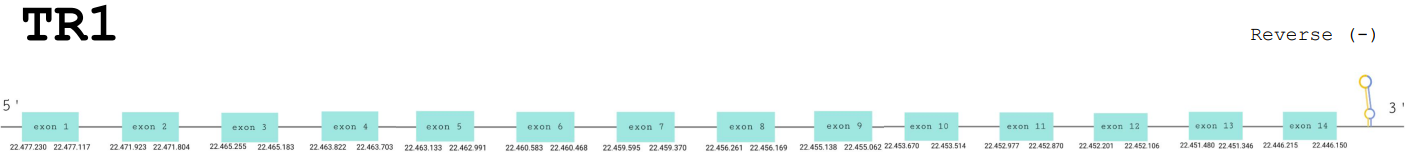
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was high: 998. The selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence. Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein of Bos taurus.
The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 22445900 and 22445821 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein TR1.
TR2
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 38208946 and 38169950 of the scaffold BDOT02000013.1. The protein was predicted to have 14 exons (shown in the image below).
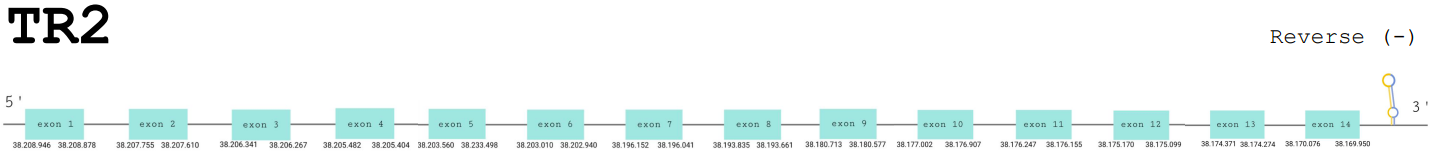
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 998. The selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence. Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein of Meleagris gallopavo.
SECIS Search3 was able to find four SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. All four of them were found in the reverse strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the rest. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 38163856 and 38163779.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein TR2.
TR3
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 36584531 and 36538684 of the scaffold BDOT02000003.1. The protein was predicted to have 16 exons (shown in the image below).
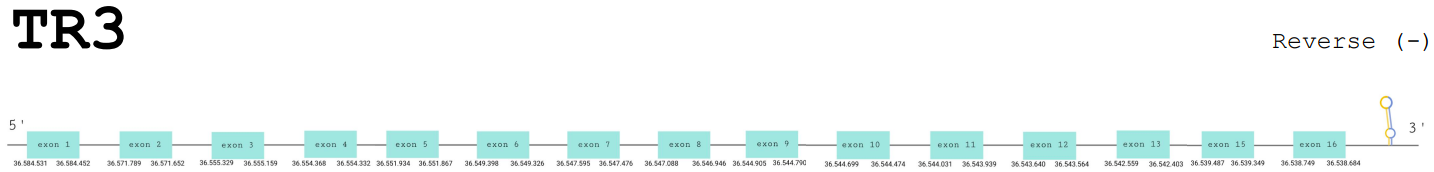
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was not really high: 700. The predicted protein does not start with a methionine and the selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence. Moreover, Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with the same protein in Gallus gallus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. One was discarded because it was found in the forward strand. The SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 36533945 and 36533866 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein TR3.
Selenoprotein K
SelK
Function
Selenoprotein K (SelK) is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) transmembrane selenoprotein, expressed at relatively high levels in immune cells. Its expression is sensitive to dietary selenium levels [12].
Protein prediction
The Selenoprotein K was not found in Paroedura picta. Although we found a hit, it was less than 200bp long and was too short for T-Coffee to make an alignment with the existing human protein.
Hence, we can conclude that this gene does not exist in our species and that there might have been a deletion throughout our species evolution.
Selenoprotein I
SelI
Function
Selenoprotein I (Sel I) catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine from CDP-ethanolamine to diacylglycerol to produce phosphatidylethanolamine, which is involved in the formation and maintenance of vesicular membranes, regulation of lipid metabolism and protein folding [13].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 159818412 and 159870774 of the scaffold BDOT02000001.1. The protein was predicted to have 9 exons (shown in the image below).
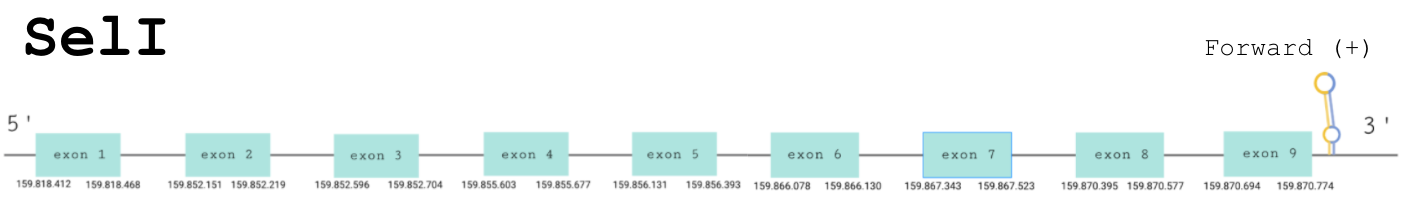
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 998. Both proteins start with a methionine and the selenocysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence. Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein in Gekko japonicus.
SECIS Search3 was able to find two SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. One was discarded because it was found in the reverse strand. The SECIS element that was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 159871899 and 159871976 of the scaffold, had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has selenoprotein SelI.
Selenoprotein N
SelN
Function
Selenoprotein N (SelN) plays an important role in cell protection against oxidative stress and in the regulation of redox-related calcium homeostasis. It regulates the calcium level of the ER by protecting the calcium pump ATP2A2 against the oxidoreductase ERO1A-mediated oxidative damage. [14]
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 18488 and 24038 of the scaffold BDOT02000819.1. The protein was predicted to have 5 exons (shown in the image below).
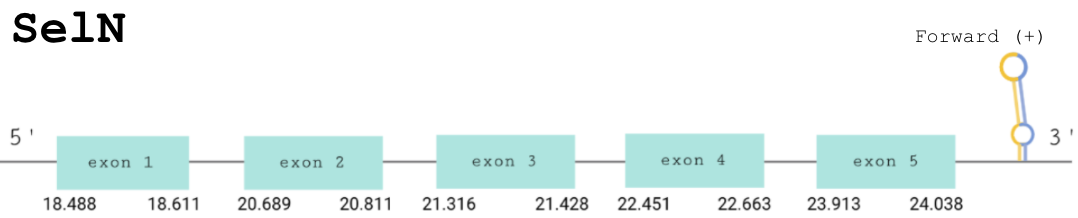
The score obtained from the T-coffee output was high: 996. There was no selenocysteine in our predicted protein and the selenocysteine of the human one aligned with a cysteine in ours: concordantly, Seblastian could not find any SECIS elements.
Therefore, we can conclude that Pareodura picta has an homologous protein to human SelN, but which contains Cys instead of Sec in the same position.
Selenoprotein P
SelP
Function
Selenoprotein P (SelP) acts as a plasma carrier of the trace element selenium in the body: it is a major selenium-containing protein in human plasma, and it is mainly synthesized in the liver. It functions as a selenium-transporter to maintain antioxidative selenoenzymes in several tissues, such as the brain and testis, and plays a pivotal role in selenium-metabolism and antioxidative defense [15].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 55.003.144 and 55.009.848 of the scaffold BDOT02000004.1. The protein was predicted to have 4 exons (shown in the image below).
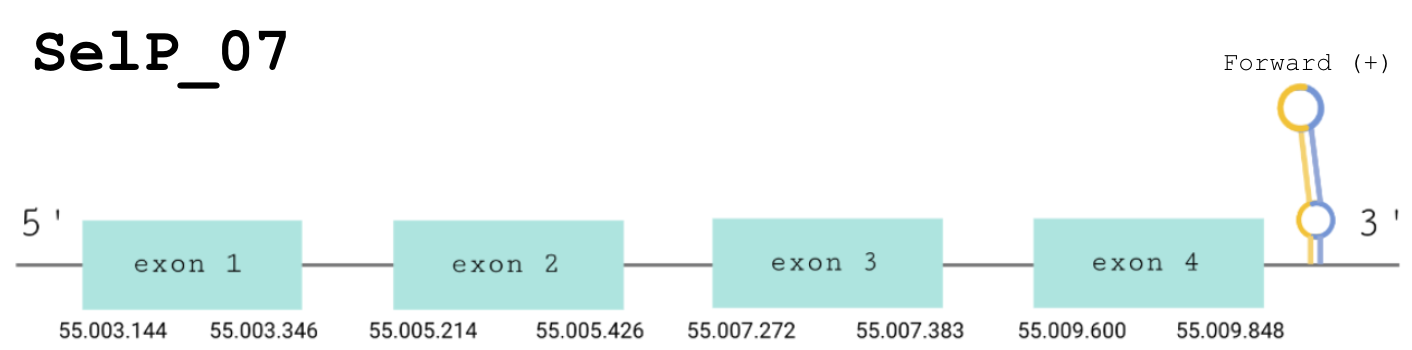
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 975. Both proteins start with a methionine, and 4 out of 5 selenocysteines found in our predicted protein have been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the human sequence. The other ones were aligned with a cysteine. Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with the homologous selenoprotein P1 in Meleagris gallopavo.
The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 55011164 and 55011238 of the scaffold and had an overall B grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has the selenoprotein SelP.
Selenoprotein R
SelR1
Function
SelR1 belongs to the methionine-R-sulfoxide reductase B (MsrB) family. It is mainly expressed in the kidney and liver, specifically in the nucleus and the cytosol. SelR1 is the only protein in the MsrB family which is considered a selenoprotein in humans, since it contains a Sec residue in the active site while other proteins in the same family do not [16].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the negative strand between the positions 850450 and 849589 of the scaffold BDOT02000018.1. The protein was predicted to have 3 (shown in the image below).
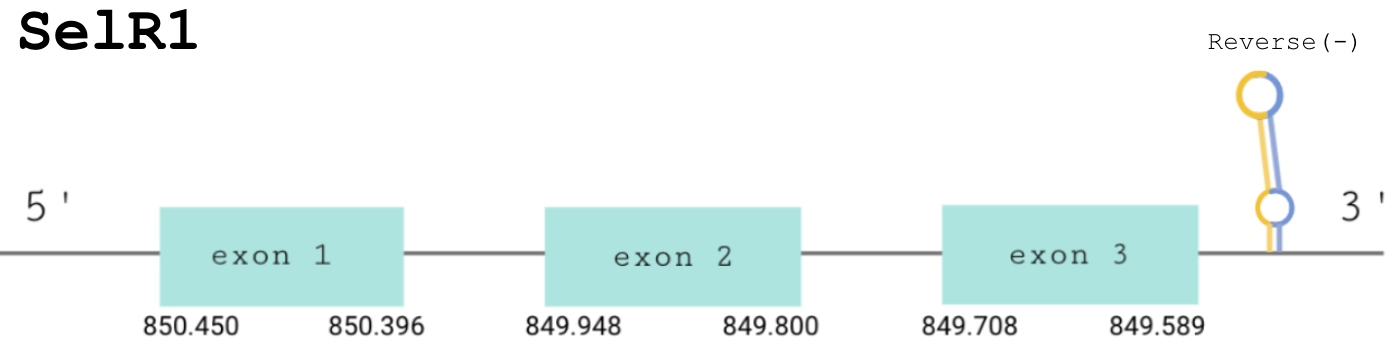
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 999. Both proteins start with a methionine and the selenocysteine found in our predicted protein has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the human sequence. Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous selenoprotein MsrB1 (SelR1) in Gekko japonicus.
The correct SECIS element was found at the 3’-UTR segment, between positions 848530 and 848455 of the scaffold and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score.
For all these reasons we can accept our prediction, confirming that Paroedura picta has the selenoprotein SelR1.
Selenoprotein S
SelS
Function
SelS (Selenoprotein S) is a selenocysteine-containing protein with roles in ER (endoplasmic reticulum) function and in inflammation. It has been implicated in ERAD (ER-associated protein degradation), and clinical studies revealed an association of a polymorphism in its promoter with cytokine levels and human diseases [17].
Protein prediction
The Selenoprotein S was not found in Paroedura picta. All the hits that were found had an e-value higher than 0.0001, so we can conclude that this selenoprotein does not exist in Pareodura picta.
Selenoprotein W
SelW2
Function
Sel W2 (Selenoprotein W2) belongs to the SelWTH family, which possesses a thioredoxin-like fold and a conserved CxxU (C is cysteine, U is Sec) motif, suggesting a redox function for this gene [18].
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 16468529 and 16471417 of the scaffold BDOT02000015.1. The protein was predicted to have 4 exons.
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 982. There is no selenocysteine found in our predicted protein. In fact, it is a Cys homologous gene, in which there is cysteine alignment. There were not found any SECIS elements in the predicted gene sequence.
Methionine sulfoxide reductase A
MsrA
Function
The Msr type A enzyme (MsrA) plays an important role as a cellular antioxidant and promotes cell survival. Therefore, it is involved in the protection of cellular proteins against oxidative stress, and through this function it can regulate life expectancy in various model organisms. Moreover, it is a thiol-dependent enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of methionine sulfide into methionine. In humans, it contains a Cys residue instead of Sec in its active place [19].
Protein prediction
We found two hits for this protein. In the first one, the protein aligned with the BDOT02000001.1 scaffold between the positions 156627289 and 156493686 in the reverse strand, which was predicted to have 5 exons. In this case, Cys residues aligned in both the human and the predicted P. picta protein, although Seblastian did not find any SECIS element. The same case occurred in the BDOT02000006.1 scaffold between the positions 75633284 and 75573003 in the reverse strand, which was predicted to have 6 exons. In this case, however, a SECIS element was found.
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high in both scaffolds. For the first it was 994 and for the second it was 996. Cysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in both human and P. picta sequences.
The correct SECIS element was found only in the 3’-UTR segment of the predicted protein from the BDOT02000006.1 scaffold, between positions 75588148 and 75588070 and had an overall A grade, defined by a good infernal and covels score. However, as we can see, the predicted SECIS is contained between exons 5 and 6 in MsrA. Nevertheless, since MsrA is not a selenoprotein, the presence of this SECIS element may be a remnant of the evolutionary legacy of other species, which may have had MsrA as a Sec-containing protein.
With all this information we deduce that the MsrA could have been duplicated during the evolution of Paroedura picta, given that we can find both high-quality hits in two different regions of its genome. Nevertheless, these are not selenoproteins, but Cys-containing homologues.
Selenoprotein R
SelR2, SelR3
Function
SelR2 is a mitochondrial enzyme that has an important role in the preservation of mitochondrial integrity by decreasing ROS and protecting mitochondrial proteins. It is expressed in the heart, kidney and the skeletal muscle. As this protein lacks Sec residue in humans, it is not considered a selenoprotein.
Protein prediction
The predicted gene for these proteins was found in the reverse strand of the same scaffold BDOT02000006.1 and between 46281524 and 46281420. The protein was predicted to have only 1 exon.
.png)
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high, nearly 900. The cysteine residue has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the human sequence: no selenocysteine was found in any of the cases.
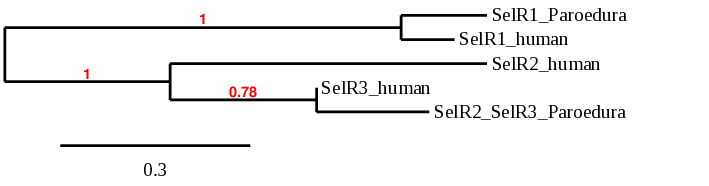
With all this information we can conclude that SelR2 and SelR3 are actually the same gene in Pareodura picta. As we can see in the following phylogenetic tree, human SelR2 diverged early from a common ancestor and specialized in Homo sapiens, while SelR3 became apparent later. In P. picta, this divergence was not observed and the gene predicted has not specialized into SelR2 nor SelR3.
Thus, we can conclude that SelR2 and SelR3 are the same protein in P. picta, and are not selenoproteins.
Selenoprotein U
SelU1, SelU2, SelU3
Function
Selenoprotein U has a restricted phylogenetic distribution, such as in chicken and fish. Mammals have cysteine-containing homologues, where it functions as a redox regulatory protein. It has a role in autophagic cell death mechanisms.
SelU1
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 7978174 and 7987922 of the scaffold BDOT02000008.1. The protein was predicted to have 5 exons
The score obtained from the T-CCoffee output was perfect: 1000. Both proteins started with a methionine and the selenocysteine present in our predicted protein aligned with a cysteine in the reference human sequence. Seblastian found a positive prediction, an alignment with an homologous protein: the redox-regulatory protein FAM213A isoform X3 in Anolis carolinensis.
SECIS Search3 was able to find three SECIS elements for this predicted gene sequence. All three of them were found in the forward strand and 3’ of the Sec, although one had a better score than the rest. This last SECIS element, of grade A, was found in between positions 7988076 and 7988140.
With all this information, we consider that SelU1 is a selenoprotein in P. picta, although it contains Cys in our reference human proteome.
SelU2
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 49.531.139 and 49.500.348 of the scaffold BDOT02000007.1. The protein was predicted to have 7 exons
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was high: 991. Cysteine has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the reference human sequence, so we can conclude they are Cys homologous genes. No SECIS element was found.
We can conclude that SelU2 exists in Pareodura picta but it is not a selenoprotein.
SelU3
Protein prediction
The SelU3 gene was not found in the Paroedura picta. All hits we obtained had an e-value higher than 0.0001, so we considered that, under our criteria, SelU3 does not exist in Paroedura picta.
Machinery
Selenophosphate synthetase
SPS2, SPS1
Function
Selenophosphate synthetase (SPS) was initially detected in bacteria and was shown to synthesize selenophosphate, the active selenium donor. However, mammals have two SPS paralogues, which are designated SPS1 and SPS2. Although it is known that SPS2 catalyses the synthesis of selenophosphate, the function of SPS1 remains largely unclear. However, The knockout of Sps1 in the liver of mice preserved viability, but significantly affected the expression of a large number of mRNAs involved in cancer, embryonic development and the glutathione system. [22] SPS2 is a human selenoprotein present in the cytosol that catalyzes the reaction of selenide with AMP producing selenophosphate, which provides selenium for the biosynthesis of selenocysteine. It is necessary for the synthesis of other selenoproteins [7].
SPS2
Function
Selenophosphate synthetase 2 (SPS2) catalyzes the synthesis of the active Se donor selenophosphate that is necessary for Sec biosynthesis. Moreover, SPS2 serves an autoregulatory role in selenoprotein synthesis. [23]
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 162212094 and 162203950 of the scaffold BDOT02000003.1. The protein was predicted to have 8 exons (shown in the image below).
The score obtained from the T-Coffee output was perfect: 988. There is a selenocysteine found in our predicted protein and has been conserved and aligned with the same residue in the human sequence. The Seblastian found a positive prediction: an alignment with an homologous protein, a Selenide, water dikinase 2, in Protobothrops mucrosquamatus.
SPS1
Function
SPS1’s function is not well characterized. However, it is thought to play a role in selenoprotein synthesis. KO of this protein’s orthologs in some insects, which lack Sec biosynthesis, induces a growth inhibition and higher intracellular glutamine levels among other processes [24].
Protein prediction
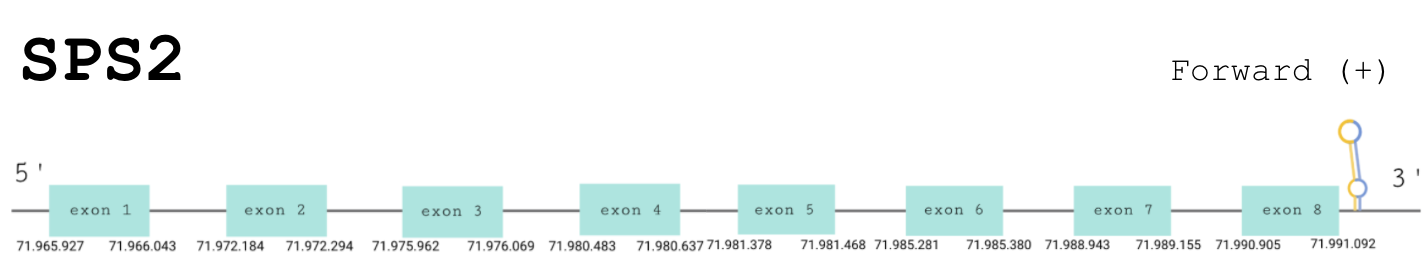
The predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 71965909 and 71991116 of the scaffold BDOT02000006.1. The exonerate software predicted them to have 7 exons.
The T-Coffee showed a perfect alignment with a score of 1000. Thus, we can conclude that SPS1 exists in P. picta and that it is homologous to the human SPS1.
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase
PSTK
Function
PTSK (phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase) phosphorylates Ser-tRNA[Ser]Sec in order to produce the phosphorylated intermediate PSer-tRNA[Ser]Sec, serving as a substrate for SecS. [25]
Protein prediction
For this protein, the predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 39161707 and 39164359 of the scaffold BDOT02000008.1. The T-Coffee showed a 984 score, so there’s a good alignment. We can conclude they are homologous proteins.
Selenocysteine synthase
SecS
Function
SecS (Sec synthase) catalyzes the conversion of the serine moiety on tRNA to selenocysteine-tRNA by incorporating selenophosphate, the active form of Se, into the amino acid backbone and forming Sec-tRNA. In humans, 4 SecS subunits form a tetramer, which binds two tRNA [Ser]Sec molecules through their long acceptor-TC arms. The interaction of tRNA[Ser]Sec with the active site of SecS induces the enzyme’s conformational change that allows the binding of O-phosphoseryl-tRNA[Ser]Sec, but not free phosphoserine, in order for the reaction to occur [8].
Protein prediction
The predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 7935540 and 7967254 of the BDOT02000010.1 scaffold. Moreover, the T-Coffee showed a 999 score, so there’s almost perfect alignment. We can conclude they are homologous proteins.
SECIS binding protein 2
SBP2
Function
SBP2, also known as SECIS binding protein 2, is stably associated with ribosomes and contains a RNA-binding domain that is known to bind SECIS elements with high affinity and specificity (X). Moreover, SBP2 is a limiting factor for selenoprotein synthesis, as knockdown of SBP2 in mammalian cells using siRNA leads to decreased expression of selenoproteins [26].
Protein prediction
This predicted gene was found in the forward strand between the positions 51705487 and 51727458 of the BDOT02000007.1 scaffold. SBP2’s T-Coffee showed a score of 959, corresponding to a good alignment. We can conclude they are homologous proteins.
tRNA Sec 1 associated protein 1
SECp43
Function
SECp43, along with SLA, is specific to eukaryotes. It interacts with the tRNA[Ser]Sec and it formes a complex. It has a nuclear localization and it may work as a chaperone for SLA and Sec-tRNA[Ser]Sec, being linked to the regulation of the synthesis of selenoproteins through methylation of tRNA[Ser]Sec and the intracellular distribution of SLA [8].
Protein prediction
This predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 87807075 and 94510502 of the BDOT02000006.1 scaffold. SBP2’s t-coffee showed a score of 999, corresponding to an almost perfect alignment. We can conclude they are homologous proteins.
Eukaryotic elongation factor
eEFsec
Protein prediction
This predicted gene was found in the reverse strand between the positions 39170152 and 39295424 of the BDOT02000003.1 scaffold. The predicted protein had a selenocysteine and was aligned with a Cysteine in the reference human sequence. Seblastian shows a low score in SECIS elements, so can not be considered a selenoprotein.
