
| Home ~ Intro ~ Project ~ Script ~ Results ~ Conclusions ~ Links |
SNPs distribution in genes Last Update: 21 March 2002 |

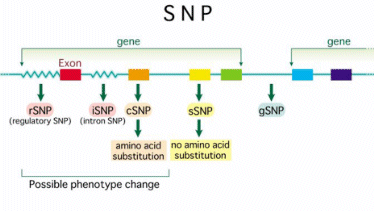
We have studied the distribution of SNPs among human genome, locating them in exons, introns or splicing sites and distinguishing the lasts between donor and acceptor ones.
The project is focused basically on the relationship between SNPs and splicing sites due to the possibility that a SNP placed there may cause a differential splicing and, so on, a non functional protein. This would be the origin of disease or susceptibility to some factors in some instances.
Our objectives were:


The programs and the statistical analysis have been done in Perl language under Linux, a Unix-type operating system, while the web site has been done in HTML programming.
To work on the project we dispose of two data files:
The original information on refGene.txt is structured this way:
NM_gene|Chromosome|Strand|Start|End(transcript)|Start|End(CDS)|Number exons|Start&End exons
Exemple:chr10 refseq cds 141296 141451 . + . NM_006624
And the folder we have worked with was designed in a more practical way, detailing the exons (CDS) for every gene (NM_gene) and chromosome.
Chromosome|refseq|CDS|Start CDS|End CDS|.|Strand|.|NM_gene
Exemple: chr10 refseq cds 141296 141451 . + . NM_006624
We have two origin files, with the same structure:
Reference|Chromosome|Start SNP|End SNP|SNP_Reference
Exemple:585 chr1 33352 33353 9493
The aspect that differences one from another is the way the data has been obtained: at snpNih.txt we find overlap SNPs, therefore they were placed studying the differences in nucleotide sequence between overlap contig clones, while at snpTsc.txt the SNPs were positioned with random genomic reads.


The objective was comparing an SNP file with the refseq.gff one to obtain the location of SNPs in genes, sorting them into exons, introns, acceptors or donor sites and to make with them statistical analysis later. We have worked with snpNih.txt although the program is applicable to both files.
Actually we have obtained two programs, one of them made thanks to J.A Abril. The script done with his collaboration has a higher level and in our opinion is more interesting to explain how it works. If you want to see the script's explanation click here.
However, this program consumes more computer memory and has been impossible to run it at our usually available computers. As both programs return comparable results the final statistics analysis has been done with the results from our script.
Statistical analysis requires running the statistical module.


>