![]()
Figure 2. Chromosome 4 (Ensembl)
In humans, the genes of VTDB, ALB, AFP and ALF constitute a multigene cluster located in the subcentromeric region of chromosome 4 (4q11-q13) (Song et al. 1999).
![]()
Figure 2. Chromosome 4 (Ensembl)
By refining the physical and meiotic maps of this region, the order and transcriptional orientations of the four genes were determined to be centromere-3-VTDB-5-5-ALB-3-5AFP-3-5-AFM-3-telomere. The transcriptional orientation of the VTDB gene is centromere-3VTDB-5-telomere, opposite to the transcriptional orientations of the ALB, AFP and AFM genes (Song et al. 1999).
The exon/intron pattern has been conserved as a characteristical feature
of this gene family. It is formed by 15 exons separated by 14 introns (Ray
et al. 1991). The exon structure of the genes has been aligned with
the domain structure of the mature protein showing that the first domain
is codified by exons 2 to 6, domain 2 by exons 6 to 10 and domain 3 by
exons 10 to 14. Equivalent exons in each domain show sufficient sequence
and structural similarity to be considered homologous (Gibbs
& Dugaiczyk, 1987).
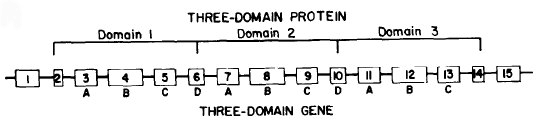
Figure 3. Gene structure (Gibbs
& Dugaiczyk, 1987)
The VTDB gene has several distinctive features which set it apart from the other members of its family. First, the protein is some 130 aa shorter than the others. This decrease in size is the result of the loss of two internal exons (12 and 13) (Nishio & Dugaiczyk, 1996). Second, exons 6 ,8, 9 and 11 are smaller than their counterparts by a total of 8 codons. These data strongly support the idea that VTDB was the first gene appeared, and that it has suffered a different evolutionary history.
Figure 4. Exon structure (Ensembl)
More than 120 variant alleles of VTDB have been identified (Kofler
et al. 1995), being GC2, GC1S and GC1F the most common ones. The
molecular differences among the 3 common alleles reside in exon 11 at codons
416 and 420. At position 416, the codon for acid aspartic (GAT) was found
for the alleles GC1F and GC2, the codon for glutamic acid (GAG) for GC1S.
At position 420, the codon for threonine (ACG) was found for GC1F and GC1S,
the codon for lysine (AAG) for GC2. These nucleotides exchanges involve
restriction sites: position 416 includes a HaeIII restriction site for
the allele GC1S and position 420 includes a StyI restriction site for allele
GC2. Thus, the 3 common genetic VTDB types can be determined by restriction
fragment analysis (Braun et al. 1992). High frecuency
of the GC2 allele corresponds, with some exceptions, to low levels of sunlight
(Mourant
et al. 1976).
Home | Introduction | Gene Analysis | Protein analysis | Evolutionary study | References