DISCUSSION
In order to characterize the selenoproteins existent in the Parus major an analysis based on its homology with another organism whose selenoproteins had previously been defined (Gallus gallus) was performed. The results of said analysis will be discussed on the next few lines.
15 kDa selenoprotein (Sel15)
Sel15 levels differentially respond to selenium supplementation. Studies in mouse suggest that this selenoprotein may have redox function and may be involved in the quality control of protein folding. This gene is localized on chromosome 1p31, a genetic locus commonly mutated or deleted in human cancers. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found for this gene.
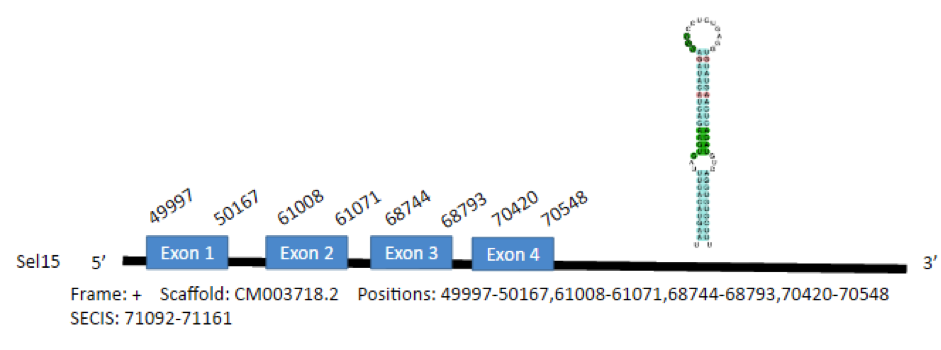
The Sel15 selenoprotein of Gallus gallus has 137 aminoacids in its sequence. We predicted 1 gene of this protein in Parus major genome and the selenocysteine was aligned. The predicted gene was found in scaffold CM003718.2 between positions 49997-50167,61008-61071,68744-68793,70420-70548. We obtained one predicted SECIS elements 3’ from the gene region in the correct strand in the positions 71092-71161.
Iodothyronine deiodinase (DIO)
Iodotironin deiosinases are integrated by 3 paralog proteins: DIO1, DIO2 and DIO3. Their functions are related with the regulation of tiroideal hormonal activity via the activation of such hormones. Those proteins are responsible for the deiodination of T4 (3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine) into its active form T3 (3,5,3'-triiodothyronine) and of T3 into T2 (3,3'-diiodothyronine). It plays a role in providing a source of plasma T3 by deiodination of T4 in peripheral tissues such as liver and kidney. On the other hand, DIO1 influences on the levels of circulating hormone. On the contrary, DIO1 mediated the removal of iode by forming triiodotrionin reverse (rT3) which is inactive. All in all, the DIO family is fundamental to preserve the levels of tiroideal horome as well as to modulate its activity.
DIO1
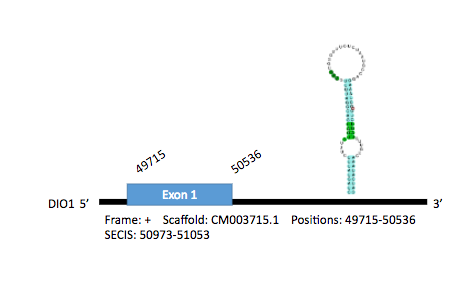
The DIO1 protein of Gallus gallus has 246 aminoacids in its sequence. There have been predicted 2 hits of this protein in Parus major genome, both in scaffold CM003715.1. Hit 1 was found between positions 51076976-51077473 of the genome in the positive strand, with only 1 exon coding for 274 aminoacids between the positions 49715-50536. 3 SECIS elements have been predicted. The first predicted SECIS was at a reliable distance from the gene, so we considered this as the best prediction (locations: 50973-51053).
The second prediction was in the same scaffold but this time in the opposite frame in the positions 41683182-41683637 in the negative strand, with one exon in the positions 50000-50455. We found 5 SECIS elements predicted but we considered that the first SECIS was the most probable one as the other was too far away from the gene region.
These hits are detected in the same scaffold and in very similar positions so we consider that they are the same gene.
.png)
DIO2
The DIO2 protein of Gallus gallus has 264 aminoacids in its sequence. There have been predicted 3 genes of this protein in Parus major genome, two of them in CM003715.1 scaffold and one in CM003718.2 scaffold.
Hit 1 was found between the positions 41683167-41694923 of the genome in the negative strand with only one exon. There were found 5 predicted SECIS elements. The predicted SECIS which was in a closer position of the gene region was the one in the locations 45537-45611.The second hit was also found in CM003715.1 scaffold, in the positions 51077036-51077467 of the genome in the positive stand with one exon. As both hits are found in the same scaffold but in opposite frames we conclude that is the same gene. The third hit (CM003718.2) was found between the positions 26378673-26380350 of the genome in the positive strand with four exons. In this case, one SECIS element was predicted in the positions 52362-52429 in the correct strand and 3’ of the region of the gene.
.png)
.png)
.png)
In conclusion, in this case we have found two genes in the scaffolds CM003715.1 and CM003718.2 that code for the DIO2 protein. We can also see that hit 1 and 2 are very similar to the gene predicted for the DIO1 protein and in addition are in the same scaffold. Thus, we can consider that is the same gene.
DIO3
The DIO3 protein of Gallus gallus has 258 aminoacids in its sequence. We predicted 3 genes of this protein in Parus gallus genome, two of them in CM003715.1 scaffold and one in CM003718.2 scaffold.
In the first hit (CM003715.1) one selenoprotein was found in the positions 51076739-51077512 in the genome in the positive strand. In this case, 3 SECIS elements were predicted, 2 of them in the correct strand and in the 3' region of the gene. They both were at a reliable distance from the gene, so we consider them as equally good predictions (locations: 51210-51290, 61969-62054).
.png)
In hit 2, one selenoprotein was found in the positions 50024-50473 in the negative strand. 5 SECIS elements were predicred, but we selected the one in the positions 45540-45620 to fulfill all the criteria.
.png)
Similarly to the previous case, we consider that this two hits correspond to the same gene. Regarding hit 3 (CM003718.2 scaffold), one selenoprotein was predicted in the positions 26380198-26380350 in the genome in the positive strand coding for four exons. One SECIS element was predicted in the positions 52359-52426 in the correct strand and 3’ from the region of the gene.
.png)
For DIO1 protein we have predicted one gene in the CM003715.1 scaffold. For the DIO2 protein, we have predicted one gene in the CM003718.2 scaffold and another in the CM003715.1 scaffold which appears to be the same gene predicted for the DIO1 protein. Regarding DIO3 protein, we have found one hit in the CM003715.1 scaffold which also appears to be the same gene predicted for DIO1 and DIO2 proteins and one hit in CM003718.2 which also coincides with the gene found in the hit 2 for the DIO2 protein.
All in all, in the DIO family we have found two genes in the scaffolds CM003715.1 and CM003718.2 but we cannot specify which isoform they code for.
Eukaryotic elongation factor (eEFsec)
Eukaryotic elongation factor has a glutathione peroxidase functions in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide and it is one of the most important antioxidant enzymes in humans. The eEFsec is a machinery protein related to the synthesis of selenoproteins.
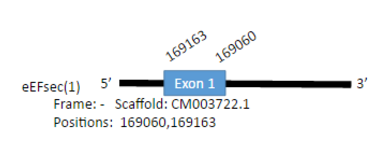
Gallus gallus has one gene encoding for a 531 aminoacids protein. We have found two hits in Parus major in two different scaffolds: CM003722.1 and CM003711.1. The first prediction was in the genomic positions 9082272-9201435, with one exon in the positions 169060-169163 and it was an homologous in Cystein in the position 448.
Glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
GPx are the largest and best-known selenoprotein family. GPx is the general name of an enzyme family with peroxidase activity whose main biological role is to protect the organism from oxidative damage as it functions in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide. The biochemical function of glutathione peroxidase is to reduce lipid hydroperoxides to their corresponding alcohols and to reduce free hydrogen peroxide to water. This family is integrated by 8 GPx homologs (GPx1-GPx8). GPx1-4 and GPx6 are selenoproteins in humans and in macaque, whereas GPx5, GPx7 and GPx8 are cysteine-containing homologues. Unlike mRNAs for other characterized glutathione peroxidases, this mRNA does not contain a selenocysteine (UGA) codon. Thus, the encoded protein is selenium-independent.
In Gallus gallus there are three different isoforms of glutathione peroxidase: GPx3, GPx7 and GPx8.
GPx3
In Gallus gallus, GPx3 gene encodes for a protein of 207 aminoacids. We have found five hits in different scaffolds namely CM003723.1, CM003715.1, CM003722.1, CM003740.1 and CM003718.2.
In the first hit (CM003723.1) there was found one selenoprotein in the positions 52043-52129, 50863-81016, 50522-50639, 50288-50387, 49970-50197 in the negative strand with 207 aminoacids. One predicted SECIS element in the positions 49575-49667 in the correct strand, in a reliable distance from the gene and in the 3' region. In the Seblastian analysis, there was found an alignment between two selenocysteins in the position 44 of exon 2.
.png)
In the second hit (CM003715.1) there was found one selenoprotein in the positions 49979-50203,50282-50629 in the positive strand with 212 aminoacids in total. One SECIS element was predicted in the positions 50696-50770 fulfilling all the criteria previously described. In the seblastian analysis, there was found an alignment between two selenocysteins in the position 41 of exon 1.
.png)
In the third hit (CM003722.1) there was found one selenoprotein in the positions 49904-50143,50243-50590 in the positive strand coding for a protein of 211 aminoacids. One SECIS element was predicted in the positions 50675-50741. In the Sebastian analysis, there was found an alignment between two selenocysteins in the position 45 of exon 1.
.png)
In both the fourth (CM003740.1) and fifth (CM003718.2) hits one selenoprotein was predicted in each case in the positions 50000-50164 and 50000-50164 respectively but no SECIS were predicted in the correct strand for neither of them. Thus, we discarded these hits as possible selenoproteins.
GPx7
In Gallus gallus, GPx7 gene encodes for a protein of 128 aminoacids. We have found four hits in different scaffolds namely CM003718.2, CM003740.1, CM003722.1, CM003715.1.
In the first hit (CM003718.2) one homologous protein was found in the genomic positions 25661212-25653369.
In the second hit (CM003740.1) we also found another homologous protein in the genomic positions 16443643-16445924.
In the third hit (CM003722.1) we found a hit for a protein in the positions 49901-50140,50240-50587 in the positive strand.
GPx8
In Gallus gallus, the GPx8 gene encodes for a protein of 123 aminoacids and is a cysteine containing homologous. We have found four hits in different scaffolds namely CM003740.1, CM003718.2, CM003722.1, CM003715.1, CM003738.1.
In the first hit (CM003740.1) one homologous protein was found in the genomic positions 16443643-16445918.
In the second hit (CM003718.1) one homologous protein was found in the genomic positions 25651212-25653363.
In the third hit (CM003722.1), a protein was predicted in the positions 49901-50140 and 50240-50587.
.png)
For the GPx family, we have found that the isoforms GPx3, GPx7 and GPx8 are coded by the same genes as we have predicted the same scaffolds in all of them. The three proteins are found in the same scaffolds: CM003715.1, CM003722.1, CM003740.1 and CM003718.2. Thus we can conclude that this family is coded by those four genes but we cannot ensure which one codifies for each isoform of the protein. When running a t-coffee between Gallus gallus protein and our predictions, in all the hits the cysteine was aligned with the selenocysteine of the GPx8 selenoprotein, so we can conclude that Parus major contains a homologous protein in this cases.
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase (PSTK)
Phosphoseryl-tRNA kinase is highly conserved in evolution. This suggests that it plays an important role in selenoprotein biosynthesis and/or regulation.
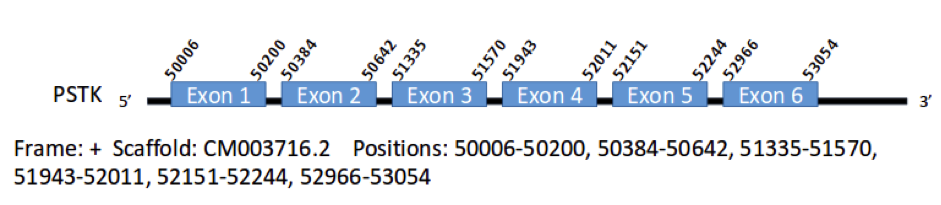
This selenoprotein has one gene in Gallus gallus encoding for 354 aminoacids. We have found a hit for it in the scaffold CM003716.2 in the genomic positions 30190025-30193073 and with 6 exons in the positions 50006-50200, 50384-50642, 51335-51570, 51943-52011, 52151-52244 and 52966-53054, which code for 314 aminoacids.
Methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA)
Msr is ubiquitous and highly conserved. The Methionine Sulfide Reductase A is an enzyme that carries out the enzymatic reduction of methionine sulfoxide (MetO) to methionine (Met). Human and animal studies have shown the highest levels of expression in kidney and nervous tissue. Its proposed function is the repair of oxidative damage to proteins to restore biological activity. Oxidation of methionine residues in tissue proteins can cause them to misfold or otherwise render them dysfunctional. Three transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. It does not contain a Sec.
The MsrA protein of Gallus gallus has 125 aminoacids in its. We had 2 predictions of the MrsA gene (CM003711.1, CM003732.1). In the first hit we found an homologous protein in the genomic positions 110712620-110728407 but we didn’t obtain any results in hit 2.
.png)
SECIS binding protein 2 (SBP2)
SBP2 encodes a nuclear protein that functions as a SECIS binding protein. If mutated, this gene leads to a reduction in activity of a specific thyroxine deiodinase, a selenocysteine-containing enzyme, and abnormal thyroid hormone metabolism. Its alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
SBP2(1)
SBP2(1) has 1,090 aminoacids in its sequence in the genome of Gallus gallus. We could not predict any genes of this protein in the genome of Parus major.
SBP2(2)
SBP2(2) has 906 aminoacids in its sequence in the genome of Gallus gallus. We predicted 2 genes of this protein in the genome of Parus major.
The first one was found in scaffold CM003740.1 between the positions 40465249 and 40483332 of the genome in the positive strand, with 13 exons in the positions 31911-32025, 35221-35366, 35892-36047, 38697-38798, 40081-40200, 41383-41515, 44043-44212, 44947-45085, 45535-45664, 47389-47609, 48343-48497, 48930-49131 and 49849-49994, which code for 851 aminoacids.
.png)
The second one was found in scaffold CM003720.1 between the positions 9811238 and 9817756 of the genome in the negative strand, with 7 exons in the positions 49899-50009, 48100-48294, 46879-47011, 45744-45873, 44844-45064, 44032-44186, 43491-43571, which code for 342 aminoacids. The best hit in this case would probably be the first one, as it has a more appropriate E-value, a higher BLAST score and it codes for a total number of aminoacids (851) that is closer to the observed number of aminoacids in Gallus gallus (906) than is the number of aminoacids of the second hit (342).
.png)
SBP2(3)
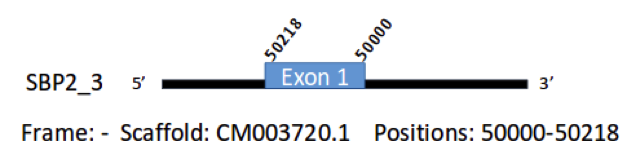
SBP2(3) has 73 aminoacids in its sequence in the genome of Gallus gallus. We predicted a gene of this protein in the genome of Parus major. This gene was found in scaffold CM003720.1 between the positions 9811097 and 9811315 of the genome in the negative strand, with one exon in the position 50000-50218, which codes for 73 aminoacids.
tRNA Sec 1 associated protein 1 (SECp43)
This protein regulates selenoprotein expression.
The sequence of the protein encoded by SECp43 in Gallus gallus has 310 aminoacids. We did not find any hits for this protein in the genome of Parus major.
Selenocysteine synthase (SecS)
The amino acid selenocysteine is the only amino acid that does not have its own tRNA synthetase. Instead, this amino acid is synthesized on its cognate tRNA in a three step process. The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the third step in the process, the conversion of O-phosphoseryl-tRNA(Sec) to selenocysteinyl-tRNA(Sec).
SecS(1)
SecS(1) in Gallus gallus has 467 aminoacids in its sequence and it is a cysteine containing homologous. We predicted 1 gene of this protein in the Parus major genome. The predicted gene was found in scaffold CM003710.1, containing one exon on the positive strand between positions 50000-50123.
.png)
SecS(2)
SecS(2) in Gallus gallus has 165 aminoacids in its sequence and it is a cysteine containing homologous. We predicted 1 gene of this protein in Parus major genome in the same scaffold as the previous one, with 1 exon on the positive strand but on a different position: 49991-50157.
.png)
Selenophosphate synthetase (SEPHS)
This gene encodes an enzyme that synthesizes selenophosphate from selenide and ATP. Selenophosphate is the selenium donor used to synthesize selenocysteine.
The SEPHS protein in Gallus gallus contains 397 aminoacids. One hit was found in the Parus major genome, in the scaffold CM003714.1, on the negative strand of the chromosome and containing just one exon in the position 69237-69429.
.png)
Selenoprotein I (SelI)
This gene encodes a multi-pass transmembrane protein that belongs to the CDP-alcohol phosphatidyltransferase class-I family. It catalyzes the transfer of phosphoethanolamine from CDP-ethanolamine to diacylglycerol to produce phosphatidylethanolamine, which is involved in the formation and maintenance of vesicular membranes, regulation of lipid metabolism, and protein folding. The sequence of the protein SelI of Gallus gallus contains 400 aminoacids. No selenoproteins could be predicted for SelI in the genome of Parus major.
Selenoprotein K (SelK)
This selenoprotein contains a selenocystene residue (Sec) at its active site. It is localized to the endoplasmic reticulum and is highly expressed in the heart, where it may function as an antioxidant.
SelK
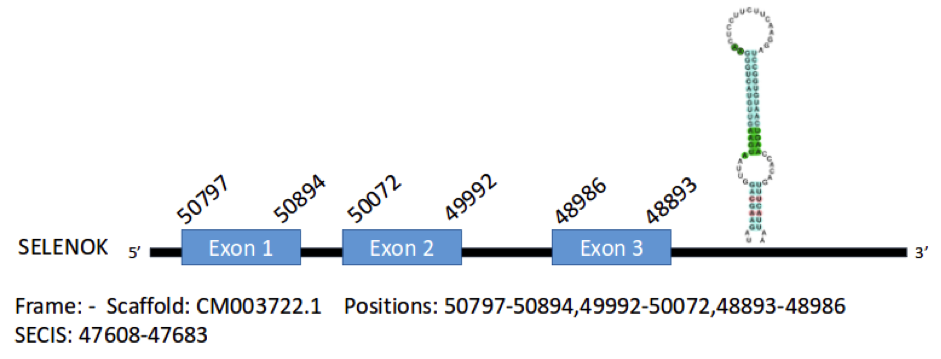
The sequence of the protein SelK of Gallus gallus contains 95 aminoacids. We have predicted one gene encoding for this protein in the genome of Parus major, in the scaffold CM003722.1. It is located in the negative strand and contains 3 exons in the positions 50797-50894, 50072-49992 and 48986-48893, coding for a total of 91 aminoacids. A SECIS element has been predicted, which extends from position 47608 to position 47683 of the gene.
SelK isoforms 2 and 3
The SelK(2) selenoprotein of Gallus gallus has 89 aminoacids in its sequence and SelK(3) has 87. We did not predict any gene for these two isoforms in the Parus major genome.
Selenoprotein N (SelN)
This selenoprotein contains a selenocystene residue (Sec) at its active site. Its function is not well understood, but it is known that mutations in this gene lead the classical phenotype of multiminicore disease and congenital muscular dystrophy with spinal rigidity and restrictive respiratory syndrome.
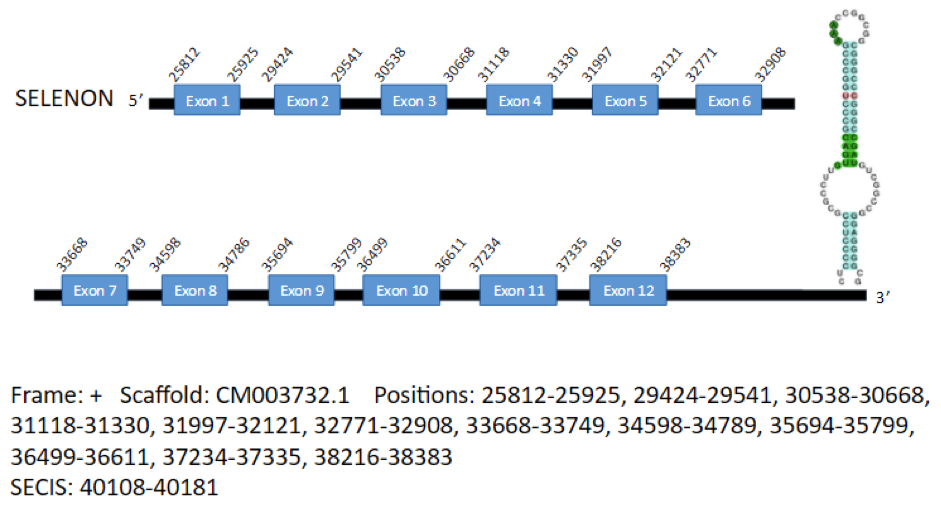
The sequence of the protein SelN of Gallus gallus contains 530 aminoacids. We predicted one gene encoding for this protein in the genome of Parus major, in the scaffold CM003732.1. It is located in the positive strand and contains 12 exons in the positions 25812-25925, 29424-29541, 30538-30668, 31118-31330, 31997-32121, 32771-32908, 33668-33749, 34598-34789, 35694-35799, 36499-36611, 37234-37335 and 38216-38383, coding for a total of 533 aminoacids. A SECIS element has been predicted, which extends from position 40108 to position 40181 of the gene.
Selenoprotein O (SelO)
This selenoprotein contains a selenocystene residue (Sec) at its active site. Its function is not well known.
The sequence of the SelO of Gallus gallus contains 364 aminoacids in the case of the isoform SelO1, 198 aminoacids in the case of SelO2, 629 aminoacids in the case of isoform SelO3 and 182 in the case of SelO4. We predicted 6 hits encoding for this protein in the genome of Parus major.
SelO1
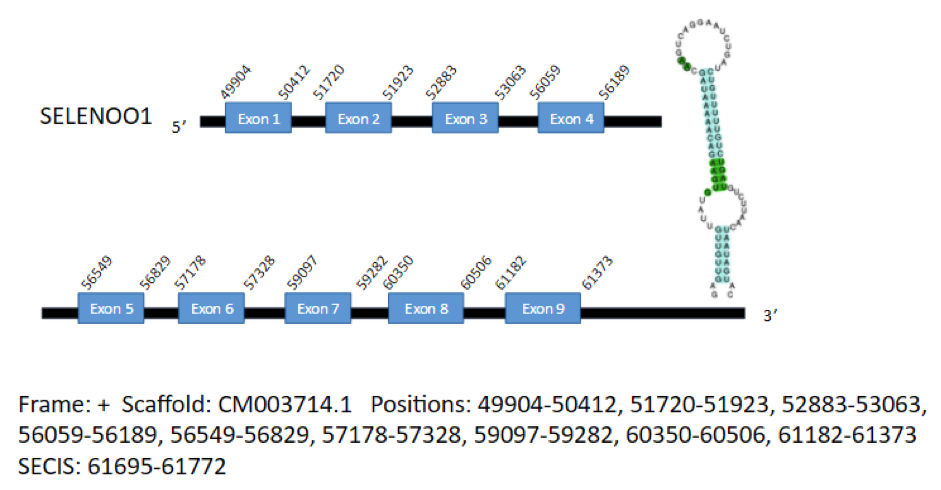
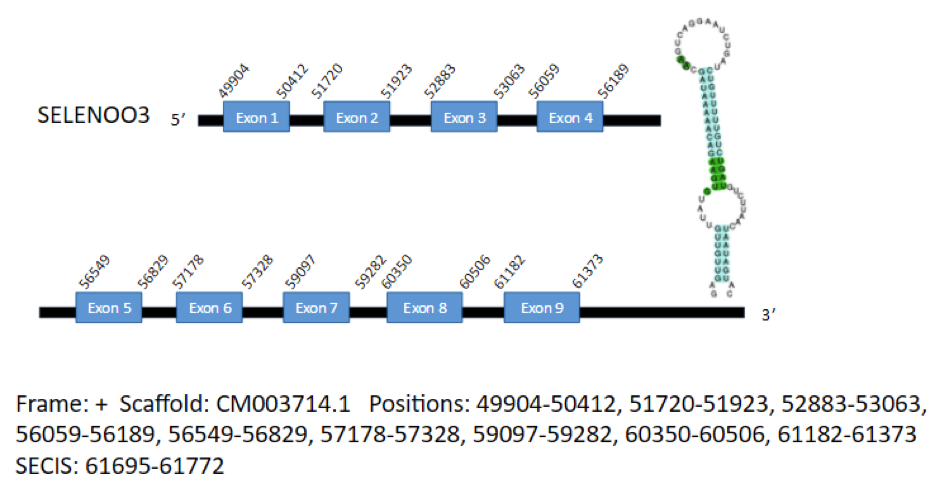
The first hit corresponds to the isoform SelO1 and is located in the positive strand of the scaffold CM003714.1 and contains 9 exons in the positions 49904-50412, 51720-51923, 52883-53063, 56059-56189, 56549-56829, 57178-57328, 59097-59282, 60350-60506 and 61182-61373, coding for a total of 664 aminoacids. A SECIS element has been predicted, which extends from position 61695 to position 61772 of the gene.
SelO2
Two hits for this isoform were predicted in Parus major.
The first hit was located in the scaffold CM003710.1, on the positive strand and containing one exon in the position 50000-50050.
.png)
The second hit was located in the scaffold CM003714.1, on the positive strand and containing 9 exons in the positions 49613-50121, 51429-51632, 52592-52772, 55768-55898, 56258-56538, 56887-57037, 58806-58991, 60059-60215, and 60891-61082.
.png)
SelO3
The second hit (SelO3) is located in the same scaffold and strand as SelO1 and has the same number of aminoacids (664), but it has a different start postion (18641791). The number of exons and the SECIS element predicted are also the same.
SelO4
Two hits for this isoform were predicted in Parus major. However, they are the same as in Sel04 and have the same number of exons (despite havingslightly different positions in the scaffold CM003714.1).
.png)
.png)
These results are consistent with the existance of different isoformes of SelO, such as are SelO1 and SelO3 and Sel02 and SelO4 in this case. Considering that they are both located at the same scaffold and that the predicted exons and SECIS are the same, we hipothesise that they are both the same gene. In the case of the selenoproteins (SelO1 and SelO3), the gene probably correponds to the isoform SelO1, as its predicted aminoacidic sequence lenght is similar to the one of the SelO1 of Gallus gallus. Regarding the machinery proteins (SelO2 and SelO4), we can not discern which isoform the gene corresponds to.
Selenoprotein P (SelP)
This gene encodes a selenoprotein containing multiple selenocysteine (Sec) residues. SelP is an extracellular glycoprotein, and what is unusual about it is that it contains multiple Sec residues per polypeptide. It is an heparin-binding protein that appears to be associated with endothelial cells, and that seems to function as an antioxidant in the extracellular space and to be involved in Se transport to the different organs and tissues.
The sequence of the SelP of Gallus gallus contains 267 aminoacids in the case of the isoform SelP1 and 251 aminoacids in the case of isoform SelP2.
SelP1
We predicted two hits (paralogous copies) for SelP1 in Parus major: the first one is located in the negative strand of the scaffold CM003718.2 and contains 4 exons in the positions 50653-50855, 50343-50555, 50081-50216 and 49209-49451, coding for 265 aminoacids. The predicted selenoprotein has a SECIS element located it the positions 48884 to 48958.
.png)
The second one is located in the negative strand of the scaffold CM003740.1 and contains 4 exons in the positions 53076-53266, 51676-51888, 49994-50111 and 48457-49113, coding for 393 aminoacids. The selenoprotein predicted in this case has two SECIS elements located it the positions 48072 to 48143 and from 47440 to 47508 of the gene, being the first one closer to our gene and thus, the most probable one.
.png)
SelP2
Regarding the isoform SelP2, the sequence of the protein in Gallus gallus contains 251 aminoacids. Two hits were found in the genome of Parus major.
The first hit was located in the scaffold CM003718.2, on the negative strand of the chromosome, and containing 4 exons in the positions 50548-50750, 50238-50450, 49976-50111 and 49104-49346. A SECIS element was predicted in the position 48779-48853.
.png)
The second hit was located in the scaffold CM003740.1, on the negative strand of the chromosome, and containing 4 exons in the positions 54187-54377,52787-52999,51105-51222,49568-50224. Two SECIS elements were predicted in the positions 49183-49254 and 48551-48619 respectively. Since both of them met our criteria, none of them could be discarded.
.png)
Selenoprotein R (MSRB)
This protein belongs to the methionine sulfoxide reductase (Msr) protein family which includes repair enzymes that reduce oxidized methionine residues in proteins. It is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SEPX1 gene.
MSRB1
This protein belongs to the methionine sulfoxide reductase B (MsrB) family, and it is expressed in a variety of adult and fetal tissues.
In Gallus gallus the gene encodes for a 107 aminoacid protein. We have found one hit in the scaffold CM003724.1 of Parus major with one selenoprotein predicted in the positions 50719-50773,50233-50375,50008-50122,49507-49535.

MSRB3
The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the reduction of methionine sulfoxide to methionine. This enzyme acts as a monomer and requires zinc as a cofactor. Several transcript variants encoding two different isoforms have been found for this gene. One of the isoforms localizes to mitochondria while the other localizes to endoplasmic reticula.
Two hits for this gene were found in the Parus major genome, in the scaffolds CM003714.1 and CM003710.1.
The first hit (CM003714.1) contains one exon on the positive strand in the positions 50000-50115.
.png)
The second hit (CM003710.1) contains one exon on the negative strand in the positions 50000-50092.
.png)
Selenoprotein T (SelT)
This gene encodes a selenoprotein, which contains a selenocysteine (Sec) residue at its active site, although its function has not been defined.
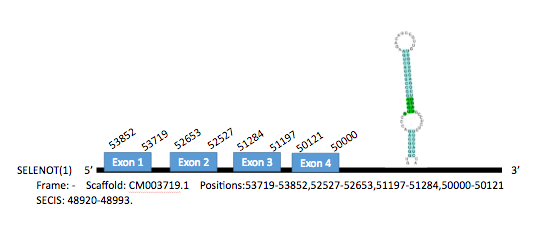
The sequence of the SelT of Gallus gallus contains 197 aminoacids. We predicted one gene encoding for this protein in the genome of Parus major in the scaffold CM003719.1, located in chromosome 9 in its negative strand. It contains 5 exons in the positions 54999-55111, 53719-53829, 52527-52653, 51197-51284 and 50000-50121. A SECIS element has also been predicted, which extends from position 48920 to position 48993 of the gene.
Selenoprotein U1 (SelU1)
It is known that this protein is expressed in bone, brain, liver and kidney. However, its function is not clear.
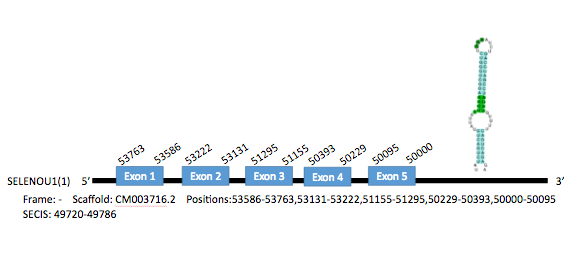
The Gallus gallus SelU1 protein consists of 227 aminoacids. One gene encoding for this protein has been found in Parus major in the scaffold CM003716.2, located in chromosome 6 and with 5 exons in the positions 53586-53772, 53131-53222, 51155-51295, 50229-50393 and 50000-50095. There were 2 SECIS elements predicted for this selenoprotein, but one of them was discarded since it was located in the opposite strand. The SECIS element selected is located in the position 49720-49786 of the gene.
Thioredoxin reductase (TXNRD)
This gene encodes a member of the family of pyridine nucleotide oxidoreductases. This protein reduces thioredoxins as well as other substrates, and plays a role in selenium metabolism and protection against oxidative stress. The functional enzyme is thought to be a homodimer which uses FAD as a cofactor. Each subunit contains a selenocysteine (Sec) residue which is required for catalytic activity. Alternative splicing results in several transcript variants encoding the same or different isoforms.
TXNRD
The Gallus gallus TXNRD protein contains 511 aminoacids. Two genes that encoded for this isoform were found in Parus major.
The first hit was located in the scaffold CM003714.1, on the negative strand of the chromosome, and containing 6 exons in the positions 66483-66547, 64881-65106, 62691-62783, 60916-60992, 59129-59285, 56926-57033, 55478-55573, 53182-53316, and 50000-50065. A SECIS element was predicted in the position 49674-49750.
.png)
The second hit was located in the scaffold CM003725.1, on the positive strand of the chromosome, and containing 13 exons in the positions 49997-50145, 50460-50534, 51354-51432, 52386-52448, 52789-52859, 56673-56787, 58196-58370, 66764-66900, 72186-72281, 72491-72583, 73359-73430, 75219-75316, and 77575-77701. One SECIS elements was predicted in the position 80575-80652.
.png)
TXNRD2
The TXNRD2 protein in Gallus gallus constists of 517 aminoacids. Two genes that encoded for this isoform were found in Parus major.
The first hit was located in the scaffold CM003725.1, but this time on the positive strand of the chromosome, and containing 13 exons in the positions 52445-52593, 52908-52982, 53802-53880, 54834-54896, 55237-55307, 59121-59235, 60644-60818, 69212-69348, 74634-74729, 74939-75031, 75807-75878, 77667-77764, and 80023-80149. A SECIS element was predicted in the position 83023-83100.
.png)
The second hit was located in the scaffold CM003714.1 but on the negative strand of the chromosome, and containing 9 exons in the positions 63301-63365, 61699-61924, 59509-59601, 57734-57810, 55947-56103, 53744-53851, 52296-52391, 50000-50134, and 46818-46883. One SECIS elements was predicted in the position 46492-46568.
.png)
TXNRD3
In Gallus gallus, the TXNRD3 protein contains 606 aminoacids. Two genes that encoded for this isoform were found in Parus major.
The first hit was located in the scaffold CM003722.1, on the positive strand, and with 16 exons on the positions 49997-50119, 55526-55586, 57160-57269, 57440-57553, 59348-59420, 60264-60383, 60771-60913, 62301-62416, 62524-62749, 63001-63093, 63535-63611, 64161-64317, 64520-64627, 65511-65606, 65813-65947, and 66079-66144.
.png)
The second hit was located in the scaffold CM003725.1, on the positive strand of the chromosome, and containing 13 exons on the positions 51384-51532, 51847-51921, 52741-52819, 53773-53835, 54176-54246, 58060-58174, 59583-59757, 68151-68287, 73573-73668, 73878-73970, 74746-74817, 76606-76703, and 78962-79088. One SECIS element was predicted in the position 81962-82039.
.png)