INDEX
- Abstract.
- Biointroduction.
- Program.
- Conditions of usage.
- Current Results.
- Tools.
- Links & references.
Abstract
This program allows the user detect motifs of transcriptional factors (TF) in your sequences/s. Each TF binds to a given consensus sequence that can be schematized through a Positional Weight Matrices (PWM).
Using your own input PWMs the program scans your sequences searching for the consensus detailed in them. Therefore, the user can identify the transcriptional factors that are helping the RNA polymerase in the transcription (as shown in the picture below).
If you want to use this software, click here.
Biointroduction
In eucharyotic organisms, the gene expression regulation is nowadays one of the least known biological processes given mainly to the great complexity and the high number of factors that are implied. Essentially, it's thought that the most important gene expression checkpoint is the DNA to RNA transcription, but it seems quite probable that there are other types of control: pre-transcriptional (as chromosomal structure, CpG islands, methylation...) or post-traductionals (transport, mRNA degradation, protein synthesis regulation...).
The eucaryothic gene transcription
is made by RNA polymerase II. The regulation of the beginning of this process
consists of two stages:
Atraction of the RNA polymerase II
to the transcriptional starting point by General Transcriptional Factors
(FT) as TATA box, ... that allow the starting point recognisement
by the RNApol II through binding the DNA strand and the RNA pol II
at the same time.
Transcriptional starting according to given productivity and need paramethers of the encoded protein. These paramethers depend on a combination of gene specific Transcriptional Factors that act together closely binded to the former to the starting point region. They can be positive (activators) or negative (inhibitors) regulators.
Given that multiple FTs and their binding sites are known and that the
publishing of several genomes has reported us several regulator sequences,
the necessity of bioinformatic tools to predict which combinations of FTs
regulate each gene is made clear. A simple way of dealing with the problem
is to use Positional Weight Matrices (PWM) previously derived from real
binding sites collections, to build a list of candidate regions along a
promoting sequence. In TRANSFAC data base, there is the widest collection
of PWM for protein/DNA binding sites.
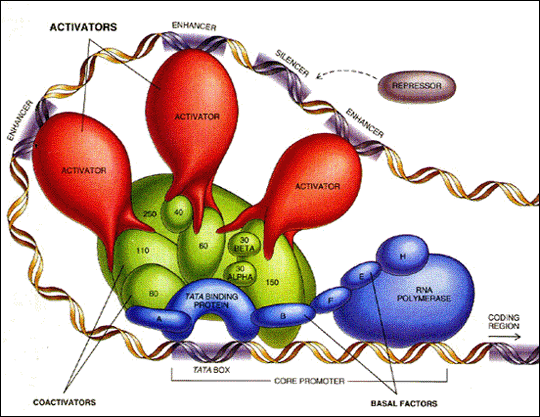
Fig. 1. This picture shows the basic mechanism of transcriptional control, with the RNA Pol II and the FT (TATA binding proteins...) as basic elements.
SCANNER can use more than one sequence
and scan them for more than one FT at a time, saving time and effort to
the user.
For
further information about the programming details click here!
There are several remarkable points
about the usage of this program:
The output file will be in HTML
format and must be opened with a compatible internet browser.
To go to the results page (outfile) of the last SCANNER execution, click here!
We tested the program with examples of PWM, that we have searched in TRANSFAC, and sequences, from GeneBank (both referenced at the end of the page). With these trials we obtained the default threshold.
-TRANSFAC
Program.
This software is based in comparisons of PWM with input DNA sequences in order to find FT motifs. The program runs along each sequence drawing a sliding window (the sliding window width is equal to the PWM number of rows) for each position.
Every sliding window is scored according to the values of the PWM giving a log-likelihood ratio.
These resulting scores are filtered: if they are higher than a threshold they automatically go to the Current Results outfile and are considered to be very probable binding sites.
This process is repeated for the different matrices and then for the following sequences.
Conditions of usage.
The input sequences must be in
FASTA format (no spaces at the end of
lines, and no more than one change of line character per line are allowed).
The input matrices must be in TRANSFAC format
or similar (several spaces between the scores are not allowed),
with "#" between each matrix followed by its name, and bases alphabetically
ordered (ACGT).
Current results.
Tools.
This software has been programmed in Perl language, a variety of C. The webpages have been done in HTML. Both were created with Emacs (text editor in LINUX OS).
Links & references.
-NCBI
-TRANSFAC database as a bridge between sequence data libraries and biological function. Wingender E, Karas H, Knuppel R. Pac Symp Biocomput 1997;:477-85
By: Guiomar
Solanas & Alex Vendrell. With contributions of Enrique Blanco.
For further information... Send
an e-mail to the authors.