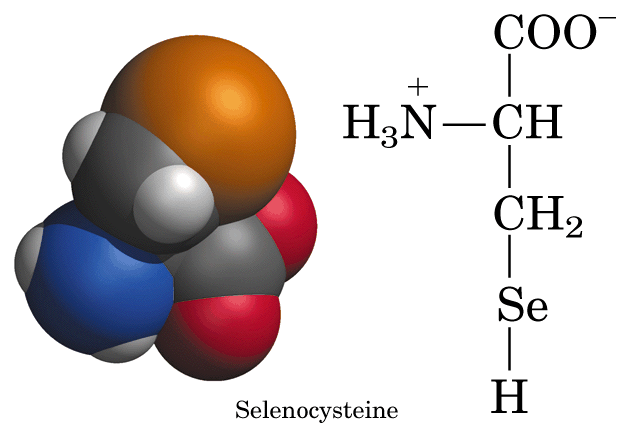- Selenium:
- Selenium is a trace mineral that is essential to good health.It is incorporated into proteins to make selenoproteins, which are important antioxidant enzymes.
- Selenocysteine:
- Selenocysteine (Sec) is a rare amino acid, which was discovered as the 21st amino acid about a decade ago. Proteins containing selenocysteine are consequently called selenoproteins. Selenocysteine is encoded by the UGA-codon, which is usually a STOP-codon encoding the end of translation by the ribosome. It has been shown that in the case of selenocysteine, termination of translation is inhibited in the presence of a specific mRNA sequence in the 3'-region after the UGA-codon that forms a hairpin like structure (called "Sec insertion sequence" (SECIS)).
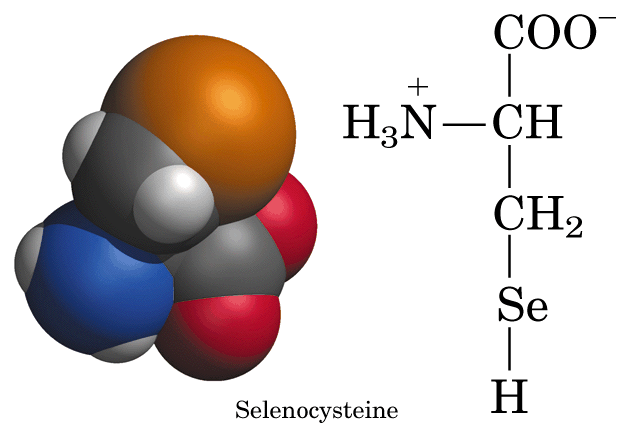 |
| Figure 2: Selenocysteine |
- SNPs:
- Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP (pronounced "snip"), are small genetic changes, or variations, that can occur within a person's DNA sequence. The genetic code is specified by the four nucleotide "letters" A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters C, G, or T.
On average, SNPs occur in the human population more than 1 percent of the time. Because only about 3 to 5 percent of a person's DNA sequence codes for the production of proteins, most SNPs are found outside of "coding sequences". SNPs found within a coding sequence are of particular interest to researchers because they are more likely to alter the biological function of a protein.
- EST:
- (Expressed Sequence Tag): A unique stretch of DNA within a coding region of a gene that is useful for identifying full-length genes and serves as a landmark for mapping. An EST is a sequence tagged site (STS) derived from cDNA.
An STS is a short segment of DNA which occurs but once in the genome and whose location and base sequence are known. STSs are detectable by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), are helpful in localizing and orienting mapping and sequence data, and serve as landmarks in the physical map of the genome.